We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
As the occurrence of data breaches and privacy violations increase, it has become essential to establish comprehensive regulations that safeguard the rights and privacy of individuals. One such regulation that has garnered significant attention is the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), containing GDPR Principles that outline the idea surrounding Data Protection.
These Principles aim to provide individuals with control over their data and strengthen Data Protection practices across organisations. To comply with it, it is crucial to understand these key Principles and how they impact businesses.
So, read this blog to explore the seven key GDPR Principles for Data Protection to impact your organisation and protect users’ data.
Table of Contents
1) What is GDPR?
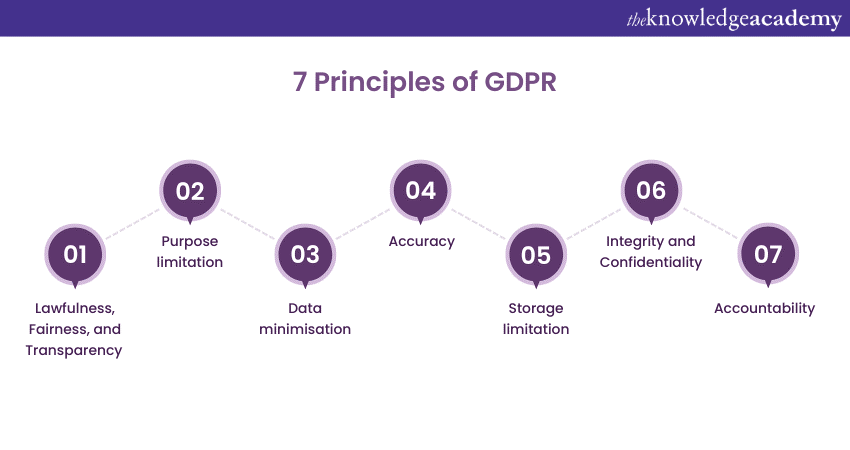
2) The seven GDPR Principles
a) Lawfulness, fairness, and transparency
b) Purpose limitation
c) Data minimisation
d) Accuracy
e) Storage limitation
f) Integrity and confidentiality
g) Accountability
3) What is the significance of these principles?
4) Conclusion
What is GDPR?
GDPR is a set of regulations which were developed to protect data of individuals residing in the European Union (EU). GDPR Scope is applicable to all the organisations that holds personal data of EU citizens, regardless of their physical location. GDPR risk assessment enhances data privacy rights, imposes obligations on data controllers and processors, and empowers individuals with more control over their data.
Understanding GDPR Principles
In 2018, upon the introduction of GDPR, it became challenging for many companies to adhere with the privacy requirements. These Challenges of GDPR are still elevant in the present day, as handling and processing personal data correctly is an ethical responsibility and a legal requirement. Failing to abide by this requirement may lead to huge fines, loss of reputation, and financial consequences.
The concern is that GDPR seems like a lengthy policy written in complex language, and it is only understandable with the help of a lawyer. However, GDPR requirements are based on seven Principles, making it easier to understand. Understanding these seven Principles makes it easier to understand the requirements and comply with GDPR. This simplified version aims to introduce GDPR to people just beginning to understand Data Protection and GDPR.
The GDPR Principles aims to empower individuals by granting them greater control over their data. They provide individuals with rights such as the following:
a) The right to access data
b) The right to rectify inaccuracies
c) The right to restrict processing
d) The right to erasure
e) The right to object to processing
f) The right to portability of data.
These rights ensure that individuals can manage their data and make informed decisions regarding its use. In addition to individual rights, the GDPR imposes obligations on organisations that process personal data. These obligations include the following:
a) Obtaining valid consent for data processing
b) Implementing effective security measures to protect data
c) Conducting privacy impact assessments
d) Appointing a Data Protection Officer (DPO)
e) Maintaining documentation to demonstrate compliance
Improve your understanding of data protection with our GDPR Training Courses now!
The seven GDPR Principles
The primary Benefits of GDPR is to establish a framework that ensures the lawful, fair, and transparent processing of personal data while empowering individuals to understand and monitor the ways their data is used. The seven GDPR Principles are as follows:
1) Lawfulness, fairness, and transparency
Out of the seven GDPR Principles, the first one emphasises the importance of processing personal data in a lawful, fair, and transparent manner. It sets the foundation for responsible data handling practices and aims to ensure that individuals are informed about and have control over how their data is used. Let's look at each of the terms in detail:
a) Lawfulness: The principle of lawfulness emphasises that organisations must have a legitimate basis for processing personal data. This means that data processing should align with one of the GDPR-specified legal grounds.
These legal grounds include adherence to the following:
1) Individual's consent
2) Fulfilling contractual obligations
3) Complying with legal obligations
4) Protecting vital interests
5) Performing tasks in the public interest provided they do not override the individual's rights and freedoms
Let us understand lawfulness using an example. If you sign up to receive a newsletter from a service provider, they most often require your name and email address to initiate this request. The service provider needs to obtain a legal basis to request such information.
This can be implemented by providing the users with an option to consent to ask for this information. It is also important to provide users with the option to limit or decide upon the information that they wish to provide; for example, details like users' job profiles and annual salary brackets may be irrelevant. Upon receiving the consent, the service provider needs to document the consent in whichever form it was received, in case it is asked for.
b) Fairness: Fairness in data processing entails treating individuals fairly and not using their data unexpectedly or unjustifiably. Organisations should process personal data consistently with the individual's reasonable expectations. This includes using the data only for specified purposes and avoiding unfair or discriminatory practices.
Data that the service provider is processing must also be fair. Let us understand this with the help of an example:
If your company sells clothing products, your customers expect to receive information regarding clothing, such as the latest trends, new additions, etc. The service provider is not expected to use this database to share information irrelevant to the intent upon which the customer has registered.
c) Transparency: Transparency is a crucial aspect of the GDPR Principles and requires organisations to provide individuals with clear and easily understandable information about how their data will be processed.
Transparency involves adhering to the following:
a) Being honest about the purposes for collecting the data,
b) Following the legal basis for processing,
c) Providing names of any third parties with whom the data can be shared
d) Providing information about the period for which data will be retained
Service providers are expected to be transparent in communicating aspects of 'what', 'how', and 'why' concerning the user data they collect and process. Users whose data is collected are referred to as "data subjects" in GDPR. They, have the right to know the data that service provider is collecting, how it is collected, and why the data is processed. Service providers can accomplish this by providing a privacy policy clearly stating these factors and providing users with Data Protection Officer (DPO) contact information.
2) Purpose limitation
The second principle is the principle of purpose limitation. It highlights the importance of collecting and processing personal data for specified and legitimate purposes. Organisations must ensure that data is not processed in a way that nullifies the original purpose.
Organisations need to clearly define the purposes for which personal data is collected to comply with the principle of purpose limitation. They should specify these purposes to individuals at the time of data collection and ensure that the data is used only for those specific purposes. Any subsequent data processing should be compatible with the initial purpose and must stay within what is reasonable and expected by the individuals.
Purpose limitation essentially means that the user data collected by the service provider must not be used for any purpose other than what was originally stated. Let us understand this with the help of an example:
If a service provider collects the user's secondary email address, stating in consent that it is required as backup contact information. In this case, the service provider cannot use this detail to send customised content based on the user's geographical location. This would be considered as using the user's personal data for different purposes.
Since there are such strict regulations surrounding the use of personal data, teams which handle data of such nature in a company must be trained so they do not accidentally use data in a non-compliant manner. Making teams aware of the privacy policy is the best way to ensure that the personal data which is collected is used legally.
3) Data minimisation
Data minimisation is a fundamental Principle that emphasises the importance of collecting and processing only the least amount of personal data necessary to fulfil the specified purpose. It promotes a cautious approach to data handling, encouraging organisations to limit the collection and retention of personal information to what is essential and relevant.
To comply with this Principle, organisations should carefully evaluate the type and extent of personal data they collect. They should determine the specific data elements required to achieve the intended purpose and avoid collecting excessive or unnecessary information. By collecting only what is strictly needed, organisations can minimise the privacy risks of storing and processing personal data.
Data minimisation means that the service provider must gather only necessary data. Let us understand this with the help of an example. If a user signs up with a gaming company to receive the latest updates, upon signing up, user data such as 'job profile' and 'annual income' become irrelevant to the user's intent. Hence, data of such nature are not necessary. Knowing how to correctly implement data minimisation is critical in determining what is a GDPR breach. and reducing the chances of data breaches.
4) Accuracy
The fourth Principle of GDPR is the Principle of accuracy. It refers to the importance of maintaining accurate and up-to-date personal data. Organisations are responsible for ensuring that the personal data they process is correct, complete, and relevant for the intended purposes.
This involves implementing appropriate measures to verify data accuracy during collection and throughout the data processing lifecycle. Organisations should consider implementing data validation procedures such as:
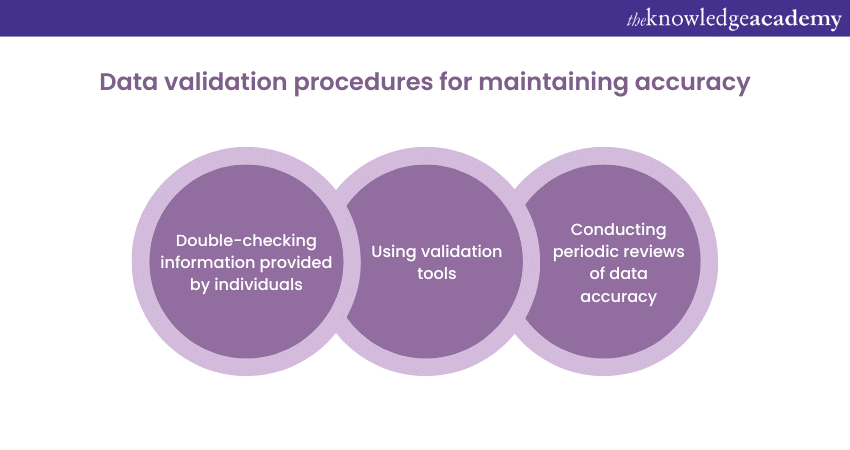
a) Double-checking information provided by individuals
b) Using validation tools
c) Conducting periodic reviews of data accuracy
It is integral to note that regular data cleansing activities can help identify and rectify any inaccuracies. These activities ensure that the personal data remains reliable and fit for purpose.
Let us understand accuracy with the help of an example. For instance, a user has signed up with a gaming company to receive updates using an email address. If the user decides to change his/her primary email address, then the current email address used to send updates the is no longer accurate. To avoid such scenarios, the service providers must ensure they provide options to the user for updating their personal information to maintain accurate data of the user at all times.
5) Storage limitation
The Principle of storage limitation refers to the significance of retaining personal data only for the period necessary to fulfil the purposes. Organisations must establish appropriate retention periods and ensure that personal data is securely disposed of once it is no longer needed.
This evaluation should consider legal requirements, contractual obligations, business needs, and other relevant factors. Retention periods may differ based on the type of data and the reason of its processing.
For instance, financial records might be subject to longer retention due to legal and regulatory obligations. At the same time, customer contact information might only need to be retained for the duration of the business relationship.
Let’s consider another example. If a user decides to unsubscribe from receiving the latest update, then keeping their personal data after they have unsubscribed does not make sense. Since the purpose of providing personal details was to receive updates, and if the purpose does not exist any longer, then the need to store users' personal data must not either.
In some scenarios, keeping personal data for a certain time period or making the personal data anonymous for analytical or historical purposes may be relevant. These scenarios are exceptions, and rules must be carefully considered before implementing measures of such nature.
Ready to navigate the complexities of GDPR? Sign up for our Certified EU General Data Protection Regulation (EU GDPR) Foundation And Practitioner Course now!
6) Integrity and Confidentiality
The sixth Principle is the principle of integrity and confidentiality. It highlights the importance of protecting personal data against unauthorised or unlawful processing and ensuring its accuracy and security.
Organisations must implement measures to ensure that personal data remains intact, unaltered, and consistent. This includes protecting data from accidental or intentional modifications or corruption via implementing access controls, regularly backing up data, and employing encryption techniques to protect data during transmission and storage.
Integrity and confidentiality refer to the steps a service provider must take to ensure that unauthorised people do not access personal data provided by the user. This includes people within the company; also, users' personal data must only be accessible to relevant people within the company.
Service providers must integrate systems and implement relevant measures to avoid data manipulation and to protect users' information from cyberattacks and breaches.
7) Accountability
This Principle places the responsibility on organisations to demonstrate GDPR compliance with the Data Protection Laws and to be accountable for their data processing practices.
Organisations must be transparent about their data processing activities, document their policies and procedures, and establish effective mechanisms to implement and monitor Data Protection measures. They should also appoint a designated person or team for Data Protection.
For example, if a service provider uses consent as a legal basis to process the acquired personal data, ensuring adherence to the rules and regulations, then, the service provider must document how and when this consent was received. To implement this, service provider can integrate systems which record consent.
GDPR also requires the service providers to take organisational measures in addition to technical measures. This means training your teams that handle personal data on aspects such as not using personal data other than its original intent or not re-using the personal data.
What is the significance of GDPR Principles?
Answering why is GDPR important is reflect the core of what GDPR stands for. They are defined at the beginning of the legislation and are meant to outline all the aspects of the regulations. They do not consist of hard and fast rules, but rather present an idea that should shape Data Protection. Complying with these fundamental GDPR Principles is a foundation for building robust Data Protection practices.
Article 83(5)(a) highlights that non-compliance with the basic Principles for processing personal data is subjected to the highest order of administrative fines. This translates to a fine of up to £17.5 million, or 4% of your total global annual turnover, whichever is higher.
Conclusion
GDPR establishes a strong framework for Data Protection, emphasising the importance of lawfulness, fairness, and transparency in data processing. Understanding the seven key principles of GDPR is crucial for organisations that handle personal data. We hope the contents of this blog helped you learn about the GDPR Principles and hence, understand the functioning of it better.
Become a proficient Data Protection Officer and lead your organisation towards GDPR compliance with our Certified Data Protection Officer (CDPO) Course now!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming IT Security & Data Protection Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Certified EU General Data Protection Regulation (EU GDPR) Foundation and Practitioner
Certified EU General Data Protection Regulation (EU GDPR) Foundation and Practitioner
Tue 7th May 2024
Sat 25th May 2024, Sun 26th May 2024
Mon 8th Jul 2024
Sat 14th Sep 2024, Sun 15th Sep 2024
Mon 23rd Sep 2024
Mon 18th Nov 2024
Sat 7th Dec 2024, Sun 8th Dec 2024







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


