We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
What is Healthcare Management? This subject often needs clarification for many. Healthcare Management is a crucial discipline at the heart of the Healthcare system. The need for effective management becomes more pronounced as the Healthcare landscape grows increasingly complex.
In this blog, we'll learn What is Healthcare Management and understand its different aspects. Healthcare Management has proved beneficial in driving quality patient care and promoting cost-efficient practices.
Table of Contents
1) The importance of Healthcare Management
2) Key functions and roles in Healthcare Management
3) Challenges in Healthcare Management
4) The future of Healthcare Management
5) Conclusion
The importance of Healthcare Management
Effective Healthcare Management is paramount for successful Healthcare organisations and the overall Healthcare system. It serves as a guiding force, steering the course of Healthcare delivery towards excellence. Let us go over some of the importance of Healthcare Management:
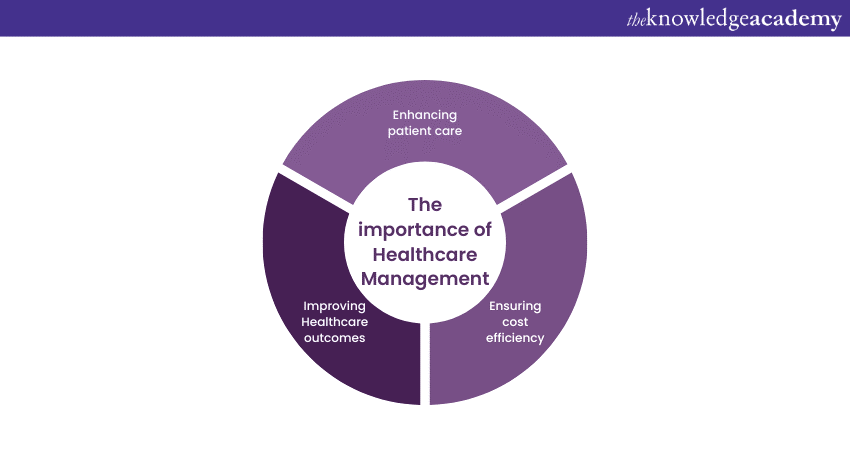
Enhancing patient care
a) Quality improvement initiatives: Healthcare Management is instrumental in implementing quality improvement initiatives to enhance patient care standards. These initiatives involve setting measurable goals, monitoring key performance indicators, and continuously refining Healthcare processes to ensure optimal patient outcomes.
b) Patient-centred approach: Healthcare Managers champion a patient-centred approach, placing the patient at the core of care delivery. Healthcare professionals work together to ensure personalised and compassionate care that meets each patient's unique needs through effective communication and collaboration.
c) Efficient resource allocation: Effective Healthcare Management ensures the appropriate allocation of resources, including medical equipment, staff, and facilities, to deliver timely and efficient patient care. This optimises patient flow, reduces waiting times, and minimises the risk of medical errors.
d) Patient safety protocols: Healthcare Managers develop and implement robust patient safety protocols to safeguard against medical errors, infections, and other adverse events. The organisation sets up safety protocols and ensures everyone follows them to create a safe and secure work environment.
e) Continuity of care: Healthcare Management facilitates seamless care transitions through effective care coordination. They ensure that patient information is accurately shared among Healthcare providers, resulting in enhanced continuity of care and reduced chances of treatment duplication.
f) Clinical training and education: Healthcare Managers invest in ongoing clinical training and education for Healthcare professionals. Patient care quality is continually improved by keeping staff up to date with the latest medical advancements and best practices.
Ensuring cost efficiency
a) Budget planning and management: Healthcare Management involves meticulous budget planning and management to allocate resources optimally. By carefully assessing financial needs and streamlining expenditures, Healthcare organisations can achieve cost efficiency without compromising patient care quality.
b) Value-based care models: Healthcare Managers embrace value-based care models, focusing on delivering high-quality care while controlling costs. These models incentivise Healthcare providers to prioritise preventive care and reduce unnecessary treatments, ultimately improving patient outcomes and reducing Healthcare expenses.
c) Resource utilisation analysis: Healthcare Management conducts regular analyses of resource utilisation to identify areas of potential waste or inefficiency. This data-driven approach enables Healthcare organisations to make informed decisions about resource allocation, reducing costs and enhancing productivity.
d) Negotiating with vendors and suppliers: Healthcare Managers deal with vendors and suppliers to secure favourable terms for medical supplies, equipment, and pharmaceuticals. These strategic partnerships can lead to cost savings and improved access to essential resources.
e) Process optimisation: Healthcare Management streamlines administrative and clinical processes to eliminate redundancies and bottlenecks. Healthcare organisations can reduce operational costs and enhance patient care by improving workflow efficiency.
f) Preventing unnecessary readmissions: Healthcare Managers implement initiatives to prevent unnecessary hospital readmissions, which can significantly impact Healthcare costs. Healthcare organisations can reduce readmission rates and associated expenses by providing effective post-discharge support and follow-up care.
Learn the skills to manage a team of any size, sign up for Introduction To Performance Management now!
Improving Healthcare outcomes
a) Evidence-based practice: In Healthcare Management, it is essential to prioritise evidence-based practice. Healthcare decisions and treatments are based on scientific research and proven best practices. By following this approach, patient outcomes are improved, and the risk of medical errors is reduced.
b) Clinical pathways and protocols: Healthcare Managers develop and implement clinical pathways and protocols that outline standardised treatment plans for specific medical conditions. These guidelines help Healthcare professionals deliver consistent, high-quality care, leading to improved patient outcomes.
c) Patient education and engagement: Healthcare Management emphasises the importance of patient education and engagement in managing their health. Patients who are well-informed and involved in their treatment are more likely to follow their Healthcare plans, resulting in improved health outcomes and fewer instances of returning to the hospital.
d) Outcome monitoring and analysis: Healthcare Management establishes systems to monitor and analyse patient outcomes regularly. By tracking key performance indicators and benchmarking against industry standards, Healthcare organisations can identify areas for improvement and implement targeted interventions.
e) Continuous quality improvement: Healthcare Managers foster a culture of continuous quality improvement, encouraging Healthcare professionals to reflect on their practices and seek opportunities for enhancement. This iterative process leads to ongoing improvements in patient care and outcomes.
f) Interdisciplinary collaboration: Healthcare Management facilitates interdisciplinary collaboration among Healthcare teams. Improved communication and teamwork among different specialities result in comprehensive and well-coordinated care, ultimately benefiting patient outcomes.
g) Emphasis on preventive care: Healthcare Managers prioritise preventive care initiatives to detect health issues early and intervene proactively. By addressing health risks and promoting healthy lifestyles, Healthcare organisations can reduce the incidence of chronic diseases and improve overall health outcomes.

Key functions and roles in Healthcare Management
Healthcare Management encompasses a diverse array of essential functions and roles critical for the smooth operation of Healthcare organisations. Some of them are:
Healthcare leadership and governance
a) Strategic planning: Healthcare leaders develop long-term strategic plans that align with the organisation's mission and vision. These plans set clear objectives and guide decision-making to achieve organisational goals.
b) Decision-making and policy implementation: Healthcare leaders make critical decisions and implement policies that influence the organisation's operations, patient care, and overall performance.
c) Stakeholder engagement: Healthcare leaders collaborate with various stakeholders, including medical staff, administrators, board members, and community members, to ensure a shared vision and foster a culture of transparency and accountability.
d) Ethical and regulatory compliance: Healthcare leaders uphold ethical standards and ensure compliance with Healthcare regulations, laws, and industry standards, safeguarding the organisation's integrity and reputation.
Financial management and budgeting
a) Budget development: Healthcare Managers are responsible for creating comprehensive budgets that allocate resources to various departments and initiatives within the Healthcare organisation.
b) Financial analysis: Healthcare Managers conduct financial analyses to assess the organisation's financial health, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions.
c) Cost control measures: Healthcare Managers implement measures to reduce unnecessary expenditures while maintaining high-quality patient care.
d) Revenue generation: Healthcare Managers explore opportunities to increase revenue, such as expanding services, negotiating contracts, or optimising reimbursement processes.
Human resources and talent management
a) Recruitment and selection: Healthcare Managers oversee the recruitment and selection process, attracting and hiring qualified Healthcare professionals who align with the organisation's values and mission.
b) Training and development: Healthcare Managers are responsible for providing regular training and development opportunities to improve the skills and knowledge of the Healthcare workforce. This ensures that the staff is competent in delivering quality care.
c) Performance management: Healthcare Managers implement performance management systems, conducting regular evaluations to assess employee performance, provide feedback, and recognise achievements.
d) Workforce planning: Healthcare Managers engage in strategic workforce planning, anticipating future staffing needs and ensuring the right mix of Healthcare professionals to meet patient demand.
Information technology and Healthcare informatics
a) Electronic Health Records (EHR): Healthcare Managers oversee the implementation and maintenance of EHR systems, enabling secure and accessible patient health information, improving care coordination, and reducing medical errors.
b) Health Information Exchange (HIE): Healthcare Managers facilitate health information exchange between different Healthcare providers and organisations, promoting seamless data sharing and continuity of care.
c) Data analytics: Healthcare Managers rely on data analytics tools to extract valuable insights from vast amounts of Healthcare data. This helps them make decisions based on evidence, manage population health, and undertake initiatives to improve the quality of Healthcare.
d) Telemedicine and telehealth: Healthcare Managers explore and integrate telemedicine and telehealth technologies, enabling remote consultations, virtual care delivery, and improving access to Healthcare services, especially in rural or underserved areas.
Challenges in Healthcare Management
Healthcare Management is a complex field and faces numerous challenges in its quest to deliver high-quality patient care and ensure the effective functioning of Healthcare organisations. Let us look at some of these challenges:
Evolving Healthcare policies and regulations
a) Frequent policy changes: Healthcare Managers must continuously monitor and adapt to frequent changes in Healthcare policies and regulations at the local, state, and federal levels. These changes can impact reimbursement models, quality standards, and operational requirements.
b) Compliance challenges: Staying compliant with many Healthcare regulations, such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) and the Affordable Care Act, requires meticulous attention to detail and the development of robust compliance programs.
Reimbursementc) complexity: Evolving reimbursement models, including value-based care and alternative payment models, present challenges in accurately documenting and reporting Healthcare services to ensure appropriate reimbursement.
Balancing quality and cost
a) Efficiency in resource allocation: Healthcare Managers carefully allocate resources to ensure cost-effectiveness without compromising patient care quality. This involves optimising staffing levels, managing inventory efficiently, and identifying areas for cost savings.
b) Evidence-based decision making: Healthcare Managers rely on evidence-based practices and clinical guidelines to make informed decisions prioritising quality patient care while avoiding unnecessary and costly treatments.
c) Preventive care and population health: Emphasising preventive care and population health initiatives helps Healthcare managers reduce the burden of costly chronic conditions through early detection and disease management.
Addressing Healthcare disparities
a) Access to Healthcare: Healthcare Managers work towards ensuring equitable access to Healthcare services for all individuals, regardless of socioeconomic status, geographic location, or cultural background.
b) Culturally competent care: Healthcare Managers promote culturally competent care, ensuring that Healthcare professionals understand and respect diverse cultural beliefs and practices, improving patient satisfaction and health outcomes.
c) Language services: Healthcare Managers implement language services, such as interpretation and translation services, to overcome language barriers and enhance communication with patients with limited English proficiency.
The future of Healthcare Management
The future of Healthcare Management promises to be dynamic and transformative as the industry continues to evolve. Advancements in technology, such as artificial intelligence, telemedicine, and health informatics, will revolutionise how Healthcare organisations operate and deliver care. Let us look at some aspects:
Embracing technological advancements
a) Electronic Health Records (EHR): Healthcare organisations will increasingly adopt advanced EHR systems to streamline patient information management, enhance care coordination, and facilitate data exchange between providers.
b) Telemedicine and virtual care: Telemedicine will become more prevalent, allowing Healthcare providers to conduct remote consultations, monitor patients remotely, and expand Healthcare access, especially in remote or underserved areas.
c) Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: AI applications will support clinical decision-making, early disease detection, and personalised treatment plans, improving diagnostic accuracy and patient outcomes.
Be able to gain high productivity with minimum resources, sign up for our Introduction To Managing People now!
Advancing patient-centered care
a) Personalised treatment plans: Advancements in Healthcare technology and data analytics allow Healthcare providers to create customised treatment plans tailored to individual patient needs, preferences, and medical histories.
b) Shared decision-making: Patient-centered care emphasises shared decision-making between Healthcare professionals and patients, empowering individuals to actively participate in treatment choices based on their values and preferences.
c) Communication and patient engagement: Healthcare providers focus on open communication and active patient engagement, fostering a collaborative relationship that encourages patients to actively manage their health.
Innovations in Healthcare Management
a) Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: AI and machine learning applications transform Healthcare Management by optimising resource allocation, predicting patient outcomes, and streamlining administrative processes.
b) Wearable health devices and remote monitoring: Innovations in wearable health devices and remote monitoring technologies enable continuous tracking of patient health data, supporting preventive care and chronic disease management.
c) Blockchain for Healthcare: Blockchain technology enhances data security, integrity, and interoperability, benefiting Healthcare Management by safeguarding patient information and streamlining health data exchange.
Gain the confidence and skills to become a capable leader, sign up for our Management Training now!
Conclusion
This blog focused on What is Healthcare Management, its importance, the key roles, and the challenges. From telehealth and AI-driven solutions to precision medicine and patient-centred care, these advancements promise to improve patient outcomes, enhance efficiency, and create a more patient-centric and sustainable Healthcare system for the future.
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming Health & Safety Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Introduction to Management
Introduction to Management
Fri 24th May 2024
Fri 21st Jun 2024
Fri 19th Jul 2024
Fri 23rd Aug 2024
Fri 20th Sep 2024
Fri 18th Oct 2024
Fri 22nd Nov 2024
Fri 20th Dec 2024







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


