We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
In today's digital age, data privacy and protection are paramount concerns for individual's and organisations. In the UK, these concerns have been addressed by legislations, with two prominent frameworks - the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and The Data Protection Act. GDPR and Data Protection Act are two significant legislations that addresses the protection and processing of Personal Data.
According to a 2022 Statista report, the UK was surveyed to have the highest level of GDPR awareness, with over 30 per cent of citizens strongly agreeing with the policies. Further, read this blog to understand the key Difference Between GDPR and Data Protection Act in detail.
Table of Contents
1) Overview of GDPR
2) Overview of the Data Protection Act
3) Difference Between GDPR and Data Protection Act
4) What is the importance of Data Protection?
5) What are the Data Protection principles?
6) How many types of Data Protection principles are there?
7) Conclusion
Overview of GDPR
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), comprehensive privacy and Data Protection law came into effect on 25th May 2018 across the European Union (EU). It was designed to address what is a gdpr breach and surrounding data privacy give individual's more control over their personal data. The GDPR replaced the Data Protection Directive of 1995 and introduced significant changes to the way organisations handle and process personal data.
One of the key Benefits of the GDPR is to create a consistent framework for Data Protection across to know why is gdpr important? it helps to create a consistent framework for Data Protection across all EU member states. It applies to any organisation that processes the personal data of individual's residing in the EU, regardless of the organisation's location. This extraterritorial applicability ensures that data sharing individual's privacy rights are protected regardless of where their data is being processed.
The GDPR defines personal data as any information that relates to an identified or identifiable individual. This includes not only obvious data such as names, addresses, and identification numbers but also online identifiers like IP addresses and cookies. The Challenges of GDPR is collecting information like name,address,identification number,biometric or generic data.
The GDPR introduces six fundamental principles that organisations must adhere to when processing personal data. These principles include:
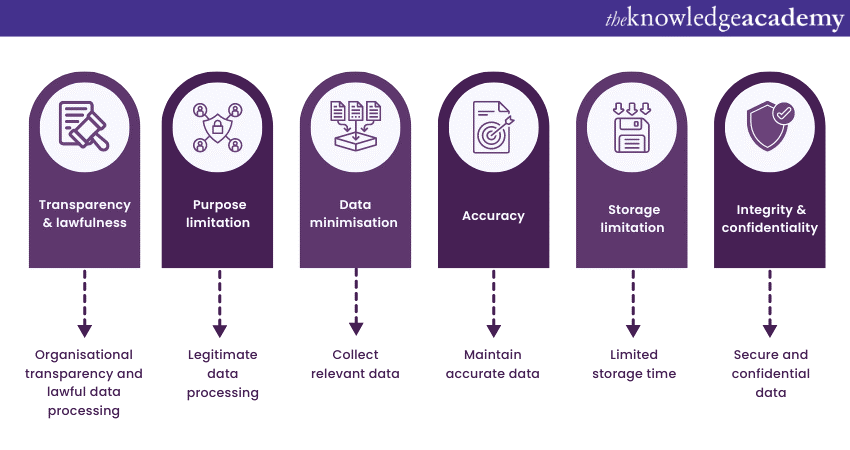
Organisations are required to process personal data fairly and lawfully, and they must have a legitimate purpose for processing and collecting only the necessary data for that purpose.
Overview of the Data Protection Act
The GDPR risk assessment is another UK legislation that governs the processing and protection of personal data. The current version of the act is the Data Protection Act 2018, which supplements and tailors the provisions of the European Union's GDPR to the UK context. The Data Protection Act 2018 builds upon the foundations established by the GDPR and addresses specific UK requirements.
The Data Protection Act 2018 applies to organisations that process personal data in the UK. It covers a wide range of personal data, including information that relates to identified or identifiable individual's. This encompasses not only basic personal details but also more sensitive data, such as health records, racial or ethnic origin, religious beliefs, and criminal records.
One of the key objectives of the Data Protection Act 2018 is to provide clarity and specificity regarding the processing of personal data for different purposes. The act includes provisions that supplement the GDPR by addressing areas not covered by the EU regulation. For example, the Data Protection Act 2018 incorporates exemptions and derogations to accommodate processing for legal purposes, national security, and law enforcement activities.
The act also includes additional safeguards and GDPR Requirements related to the processing of sensitive personal data. It sets stricter conditions for processing such data, ensuring that individuals' privacy is adequately protected. The Data Protection Act 2018 also regulates automated decision-making and profiling, ensuring that individual's are aware of and have the right to challenge decisions made by automated systems that significantly affect them.
Learn about the Data Protection, by signing up for the Data Protection Act (DPA 2018) Course now!
Difference Between GDPR and Data Protection Act
Below are the key differences between the GDPR and the Data Protection Act:
|
Parameters |
GDPR |
The Data Protection Act |
|
Scope |
Applies to all EU member states |
Applies specifically to the UK |
|
Extraterritorial applicability |
Applies to organisations processing data of EU residents |
Applies to organisations processing data in the UK |
|
Relationship to GDPR |
Forms the basis for Data Protection regulation in the EU |
Supplements and tailors GDPR provisions for the UK |
|
Processing of personal data |
Broadly covers personal data |
Covers personal data, including specific UK requirements |
|
Sensitive personal data |
Applies strict rules for processing sensitive personal data |
Imposes additional safeguards for processing sensitive data |
|
Legal purposes and exemptions |
Limited provisions for legal purposes, national security, etc. |
Incorporates exemptions and derogations for UK requirements |
|
Automated decision-making |
Regulates automated decision-making and profiling |
Ensures individual's have the right to challenge decisions |
|
Rights of individual's |
Grants enhanced rights over personal data |
Aligns with GDPR rights, with some additional provisions |
|
Regulatory authority |
Each EU member state has a supervisory authority |
Information Commissioner's Office (ICO) in the UK |
|
Penalties for non-compliance |
Fines up to 4% of global annual turnover or €20 million |
Fines up to £17.5 million or 4% of global turnover |
|
Data Handling |
GDPR is much stricter when it comes to data handling |
Data Protection has a variety of strict requirements |
What is the importance of Data Protection?
Data Protection is essential because it helps businesses to protect their customer's data and prevents it from being used for malicious purposes. Implementing strong Data Protection can help your clients feel secure and protected when using your services.
Businesses must remember that Data Protection is more than complying with the GDPR. It also protects your customers' data from being used for malicious purposes.
What are the Data Protection principles?
The GDPR Principles are a set of guidelines that Explore the disparities between GDPR and the Data Protection Act, unravelling key distinctions in their scope and regulations. This blog delves into the intricacies while highlighting the fundamental GDPR Principles.
How many types of Data Protection principles are there?
There are six Data Protection principles that businesses must comply with:
1) Any personal information should be handled justifiably and legally.
2) Personal information should only be collected for explicit and specific purposes that have been explicitly stated.
3) Personal data should be relevant and limited to what is necessary.
4) It is crucial for personal information to be precise and current. Any errors or outdated details could lead to potential issues or misunderstandings. Therefore, it is essential to ensure that personal data is always accurate and up-to-date.
5) It is imperative to ensure the confidentiality and security of personal data. Any spelling, grammar, or punctuation errors have been corrected.
6) It is crucial to ensure that personal data is not shared with unauthorised individual's or organisations. It is essential to maintain the confidentiality of personal information to prevent any potential harm or misuse.
Conclusion
GDPR and The Data Protection Act are two significant legislations that address the protection and processing of personal data. While GDPR provides a harmonised framework across the EU, the Data Protection Act tailors. The regulation places significant emphasis on protecting sensitive personal data, such as information related to an individual's health, racial or ethnic origin, religious beliefs, and biometric or genetic data, requiring organisations to conduct regular GDPR Audits to ensure compliance. By understanding the Difference Between GDPR and Data Protection Act, organisations can navigate the complexities of Data Protection regulations more effectively. They can also ensure that they handle personal data in a responsible and compliant manner, fostering trust and privacy in the digital landscape.
Understand Data Protection and implement EU GDPR compliant programs by signing up for GDPR Training Courses now!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming IT Security & Data Protection Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Certified EU General Data Protection Regulation (EU GDPR) Foundation and Practitioner
Certified EU General Data Protection Regulation (EU GDPR) Foundation and Practitioner
Sat 25th May 2024, Sun 26th May 2024
Mon 8th Jul 2024
Sat 14th Sep 2024, Sun 15th Sep 2024
Mon 23rd Sep 2024
Mon 18th Nov 2024
Sat 7th Dec 2024, Sun 8th Dec 2024
Mon 13th Jan 2025
Mon 3rd Mar 2025
Mon 14th Apr 2025
Tue 27th May 2025
Mon 14th Jul 2025
Tue 26th Aug 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


