We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

This blog highlights the essential components of a GDPR audit and the purpose behind auditing. Learn how the audit of GDPR is meant to keep data security up to date. Find out how organisations address security issues through data protection compliance and privacy protection policies that support individuals.
Whether we are aware of it or not, our personal data is more exposed than ever. Shielding people's private lives has increasingly become an issue. This is where coming to the short ends of the strings, we have GDPR Audit. Consider it like a periodic health check of organisations, which sets the pace, and organisations should not be left behind by the demands of GDPR.
Abiding by this, GDPR Audit checks are similar to the doctor's examination of a patient. They provide an organisation with a proper account of its data protection practices, the holes in security procedures, and the right course of action to enhance data security. It's time to take a more in-depth look into the GDPR Audit and its importance in creating properly protected and private data. Learn about GDPR Audits, the importance of conducting one, and how it ensures Data Protection and compliance with data privacy regulations.
Table of Contents
1) What is a GDPR Audit?
2) Why should a GDPR Audit be conducted?
3) Basic terminologies in GDPR
4) Reasons to conduct a GDPR Audit
5) GDPR Audit checklist
6) How much does a GDPR Audit cost?
7) Is GDPR Audit necessary for businesses?
8) Is a GDPR Audit legally necessary?
9) Benefits of a data privacy audit
10) Conclusion
What is a GDPR Audit?
A comprehensive survey using data protection tools is a process that entails a review of organisational practices and processes for adequate compliance with GDPR requirements. The problem is that personal data can be gathered and stored – it is no mystery or good idea how to protect it with the current regulations of GDPR. Conducting this audit can help the organisation to Note if there is any non-conformity or weakness in its implementation of Data protection and take action to correct it.
Covering these, a list of areas which deal with the very heart of the organisation's data processing is considered as the audit process goes on. This will be done by reviewing the updated Data Protection Policy in accordance with GDPR and the Data Protection Act, evaluating the existing data breach response plans, revisiting consent methodology, reconsidering data transfer practices, and reassessing the effectiveness of employee training and awareness programs.
Take control of data privacy and enhance your understanding of GDPR compliance with our Data Privacy Awareness Course now!
Why should a GDPR Audit be conducted?
Conducting a GDPR Audit is crucial for organisations to ensure they adhere to the requirements. The following reasons highlight the importance of conducting these audits regularly:
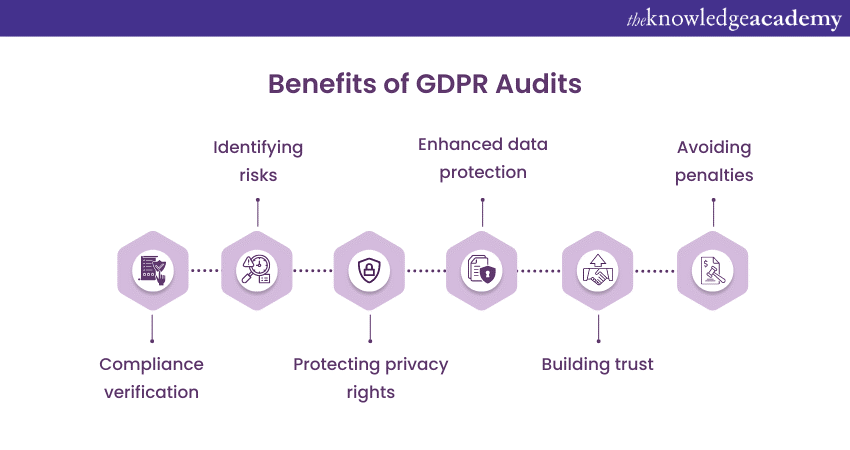
a) Compliance verification: The GDPR has developed an extensive concept of rules and regulations for issues in the processing of personal information. Organisations can perform the audits so as to be in a position to realise how well they have complied with the GDPR requirements and where they are actors of non-compliance. This empowers them to make proactive steps and schedule their data processing activities in line with GDPR standards, thus minimising the risk of non-compliance and legal sanctions.
b) Identifying risks: The auditing process clarifies the extent to which the Organisations have implemented their Data Protection provisions to recognise any system loopholes. Through learning about it and knowing its vulnerabilities, organisations can implement the necessary practices that will help them secure personal data from unauthorised access, loss, and also disclosure. This step, which is taken ahead of time to back up the data and protect the privacy of individuals, is conducive to preventing any future data breach.
c) Protecting privacy rights: Regular audits monitor whether organisations are evolving these rights or not by providing their workers with new tools to secure personal data. Organisations are able to develop trust with their customers, employees, and stakeholders by showing a willingness to sacrifice confidentiality.
d) Enhanced Data Protection: An audit can discover whether the organisation's data protection measures are effective or not, and the audits can ensure the availability of tools such as encryption, access controls, and incident response plans. The ability to find vulnerabilities or shortcomings in data security is efficient since it helps organisations lock down their security infrastructure and shield Personal data against any unauthorised or illegal usage.
e) Building trust: In an era where data breaches and privacy scandals dominate headlines, organisations prioritising Data Protection and privacy gain a competitive advantage. Regular audits showcase an organisation's commitment to data privacy and security, helping build trust among customers, partners, and stakeholders. By maintaining a solid reputation in terms of Data Protection, organisations can attract and retain customers who value their privacy.
f) Avoiding penalties: Non-compliance with GDPR can result in significant fines and penalties. By conducting audits, organisations can identify and rectify non-compliance issues before they lead to legal consequences. This proactive approach reduces the risk of penalties and ensures that enterprises operate within the legal boundaries of Data Protection regulations.

Basic terminologies in GDPR
Personal data, Sensitive Personal data, Anonymous data, Pseudonymous data, Data processing, and Controller are some basic GDPR terms you need to understand. Here are their definitions and associated abbreviations:
a) Personal data: Any information that can identify a living person is considered Personal data. This can be a combination of different pieces of information that can single out a specific person.
b) Sensitive Personal data: A special Personal data requiring extra protection. Generally, organisations need stronger reasons to process Sensitive Personal data than they do for regular Personal data.
c) Anonymous data: Data sets that are modified so that no one can recognise any person(s) (directly or indirectly) from them by any means or by anyone. Ensuring that individuals cannot be identified is a technically difficult process.
d) Pseudonymous data: Data that is altered by using a reference number or other identifier to replace names or other identifiers that are easily linked to individuals.
e) Controller: The legal person, agency, public authority, or other organisation that decides the purposes and means of Personal data processing, alone or with others.
Reasons to Conduct GDPR Audit
GDPR regulation aims to protect individuals' Personal data and privacy in the European Union (EU). The GDPR is necessary for the following reasons:
a) It gives individuals more rights and control over their data, such as the right to access, restrict, rectify, erase, or object to the processing of their data. It also gives individuals the right to data portability, the right to be informed, and not to be subject to automated decision-making or profiling.
b) It requires organisations that process Personal data to comply with certain principles and obligations, such as lawfulness, fairness, transparency, accuracy, security, and accountability. It also requires organisations to obtain valid consent from individuals, conduct Data Protection impact assessments, appoint Data Protection officers to study data breaches, and cooperate with supervisory authorities.
c) It harmonises the Data Protection laws across the EU and ensures a high level of Data Protection standards for businesses. It also provides a single set of rules and a single market for data, which can reduce costs and increase efficiency for organisations. It also facilitates the free flow of data within the EU and with third world countries with adequate Data Protection standards.
GDPR Audit Checklist
Complying with GDPR standards through this checklist created by GDPR ensures that organisations properly meet the needs of the GDPR and further protect their Data. The following steps are taken while conducting a GDPR Audit:
1) Review data processing activities
The very initial step is analysing the data processing operations of an organisation, which involves the identification of different types of Personal Data, the purposes behind processing, lawful grounds for the processing, and the retention periods. It is your responsibility to ensure that Personal data is handled lawfully, fairly, and transparently as is provided for in the Regulations on personal data processing.
2) Assess Data Protection policies and procedures
Verifying everything about data protection policies and procedures for risk assessment is an obvious need for the organisation to audit. Among other things, these must be the privacy notices given to Data Subjects, the efficacy of consent mechanisms, and the necessary contractual agreement with data processors imposed indeed.
3) Evaluate data breach response plan
Examining the entity's data breach plan is a crucial factor of auditing, and for that reason, being best done to ensure that the plan is comprehensive and effective. This requires you to make sure the right procedures are in place for data protection operations such as detection, investigation and reporting of GDPR breaches. At the same time, you should check whether the organisation has a response plan that can be immediately accessed and implemented in case a breach occurs. An appropriate notification to both the data protection authority and the affected individuals must also be assessed.
4) Examine consent mechanisms
Check the process of obtaining and dealing with the consent of Data Subjects through proper GDPR principles, such as subjects freely grating their individual consent, without any subconscious influence. Highlight the capability of the organisation to keep consent in place for different processing activities including building consent withdrawal mechanisms.
5) Assess third-party contracts and compliance
Such clauses may include provisions such as specifications of roles that would be executed by the service providers or data processors, as well as obligations to follow principles of data protection required for the GDPR. Your organisation must review third parties to verify their compliance and verify that measures taken for protecting personal data are productive.
6) Evaluate Data Subject Rights Processes
This is one of the central factors in creating GDPR, which is the increase of power of citizens with Data Subject rights. These rights let people establish themselves as the masters of their data and the means by which this data is handled. It is crucial for the auditor to perform a control verification, which will check whether the organisation's Data Subject rights request procedures are in order.
This ensures that individuals can exercise their rights effectively and the organisation is compliant with the regulations. Here are key considerations when evaluating Data Subject rights processes:
a) Access requests
b) Rectification requests
c) Erasure requests
d) Restriction of processing requests
e) Data portability requests
f) Objection requests
g) Authentication and verification
h) Internal awareness
i) Record-keeping
7) Review security measures
GDPR specifies that organisations must implement technical measures to ensure Personal data about specific individuals are not leaked, destroyed or lost. The evaluation of the technical and security precautions applied to protect personal data from unauthorised expropriation, loss, or disclosure is a must. This includes assessing the effectiveness of the following:
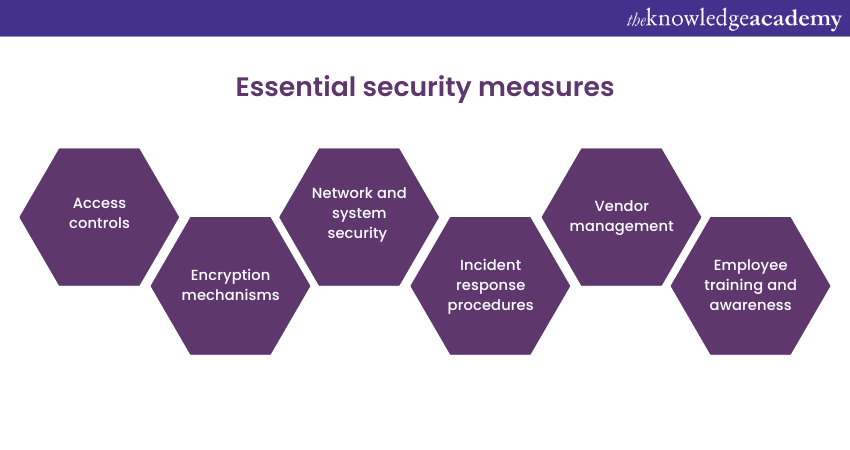
a) Access controls
b) Encryption mechanisms
c) Network and system security
d) Incident response procedures
e) Vendor management
f) Employee training and awareness
Wish to enhance your knowledge of Data Protection? Register for our Certified EU General Data Protection Regulation (EU GDPR) Foundation And Practitioner Course now!
8) Implement Privacy Impact Assessments
Verify that the organisation conducts Privacy Impact Assessments (PIAs) for high-risk processing activities. Evaluate the adequacy of PIAs in identifying and addressing privacy risks associated with data processing activities, and ensure that mitigating measures are implemented where necessary.
9) Examine data retention and disposal practices
You must review the organisation's data retention and disposal practices to ensure GDPR compliance with storage limitation principle. It is important to verify that Personal data is retained for the required period alone and is securely removed when it is no longer required.
10) Evaluate incident response and notification procedures
One of the most important steps is to assess the organisation's incident response and notification procedures for data breaches. Verify that the organisation has appropriate processes to detect, respond, and notify relevant parties in the event of a data breach.
11) Assess accountability measures
It is essential to figure out of the organisation’s leitmotif for the data violations and notification so that the incidents can be responded in an appropriate manner. Review the organization's procedures, initiate a data breach simulation and ensuring timely notification to the authorized agencies should be confirmed.
A DPO function is to be a liaison officer within an organization charged with the mission of supervising Data Protection activities and maintaining discipline. Among the many things an organization should guarantee while auditing its GDPR checklist is that it knows exactly what data it actually processes, why and how it does it.
12) Regularly review and update Data Protection measures
Ensure the organisation regularly reviews and updates its Data Protection measures to adapt to changes in GDPR requirements and emerging Data Protection best practices. Continuously monitor and improve Data Protection practices to ensure ongoing compliance and data security.
13) Personal Information Management System (PIMS)
A PIMS is a system that points out the protection of privacy as potentially affected by the processing of Personal data. A PIMS is based on ISO/IEC 27701 for Personal information management. A PIMS helps organisations to establish, implement, maintain, and continually improve their privacy policies, procedures, and practices. A PIMS also helps organisations to demonstrate their compliance with GDPR.
14) Establish a Staff Training Program on GDPR
Neglecting to train staff on the nuances of handling data can undo all GDPR compliance efforts through a single mishap. Thus, educating employees on GDPR compliance is crucial. This includes understanding the core principles of data protection, recognizing the rights individuals have under GDPR, and becoming familiar with the organization's particular policies and procedures for data protection.
How much does a GDPR Audit cost?
A data privacy audit is a service that helps you comply with the GDPR rules and regulations. The cost of a data privacy audit varies depending on the size and complexity of your business, but it usually ranges from £900 and £2,700. This includes various services, such as an initial assessment of your departments, advice for all departments, and creating recommendations and legal Data Protection documents. It also includes mandatory staff training, the creation of a privacy policy, and a basic package with Data Protection pointers.
Is GDPR Audit necessary for businesses?
It is critical to perform a GDPR audit on any business that has personal data. It enables preserving the rules that apply to the protection of data, building trust with customers, and reducing the risk of serious financial penalties imposed for malfunction in this area. Conducting regular audits is a clear manifestation of harmonized data privacy practices and, therefore, the integrity of data.
Is a GDPR Audit legally necessary?
Since a data privacy audit is not included in the GDPR, it will provide the company with a way to show it is following all the requirements. Lawful purposes have to be turned into practice, and such practice should be after getting the authority for accessing and storing Personal data. The audit shall be your means for assessing and correcting the GDPR issues you face.
Benefits of data privacy audit
Within the scope of a GDPR Audit approach, a company is able to detect that all the personal data it is able to know about may not be tabulated as per GDPR regulations. Benefits of GDPR Audit can have many advantages for an organisation, such as:
a) Compliance with GDPR: The audit is the ideal instrument for evaluating the entity for any data protection issues that can be corrected. In conjunction with penalties and any legal actions, this is the best way to be fully GDPR-compliant. The GDPR prescribes that organisations adhere strictly to the personal data protection rules of EU member states and enshrine the rights and preferences of individuals.
b) Improvement of Data Protection processes: After all the compliance requirements have been tested in a GDPR Audit and proven to be effective, the organisation could use these measures to push through with more efficient solutions to data protection. A crosscheck made by the GDPR auditor would have the potential to discover data security gaps and other significant areas like data quality, minimisation, retention, governance and accountability within the organisation.
c) Competitive advantage: The data controllers and processors which observe GDPR regulations are in reality regarded as the companies that appreciate the privacy and security of their customers and apply the latest principles in the data protection rule.
Conclusion
Conducting a comprehensive GDPR Audit is essential for organisations to ensure compliance with Data Protection regulations and safeguard the privacy rights of individuals. We hope this blog has enhanced your knowledge of GDPR Audits and the key aspect involved in them.
Elevate your understanding of GDPR regulations and ensure compliance with our GDPR Training Courses now!
Frequently Asked Questions

The 7 principles of GDPR are Lawfulness, Fairness, and Transparency; Purpose Limitation; Data Minimization; Accuracy; Storage Limitation; Integrity and Confidentiality (Security); and Accountability.

The GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) is a set of laws designed to give people more control over their personal data and how it's used by companies, primarily within the European Union.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various , including GDPR Courses, Information Systems Security Management Training and more. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Benefits of GDPR.
Our IT Security & Data Protection Blogs cover a range of topics related to GDPR, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your GDPR skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming IT Security & Data Protection Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Certified EU General Data Protection Regulation (EU GDPR) Foundation and Practitioner
Certified EU General Data Protection Regulation (EU GDPR) Foundation and Practitioner
Sat 14th Sep 2024, Sun 15th Sep 2024
Mon 23rd Sep 2024
Mon 18th Nov 2024
Sat 7th Dec 2024, Sun 8th Dec 2024
Mon 13th Jan 2025
Mon 3rd Mar 2025
Mon 14th Apr 2025
Tue 27th May 2025
Mon 14th Jul 2025
Tue 26th Aug 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


