We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Mental Health Illness is a health problem that affects a person's emotional, physical, cognitive, and behavioural well-being and requires professional treatment and support. According to The Lancet , post-pandemic, depression worldwide grew from a base of about 193 million people worldwide to 246 million, which is about 28%. These statistics clearly indicate that by increasing our general understanding, we can contribute to breaking down the stigma and promoting a healthier approach to mental well-being. Want to know how? In this blog, we will learn about What is Mental Health Illness, from its definition, types, and symptoms to its impact on individuals and society.
Table of Contents
1) Mental Health Illness Definition
2) Common types of Mental Health Illness
3) Signs and symptoms of Mental Health Illness
4) Effects of Mental Health Illness
5) How are Mental Health Illness diagnosed?
6) How can Mental Health Illness be treated?
7) Conclusion
Mental Health Illness Definition
Before we delve into its types, symptoms, and effects, we will first define What is Mental Health Illness. Mental Illness can be defined as a wide range of conditions affecting emotional, cognitive, and behavioural well-being. It involves disruptions in thoughts, emotions, and actions, often causing distress and impairing daily life. Conditions like anxiety, depression, and schizophrenia are common examples.
These illnesses can impact relationships, work, and physical health, highlighting the intricate mind-body connection. Therefore, awareness and understanding of Mental Illnesses are crucial for promoting early intervention, reducing stigma, and fostering a society that supports mental well-being through empathy, education, and appropriate treatment.

Common types of Mental Health Illness
Mental Illness encompass numerous conditions that affect the way individuals think, feel, and behave. Here, we will explore some of the most common Mental Health disorders, shedding light on their characteristics, symptoms, and potential effects:
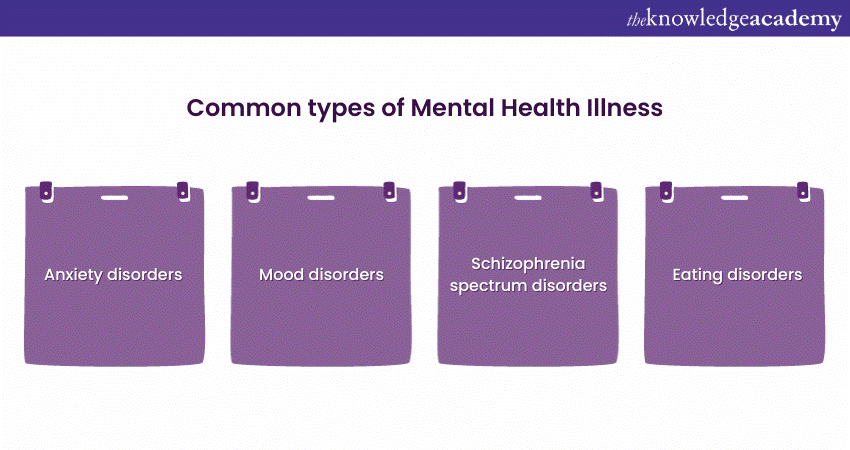
Anxiety disorders
Anxiety disorders are marked by excessive worry, fear, and unease that can interfere with regular activities. These disorders include the following:
1) Generalised Anxiety Disorder (GAD): Persistent and excessive worry about various aspects of life, often without a specific cause.
2) Panic Disorder: Sudden and intense bouts of fear that are accompanied by physical symptoms like rapid heart rate and shortness of breath.
3) Social Anxiety Disorder: It is defined as an overwhelming fear of social situations and a constant worry about being judged by others.
Mood disorders
Mood disorders primarily involve disturbances in emotional states. Two common mood disorders are as follows:
1) Depression (Major Depressive Disorder): Persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, as well as a loss of interest or pleasure in activities once enjoyed.
2) Bipolar Disorder: Characterised by alternating periods of depression and mania, which involves elevated mood, high energy levels, and impulsive behaviour.
Schizophrenia spectrum disorders
These Mental health disorders cause disruptions in thinking, emotions, and perceptions. Schizophrenia is the most well-known condition in this category, characterised by symptoms such as hallucinations, delusions, and disorganised thinking.
Eating disorders
Eating disorders are associated with distorted attitudes towards food, body image, and weight control. Some common eating disorders include:
1) Anorexia Nervosa: Intense fear of weight gain, leading to severe restriction of food intake and often extreme thinness.
2) Bulimia Nervosa: Episodes of binge eating, which is followed by compensatory behaviour such as purging.
3) Binge Eating Disorder: Regular episodes of consuming large amounts of food in a short period, which is followed by feelings of guilt and shame.
Signs and symptoms of Mental Health Illness
Now that we know the definition of Mental Health Illness and its types, we will explore its signs and symptoms. Mental Health Illnesses are complex conditions that can manifest in a variety of ways, affecting thoughts, emotions, behaviours, and even physical well-being. Here, we delve into the key signs and symptoms associated with Mental Health issues:
Emotional symptoms
The following are some of the emotional symptoms of Mental Illnesses:
1) Persistent sadness or hopelessness: Feeling down, sad, or hopeless for an extended period, often accompanied by tearfulness.
2) Excessive anxiety: Feeling constantly on edge, experiencing intense worry, and having difficulty controlling anxious thoughts.
3) Mood swings: Rapid shifts in emotions, from euphoria to deep sadness or irritability.
4) Lack of interest or pleasure: Losing interest in activities that were once enjoyable and struggling to find pleasure in life.
5) Irritability: An increased tendency to become easily annoyed, agitated, or frustrated.
Cognitive symptoms
The following are some of the cognitive symptoms of Mental Health disorders:
1) Difficulty concentrating: Struggling to focus, make decisions, or retain information.
2) Intrusive thoughts: Distressing or unwanted thoughts that can be difficult to control.
3) Disorganised thinking: Trouble connecting thoughts logically, leading to disjointed speech or writing.
4) Negative self-talk: Engaging in self-critical or self-deprecating thoughts on a regular basis.
5) Memory problems: Experiencing difficulties with short-term memory or recalling important details.
Behavioural symptoms
The following are some of the behavioural symptoms of Mental Illnesses:
1) Social withdrawal: Pulling away from social interactions, isolating oneself from friends, family, and activities.
2) Changes in appetite and sleep: Significant changes in eating habits and sleep patterns, such as insomnia or oversleeping.
3) Agitation or restlessness: Being unable to sit still, displaying signs of restlessness or nervous energy.
4) Substance abuse: Turning to alcohol, drugs, or other substances as a way to cope with emotions or stress.
5) Avoidance of responsibilities: Neglecting responsibilities at work, school, or home due to lack of motivation or energy.
Physical symptoms
The following are some of the physical symptoms of Mental Illnesses:
1) Fatigue: Feeling constantly tired, even after getting enough sleep.
2) Unexplained aches and pains: Physical discomfort with no clear medical cause.
3) Changes in appetite: Drastic weight loss or gain due to changes in eating habits.
4) Physical agitation: Restlessness, pacing, or fidgeting.
5) Insomnia or Hypersomnia: Trouble sleeping or excessive sleepiness.
Unlock a deeper understanding of Mental Health with our Psychology Masterclass – Join now for a journey towards enhanced well-being!
Effects of Mental Health Illness
Mental Illnesses can have far-reaching consequences that touch upon various aspects of an individual's life. Let's delve deeper into each of the outlined pointers:
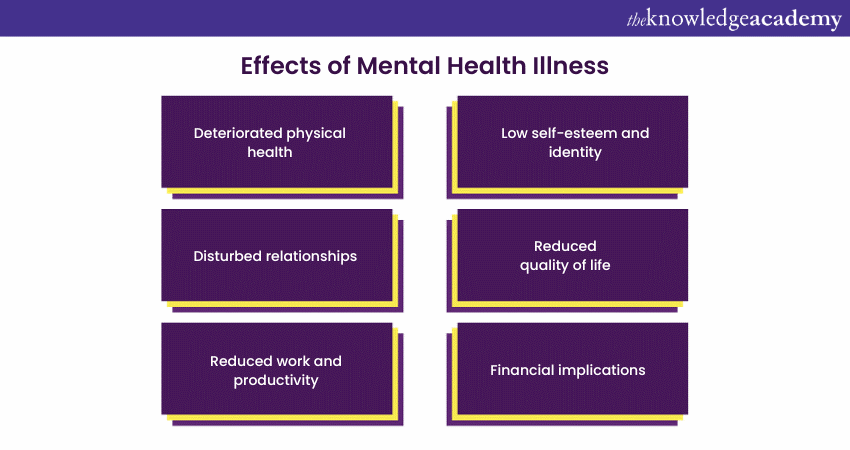
Deteriorated physical health
Mental Health and physical health are interconnected. Mental Health Disorders manifest in physical symptoms like headaches, muscle tension, and gastrointestinal problems. The prolonged stress associated with mental disorders can incapacitate the immune system, making people more prone to illnesses. Moreover, these conditions can worsen or contribute to chronic physical health conditions like heart disease, diabetes, and autoimmune disorders.
Disturbed relationships
Mental Health disorders can strain relationships in various ways. Changes in behaviour, mood swings, and social withdrawal might lead to misunderstandings or strained interactions with family, friends, and romantic partners.
Isolation is a common consequence as individuals may struggle to engage in social activities and maintain connections. Communication challenges stemming from cognitive symptoms can also hinder effective expression and understanding in relationships.
Reduced work and productivity
Work and academic performance can be significantly affected by Mental Health issues. Individuals may experience decreased productivity due to difficulties in concentration and lack of motivation.
Impaired decision-making skills can hinder problem-solving abilities. Moreover, stigma related to Mental Health in the workplace may deter individuals from seeking help or disclosing their condition. This can further impact their professional experience.
Low self-esteem and identity
Mental Health conditions can lead to negative self-perception and self-doubt. An individual's sense of identity might be compromised as their thoughts and behaviours are influenced by the illness. Feelings of guilt and shame can surface due to internalised stigma or perceived societal judgment, further undermining self-esteem and self-worth.
Reduced quality of life
Untreated Mental Health disorders can diminish overall life satisfaction and one's ability to enjoy everyday activities. Opportunities for personal and professional growth may be limited due to the barriers posed by Mental Illnesses. This can extend to the pursuit of goals and aspirations, which can be hampered by the symptoms and limitations of Mental Health conditions.
Financial implications
There can be financial implications related to Mental Illnesses. Seeking treatment, including therapy and medication, can incur costs. Lost income is a potential outcome of decreased work productivity or time off work due to symptoms. Over time, any untreated Mental Health Illnesses may lead to long-term financial challenges due to difficulties in maintaining stable employment and meeting financial responsibilities.
How are Mental Health Illness diagnosed?
It is essential to get a Mental Health diagnosis from a healthcare provider who has a specialisation mainly in Mental Health. To ensure proper treatment, it is crucial to have an accurate diagnosis. A healthcare provider will analyse your symptoms carefully in order to check your Mental Health. It is crucial to communicate your feelings to your healthcare provider. Some examples of what you should disclose include:
1) If there is a specific thing that triggers your mental health and makes it worse
2) If your Mental Health Illness is persistent or ongoing
3) When you first noticed that your Mental Health is not good or there are some changes in your Mental Health
These are not something like medical tests that can help in diagnosing your Mental Health Illness. But your healthcare provider may conduct some tests, like imaging exams or blood work, to figure out other causes that can affect your Mental Health.
How can Mental Health Illness be treated?
The following are some Mental Health Illness treatments:
a) Medication: Certain Mental Illnesses can be effectively treated with medication such as antipsychotics and antidepressants. These medications work by altering the chemicals in your brain to alleviate symptoms. It is crucial to follow your healthcare provider's instructions precisely when taking the medication. Additionally, never discontinue medication for mental health illnesses without first consulting with your healthcare provider.
b) Psychotherapy: Having a healthy conversation with Mental Health specialists can help you work through the challenges and deal with it’s the symptoms of Mental Health Illness. Psychotherapy is a one-to-one session with a healthcare professional or a group setting. Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT) is one of the examples of psychotherapy. It mainly helps you in changing your thought patterns and negative behaviour.
c) Alternative therapies: There are some Mental Health issues like depression that may treated with alternative therapies. These include examples like herbal remedies, yoga, acupuncture, massage and meditation. But before taking any supplement or herbal remedies, you must consult with your health provider as they may affect other medications.
d) Brain stimulation therapies: Not all Mental Health issues can treated with medications. There are some issues which need brain stimulation therapies. These therapies change the processing way of nerves and other cells in your brain and respond to stimuli. Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) and Electroconvulsive Therapy are examples of brain stimulation therapies.
Conclusion
Hope we could answer all your queries about What is Mental Health Illness? It is an intricate challenge that affects individuals holistically. Their effects ripple through emotions, relationships, work, and physical health. By acknowledging these impacts, raising awareness, and offering support, we can collectively work towards a more compassionate society. Prioritising mental well-being is not only essential for those facing these challenges but for society as a whole.
Elevate your understanding of Mental Health with our expert-led Mental Health Course. Sign up now to empower yourself and others!







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course




 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


