We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
In today's fast-paced and highly competitive business world, organisations are constantly seeking ways to optimise their operations and stay ahead of the curve. With Business Process Analysts’ (BPAs) expertise in analysing, improving, and redesigning Business Processes, their role plays a crucial part in helping companies streamline their workflows and achieve their strategic objectives.
In this blog, you will learn about Business Process Analysts, their importance, roles and responsibilities, as well as the skills required. Let’s dive in!
Table of Contents
1) Business Process Analyst- an overview
2) Importance of Business Process Analysts
3) Roles and responsibilities of a Business Process Analyst
4) Skills of a Business Process Analyst
5) Tools and Techniques used
6) Conclusion
Business Process Analyst – An overview
A Business Process Analyst is a highly skilled professional who specialises in evaluating, enhancing, and optimising the operational processes of an enterprise. They possess a deep understanding of business operations and utilise their analytical abilities to identify inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and areas for improvement within existing processes. Their primary goal is to streamline workflows, eliminate waste, and enhance overall efficiency to help organisations achieve their strategic objectives.
Business Process Analysts play a crucial role in helping close the gap between different departments and stakeholders within an enterprise. By collaborating with various teams, they gather valuable insights, understand their needs, and incorporate feedback into the process design.
Importance of Business Process Analysts
The importance of Business Process Analysts must be addressed in today's dynamic business landscape. Here are some key points highlighting their significance:
a) Enhanced operational efficiency: Business Process Analysts play a vital role in improving the efficiency of business operations. By identifying bottlenecks, redundancies, and areas for improvement, they streamline processes, eliminate waste, and enhance productivity. This leads to cost savings, optimised resource allocation, and improved customer satisfaction.
b) Strategic alignment: These analysts help align business processes with the organisation's goals. Evaluating current processes and identifying gaps ensures that every activity and task contributes to the objectives. This strategic alignment enables companies to stay competitive and agile in a rapidly evolving market.
c) Process optimisation: Business Process Analysts are experts in process optimisation. They employ analytical techniques, data analysis, and industry best practices to identify areas of improvement and implement changes. Through their expertise, they enhance process flow, reduce cycle times, and increase overall operational effectiveness.
d) Continuous improvement: Business Process Analysts foster a culture of continuous improvement within an enterprise. They encourage teams to embrace change, adapt to new processes, and constantly seek ways to enhance efficiency. Promoting a mindset of ongoing evaluation and optimisation ensures that the organisation remains agile and responsive to evolving market demands.
e) Improved decision-making: Their insights enable informed decision-making at all levels of the organisation. Through their data analysis and processes, they identify trends, patterns, and areas of concern. This valuable information empowers management to make strategic decisions that drive business growth and success.
f) Compliance and risk management: These analysts contribute to compliance and risk management efforts. They identify potential risks, control gaps, and compliance issues by analysing processes. They design and implement robust controls to mitigate risks, ensuring the organisation operates within legal and regulatory frameworks.
g) Customer-centric focus: These analysts consider the impact of process improvements on customer experience. Enhancing workflows and eliminating pain points improves customer satisfaction and loyalty. Their insights help businesses deliver products and services more efficiently, meeting and exceeding customer expectations.
h) Organisational agility: In an era of rapid technological advancements and market disruptions, Business Process Analysts help organisations stay agile. They assess the impact of external factors on internal processes and recommend changes to adapt to new realities. This agility enables enterprises to respond quickly to market changes, capitalise on emerging opportunities, and mitigate risks.
Roles and responsibilities of a Business Process Analyst
A Business Process Analyst plays an extremely important role in optimising a company's operations. Let's take a look at some of them below:
1) Research and observation: Their work begins with thorough research and on-site observations. By doing so, they identify the necessary tools, infrastructure, and personnel essential for streamlining various Business Processes.
2) Data collection: Data is the lifeblood of process improvement. Business Process Analysts meticulously collect crucial information by mapping out existing processes and facilitating workshops. This data serves as the foundation for more effective process engineering.
3) Process enhancement: One of their primary duties is to examine current business processes, identifying flaws and inefficiencies. Their goal is to find innovative ways to improve and optimise these processes, fostering productivity and reducing costs.
4) Automation expertise: Business Process Analysts should stay updated on the best practices and technological advancements due to the rapidly changing business landscape. Their goal is to leverage these developments for the efficient automation and streamlining of Business Processes.
5) Goal setting: Collaboration is key Business Process Analysts work closely with senior management and clients to define clear business goals and formulate strategies to achieve them successfully. This ensures alignment throughout the organisation.
6) Reporting: Apart from their analytical tasks, they are responsible for presenting their findings and insights. They prepare presentations and reports that offer qualitative analyses of industry trends, companies, and market dynamics. Additionally, they produce financial reports that senior management reviews during monthly or quarterly meetings.
7) Cross-functional communication: Effective communication is essential. Business Process Analysts maintain a line of communication with various stakeholders, including accounting professionals, project managers, project controllers, and cost centre owners. This ensures a deep understanding of business operations and helps mitigate potential risks.
8) Stakeholder engagement: They play a role in building and maintaining relationships with critical stakeholders involved in operational processes. Regular meetings and discussions ensure that objectives are clear and strategies are effective.
9) Financial analysis: Business Process Analysts dive into financial data, reviewing and analysing monthly results. Their meticulous approach ensures that any errors are promptly addressed. They also compare actual results against budget projections and communicate any variances to senior management.
10) Recommendations and data analysis: Ultimately, they act as the bridge between data and decision-making. They collect, analyse, and synthesise data to provide evidence-based recommendations for effective process improvements. These recommendations are presented in clear and actionable formats to support clients and projects.
The above responsibilities showcase the diverse role of a Business Process Analyst when it comes to optimising and enhancing Business Processes.
Elevate your business analysis skills with comprehensive Business Analyst Training. Sign up now!
Skills of a Business Process Analyst
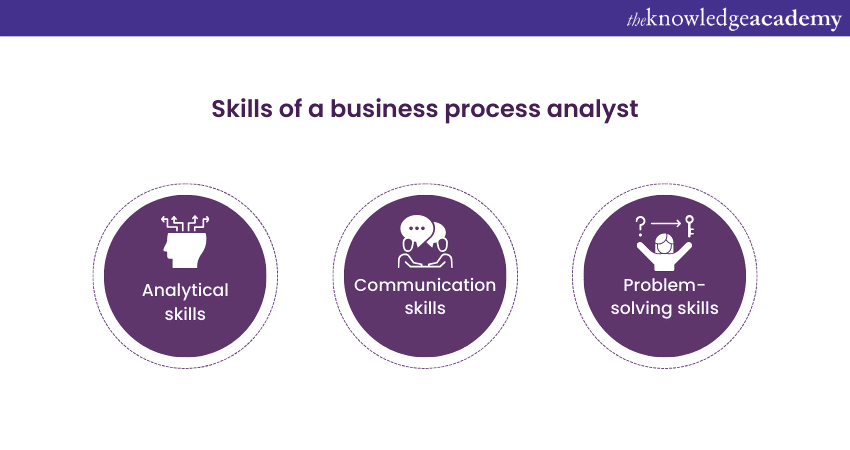
To excel in this role, a Business Process Analyst must possess unique skills and qualifications. Let's explore some of the key attributes:
Research skills
Research is a fundamental skill that Business Process Analysts must possess. The nature of their job demands them to be proficient in this skill. They rely on research skills to implement diverse business processes, find inefficiencies, and design efficient solutions.
Their research proficiency empowers Business Process Analysts to probe issues and propose enhancements to streamline business operations. The extent of their research ability directly correlates with the overall quality of outcomes they can achieve. The more capable they are at research, the more significant the improvements they can bring to the table.
Analytical skills
a) Data interpretation: Business Process Analysts are adept at interpreting and analysing large data sets. They can identify patterns, trends, and correlations within the data to uncover underlying issues or opportunities for process improvement.
b) Critical thinking: These analysts apply critical thinking skills to break down complex problems into smaller components, allowing for a comprehensive understanding of the issues. They can evaluate different perspectives, weigh pros and cons, and make informed decisions based on data-driven insights.
c) Problem identification: Analytical skills enable them to identify process inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and pain points. They use their ability to analyse and compare data to identify deviations from expected outcomes, ultimately pinpointing improvement areas.
d) Predictive analytics: Business Process Analysts employ predictive analytics techniques to forecast future outcomes and trends based on historical data. By analysing patterns and applying predictive models, they can anticipate potential risks, identify opportunities, and make proactive decisions.
e) Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems: Business Process Analysts have a working knowledge of ERP systems such as SAP, Oracle, or Salesforce. This allows them to understand the integration of Business Processes within these systems and identify opportunities for optimisation.
f) Quality management systems: Understanding Quality Management Systems (QMS) like ISO 9001 or Six Sigma methodologies equips Business Process Analysts with the knowledge and skills to implement quality control measures, conduct audits, and drive continuous improvement initiatives.
Communication skills
a) Stakeholder engagement: Business Process Analysts interact with stakeholders from various departments and levels within the organisation. Effective communication skills allow them to build rapport, listen attentively, and understand the perspectives and requirements of different stakeholders.
b) Active listening: Being an active listener enables these analysts to gather accurate and comprehensive information from stakeholders. They pay close attention to verbal and non-verbal cues, ask clarifying questions, and demonstrate empathy to understand stakeholder needs fully.
c) Interviewing and facilitation: Business Process Analysts conduct interviews and facilitate meetings with stakeholders to gather insights and requirements. They use effective questioning techniques, manage group dynamics, and encourage open and collaborative discussions to extract valuable information.
d) Clear and concise communication: Business Process Analysts communicate complex concepts and technical information clearly and concisely. They use plain language, avoid jargon, and present information in a way easily understandable by stakeholders with varying levels of expertise.
e) Presentation skills: These analysts deliver presentations to stakeholders, explaining their analysis, recommendations, and the benefits of process improvements. They use visual aids, storytelling techniques, and persuasive communication to engage the audience and gain support for proposed changes.
f) Negotiation and influencing: They often need to negotiate and influence stakeholders to gain buy-in for process improvement initiatives. They employ effective communication strategies to articulate the benefits, address concerns, and align stakeholders towards a common goal.
g) Conflict resolution: Strong communication skills enable Business Process Analysts to handle conflicts and disagreements that may arise during process improvement initiatives. They facilitate constructive discussions, actively listen to different viewpoints, and find mutually beneficial resolutions.
Enhance your stakeholder engagement skills with the Creating Effective Stakeholder Engagement Course!
Problem-solving skills
Problem-solving skills are crucial for a Business Process Analyst to effectively address challenges and identify innovative solutions. These professionals possess the ability to analyse complex problems, break them down into manageable components, and apply logical thinking to develop effective strategies. They demonstrate critical thinking, creativity, and a systematic approach to problem-solving, considering multiple perspectives and evaluating potential risks and benefits.
Business Process Analysts use their problem-solving skills to identify root causes, propose process improvements, and implement solutions that enhance efficiency, productivity, and overall organisational performance.
Technical skills
Technical Skills of Business Process Analysts include the ability to effectively use computer hardware, software, and applications to optimise business operations. Let's explore some of these skills below:
1) IT strategy development: Analysts actively participate in shaping IT strategy, necessitating a solid understanding of how technology can be strategically employed to enhance Business Processes.
2) Computer proficiency: Proficiency in computer usage is fundamental for tasks such as data analysis, modelling, and report generation, as these are core elements of the role.
3) Software proficiency: Business Process Analysts must be well-versed in various software applications, particularly those that support data analysis, process modelling, and Business Intelligence (BI).
4) Application expertise: They should be capable of effectively working with a variety of business applications, understanding their functionalities, and potentially customising them to align with specific business requirements.
5) Enhancing business operations: The ultimate goal of technical skills in this role is to enhance business operations by identifying opportunities for process automation, data-driven decision-making, and other technology-driven improvements. This proficiency directly contributes to business growth and development by increasing efficiency and competitiveness.
Writing skills
Writing skills include the ability to effectively and coherently communicate ideas and information through the written word. For Business Process Analysts, these skills are indispensable due to the requirement of producing presentations and reports as part of their job description. Let's explore these skills below:
1) Effective communication: Writing skills enable analysts to convey complex ideas, findings, and recommendations clearly and concisely. This is crucial for ensuring that their insights and strategies are easily understood by colleagues, clients, and senior management.
2) Professional presentations: Analysts often create presentations to deliver their findings to various stakeholders. Strong writing skills are essential for structuring these presentations, making them engaging, and ensuring they convey the key points effectively.
3) Documentation: Accurate and detailed documentation is essential in the field of Business Analysis. Business Process Analysts must document their observations, methodologies, and outcomes, making strong writing skills vital for maintaining a record of their work.
4) Client communication: Analysts often interact with clients to understand their requirements and provide recommendations. Effective written communication is key to building trust and conveying the value of their services.
Master the art of Business Process Mapping with our comprehensive Business Process Mapping Training.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the role of a Business Process Analyst is vital in today's dynamic business environment. They play a crucial role in analysing, improving, and optimising business processes to drive efficiency, productivity, and overall organisational success.
Business Process Analysts are equipped to tackle complex challenges and identify innovative solutions through their expertise in analytical skills, technical skills, communication skills, problem-solving skills, and various tools and techniques.
Drive operational excellence with our Lean Six Sigma Training Course!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming Business Analysis Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Certified Business Analyst Professional (CBA-PRO)
Certified Business Analyst Professional (CBA-PRO)
Thu 6th Jun 2024
Thu 10th Oct 2024
Thu 19th Dec 2024
Thu 16th Jan 2025
Thu 20th Mar 2025
Thu 19th Jun 2025
Thu 9th Oct 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course




 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


