We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a groundbreaking legislation revolutionising data protection practices and privacy rights. It has profoundly impacted businesses worldwide, reshaping how they handle personal data and placing greater emphasis on data privacy and security. However, certain Challenges of GDPR are important to be aware of for individuals and organisations.
Since the GDPR has come into play, detecting different types of violations has been easier. According to Statista, fines of over 1.67 billion have been issued due to the non-compliance of companies with general data processing principles.
Learn about the Challenges of GDPR, the complexities businesses face in ensuring compliance with it, and gain valuable insights on how to protect sensitive data.
Table of Contents
1) GDPR – A brief introduction
2) Compliance Challenges of GDPR
a) Complex regulatory requirements
b) Ensuring transparency and accountability
c) Obtaining valid consent
d) Managing data breach notifications
e) Cross-border data transfers
f) Data subject rights
g) Consequences of non-compliance
3) Effective compliance strategies
4) Conclusion
GDPR – A brief introduction
The GDPR is a comprehensive data protection regulation implemented by the European Union (EU) to safeguard individuals' privacy and personal data within the EU. It came into effect in 2018 and replaced the previous Data Protection Directive.
The main objectives of why is gdpr important are to give individuals more control over their data and to standardise data protection laws across the EU. It introduces several key principles that organisations must follow, which are as follows:
a) Lawfulness, Fairness, and Transparency
b) Purpose limitation
c) Data minimisation
d) Accuracy
e) Storage limitation
f) Integrity and Confidentiality
g) Accountability
Individuals have enhanced rights under GDPR to understand what is a GDPR breach, particularly in relation to their personal data.They can access their data, rectify inaccuracies, erase their data in certain circumstances, restrict processing, and object to the processing of their data. Organisations must be prepared to handle data subject rights requests and respond within specified timeframes.
GDPR is beneficial to multiple individuals, organisations, and society. Here are some key benefits of GDPR:
a) Enhanced data protection
b) Individual Rights and empowerment
c) Transparent data practices
d) Harmonisation on data protection laws
e) Compliance culture
Take the next step towards GDPR compliance and enhance your understanding of data protection with our GDPR Training Courses now!
Compliance Challenges of GDPR
The implementation of GDPR presents several key challenges for businesses striving to achieve compliance. These challenges include:
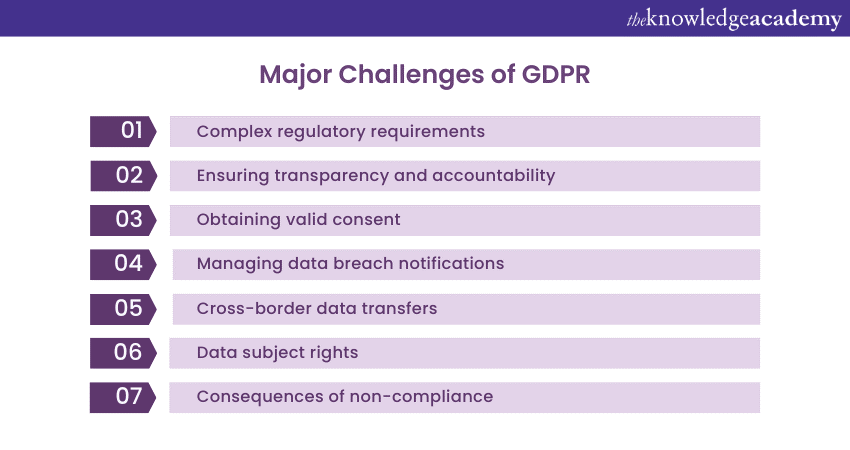
1) Complex regulatory requirements
One of the major GDPR challenges includes the complex framework of regulatory requirements that organisations must navigate. From establishing legal bases for data processing to implementing privacy by design and default principles, businesses need a comprehensive understanding of GDPR's provisions. Ensuring compliance across various aspects of the regulation can be overwhelming, especially for organisations with limited resources or expertise in data protection.
Under GDPR, the complex regulatory requirement of "Privacy by Design and Default" mandates organisations to integrate the protection of privacy and data into the design and development of their products, services, and systems.
For example, a software development company creating a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system must involve privacy experts, conduct data protection impact assessments, implement privacy features, and document compliance efforts to meet this requirement. This ensures data protection from the early stages and fosters trust with customers. Compliance requires careful planning, collaboration, and ongoing monitoring.
2) Ensuring transparency and accountability
GDPR places a strong emphasis on transparency and accountability in data processing. Organisations must provide individuals with clear and concise information on the manner of data collection and the way it is used and shared.
This involves drafting privacy notices and policies that are easily accessible and understandable to individuals. Implementing mechanisms for accountability, such as maintaining records of processing activities, can also be a challenge for businesses, especially those operating across multiple systems and departments.
3) Obtaining valid consent
Another of the GDPR challenges includes organisations having to obtain valid and informed consent from individuals before collecting and processing their data, and the consent must be given freely, specifically, informed, and unambiguous.
Enterprises must carefully review their consent mechanisms, ensuring that consent requests are clear, granular, and separate from other terms and conditions. Obtaining valid consent can be particularly challenging when dealing with complex data processing activities or sensitive categories of personal data.
4) Managing data breach notifications
GDPR mandates organisations to notify supervisory authorities promptly and affected individuals at the occurrence of a data breach. This requires establishing robust incident response plans, including mechanisms for detecting, investigating, and mitigating data breaches. Developing efficient processes to assess the severity of breaches and determine the appropriate notification steps can be complex, especially for organisations dealing with large volumes of data.
5) Cross-border data transfers
GDPR imposes restrictions on transferring personal data to countries that do not offer ample data protection and outside the EU. Organisations must ensure that appropriate safeguards, such as binding corporate rules, are in place when transferring data internationally.
With the invalidation of the Privacy Shield framework, organisations face additional challenges in finding suitable transfer mechanisms, potentially requiring case-by-case assessments and additional safeguards.
6) Data subject rights
GDPR grants individuals various rights regarding personal data, including access, rectification, restrict processing, and erasing data. Organisations must establish processes to handle data subject rights requests within the specified timeframes and verify individuals' identities properly. Managing a large volume of requests and maintaining a centralised system to track and respond to these requests can be challenging for organisations.
7) Consequences of non-compliance
Non-compliance is one of the most common GDPR challenges, as it can lead to significant consequences, including substantial fines and reputational damage. Organisations must diligently comply to avoid the financial and reputational risks associated with violations. The potential impact of non-compliance poses a constant challenge for businesses, necessitating ongoing monitoring, review, and adjustment of their data protection practices.
Become a certified GDPR Foundation professional by signing up for our Certified EU General Data Protection Regulation (EU GDPR) Foundation Course now!
Effective compliance strategies
Compliance with GDPR requires organisations to adopt effective strategies and implement best practices to ensure ongoing adherence to the regulation within the GDPR Scope.. Here are some key compliance strategies and best practices:

a) Establish a data protection framework: Develop a comprehensive framework encompassing policies, procedures, and guidelines aligned with GDPR requirements.This framework should outline roles, responsibilities, data processing principles, consent mechanisms, and data subject rights processes. Ensure to regularly review and update the framework to reflect changes in the regulatory landscape and organisational needs.
b) Conduct Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs): Performing DPIAs to assess and mitigate privacy risks associated with data processing activities is an effective strategy. Identify and evaluate potential risks to individuals' rights and freedoms, implement necessary safeguards, and document the assessment process. DPIAs should be conducted for high-risk processing activities and regularly reviewed to ensure ongoing compliance.
c) Implement Privacy by Design and Default: Integrate privacy and data protection considerations into the design and development of products, services, and systems. From the outset, embed privacy features, such as data minimisation, purpose limitation, and security measures. Adopt privacy-friendly defaults and ensure that only necessary personal data is collected and processed.
d) Ensure transparent data practices: Another effective GDPR compliance strategy is to provide individuals with clear and concise information about how their personal data is collected, used, and shared.
Draft privacy notices and policies that are easily accessible written in plain language, and include relevant details about data processing activities. Communicate any updates or changes to individuals in a timely and transparent manner.
e) Implement security measures: You can adopt the required organisational and technical security practices to protect personal data from unauthorised access, disclosure, alteration, or destruction.
Implement encryption, access controls, regular system updates, and employee training on security best practices. Conduct regular security assessments and audits to detect and address vulnerabilities.
f) Train employees: Provide comprehensive training and awareness programs to employees on GDPR Principles,data protection obligations, and their roles in ensuring compliance. It is imperative to constitute a culture of privacy and data protection within the organisation, emphasising the importance of handling personal data securely and responsibly.
g) Monitor and audit compliance: Regularly review data protection practices, conduct internal audits, and perform periodic assessments to identify areas for improvement. Implement data security rules and processes that allow for continual compliance monitoring and GDPR risk assessment.
h) Engage with legal experts: It is important to engage legal experts or consultants to provide guidance on interpreting and implementing GDPR requirements. You can also take part in industry forums and attend conferences to gain insights into best practices and emerging trends in data protection.
Conclusion
GDPR has brought significant changes to the landscape of data protection and privacy. It has placed individuals' rights and interests at the forefront, empowering them with greater control over their data. However, navigating the intricacies of GDPR compliance can be challenging for businesses. We hope this blog has enhanced your understanding of the Challenges of GDPR and the strategies which can be used to achieve GDPR compliance.
Elevate your expertise in GDPR implementation and compliance. Register for our Certified EU General Data Protection Regulation (EU GDPR) Practitioner Course now!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming IT Security & Data Protection Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Certified EU General Data Protection Regulation (EU GDPR) Foundation and Practitioner
Certified EU General Data Protection Regulation (EU GDPR) Foundation and Practitioner
Sat 14th Sep 2024, Sun 15th Sep 2024
Mon 23rd Sep 2024
Mon 18th Nov 2024
Sat 7th Dec 2024, Sun 8th Dec 2024
Mon 13th Jan 2025
Mon 3rd Mar 2025
Mon 14th Apr 2025
Tue 27th May 2025
Mon 14th Jul 2025
Tue 26th Aug 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


