We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Unix vs Linux stands as two powerful contenders in the world of Operating Systems (OS), each with unique features and capabilities. Understanding the differences and similarities between these two systems is crucial for making informed decisions and choosing the right platform for various applications.
According to Statista, about 45% of professional developers worldwide use Linux and Unix-based operating systems. This blog compares Unix and Linux. No matter which profession you pursue, a developer, or a curious technology enthusiast, read this informative blog to navigate this informative blog will provide valuable insights to help you navigate the intricate landscape of Unix vs Linux and make informed decisions.
Table of Contents
1) Understanding Unix and Linux
2) Difference between Unix and Linux
3) Factors to consider
4) Making the decision
5) Conclusion
Understanding Unix and Linux
To understand what is Unix vs Linux OS, let's start with their respective histories. They are both widely used operating systems with distinct characteristics and advantages. While Unix has a long history dating back to the 1970s, Linux emerged as a Unix-like system in the 1990s.
Unix is a robust and stable operating system known for its scalability and security. It has a robust architecture and a modular design that allows for efficient resource management. Unix provides a multi-user environment with strong user permissions, making it ideal for enterprise-level applications. However, Unix can be more expensive to acquire and maintain due to licensing costs.
On the other hand, Linux is a free and open-source operating system that shares similarities with Unix. It offers a wide range of distributions, such as Ubuntu, Fedora, and Debian, each with its own characteristics and target audience. It is highly customisable and adaptable to various hardware platforms, making it popular among enthusiasts and developers. It benefits from a large, active community, ensuring continuous development, support, and frequent updates.
Both Linux and Unix provide a command-line interface and support a variety of programming languages and tools. They offer powerful networking capabilities, making them suitable for server environments. However, Unix may have a more mature software ecosystem and a wider range of commercial applications than Linux.
When considering performance and system requirements, Unix has a reputation for stability and reliability. It is often chosen for mission-critical applications that require uninterrupted operation. However, thanks to its active development and optimisation efforts, Linux can excel in performance and efficiency, especially on newer hardware.
When choosing between Linux and Unix, it's essential to consider factors such as community support, security, and customisation. It benefits from long-standing community support and well-established security measures. However, Linux's open-source nature allows for rapid development, quick bug fixes, and enhanced security through community collaboration.

Difference between Unix and Linux
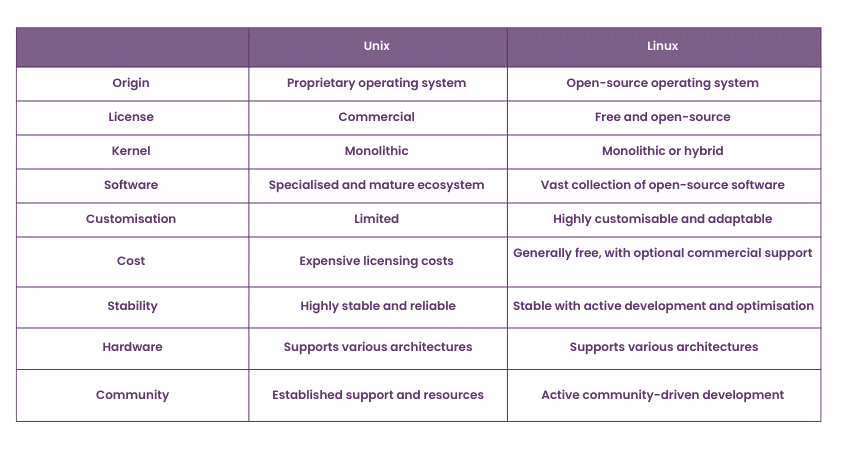
Linux vs Unix are two prominent operating systems with distinct features and capabilities. Understanding the similarities and differences between them is essential for making informed decisions. This table compares Linux and Unix, exploring their architecture, user interface, software availability and performance.
Architecture and Kernel
Linux and Unix share a similar architectural foundation. Both operating systems follow a multi-user, multitasking model, allowing different users to access the system simultaneously. They are built on a monolithic kernel design, where the kernel acts as the core component, handling essential tasks like memory management, process scheduling, and device control.
However, Unix generally refers to a family of proprietary operating systems, while Linux is an open-source variant developed by Linus Torvalds. It is often considered a Unix-like system due to its compatibility with Unix standards and APIs.
User interface and desktop environment
Linux and Unix offer various user interfaces and desktop environments. Unix systems typically provide a Command-Line Interface (CLI), emphasising the use of the terminal for executing commands and managing the system.
In contrast, Linux distributions offer a broader range of Graphical User Interfaces (GUIs) and desktop environments. Popular options include GNOME, KDE, Xfce, and LXDE. These interfaces provide an attractive and easy-to-use platform featuring icons, menus, and windows that simplify user navigation and interaction with the system.
Software and application availability
Linux and Unix differ in terms of software and application availability. Unix, being a proprietary system, often comes bundled with a specific set of applications and software packages tailored to its respective distribution. Commercial Unix systems, such as AIX, HP-UX, and Solaris, provide a wide range of specialised software for various industries.
In contrast, Linux distributions offer extensive software repositories and package managers, allowing users to easily access and install a vast collection of free and open-source applications. The Linux ecosystem also benefits from a vibrant community of developers who contribute to the development and availability of software.
Elevate your Linux administration skills to new heights! Join our Administering Linux Systems training course and gain the expertise to efficiently manage and optimise your Linux infrastructure.
Performance and system requirements
Linux and Unix exhibit differences in performance and system requirements. Unix systems are renowned for their stability, scalability, and ability to handle high workloads efficiently. They excel in mission-critical environments and can run on various hardware architectures.
On the other hand, Linux distributions have made significant strides in optimising performance, especially on modern hardware. It is known for its efficiency, faster booting times, and the ability to operate on older hardware configurations. Its active development and optimisation efforts contribute to a smooth and responsive user experience, making it suitable for both resource-constrained systems and high-performance environments.
Unix vs Linux commands
There are several similarities when comparing Unix vs Linux commands. These similarities are due to their shared roots and compatibility. Both operating systems provide a wide range of powerful command-line utilities for system administration, file management, networking, and programming. Common commands such as ls, cd, mkdir, rm, and grep work identically across Linux and Unix environments.
Depending on the specific distribution, there may be slight variations in command options, syntax, and the availability of certain tools. Overall, familiarity with Unix commands translates well to Linux systems, making navigating and managing files, processes, and system configurations easier.
Don’t know where to start with Linux? Try our LINUX Fundamentals course for jump start!
Factors to consider
When deciding between Linux and Unix, several key factors come into play. Hardware compatibility, software requirements, community support, security, and customisation options are among the considerations. In this section, we will explore these factors and help you decide which operating system suits your needs best.
Purpose and use case
When choosing between Linux and Unix, consider your purpose and specific use case. It is often preferred for enterprise-level applications, while it offers versatility for various scenarios, such as desktop computing, server management, embedded systems, and development environments. Assessing your specific needs will guide you in selecting the appropriate operating system.
Community and support
The community and support surrounding an operating system are crucial factors to consider. Unix systems typically have official vendor support, with specialised assistance for specific distributions. Linux, being open-source, benefits from a vast and active community of developers, enthusiasts, and online forums, providing comprehensive support, regular updates, and a wealth of resources.
Security and stability
Both Linux and Unix prioritise security, but their approaches may differ. With its proprietary nature, Unix often incorporates built-in security features and undergoes rigorous testing. Linux, being open-source, benefits from community-driven security audits, prompt bug fixes, and the ability to leverage various security tools and practices.
Customisation and flexibility
Consider the level of customisation and flexibility required for your system. Unix systems tend to provide fewer customisation options due to their proprietary nature, focusing on stability and standardisation. Linux, being open-source, offers extensive customisation capabilities, allowing users to tailor the system to their preferences, modify source code, and choose from a wide range of desktop environments and software packages.
Wish to learn more about programming in Linux? Try our Linux Shell Programming Course!
Making the decision
When choosing between Linux and Unix, assessing your individual needs and preferences is crucial. Consider the intended use case, whether it's for personal use, development, or enterprise-level applications. Evaluate factors such as hardware compatibility, software requirements, community support, security, and customisation options.
Unix's proprietary nature may be preferred in certain industries that require specialised software and long-term stability. Open-source Linux offers a broader range of distributions, each with its own characteristics and target audience. It provides flexibility, customisation, and an active community. To evaluate which operating system suits specific requirements:
a) You must carefully compare the key differences.
b) Consider factors like architecture, user interface, software availability, performance, and system requirements.
c) Assess the level of support and resources available from the community and official sources.
Ultimately, the decision should align with your needs, budget, desired level of customisation, and the specific requirements of your use case. Regularly reassess your needs and stay informed about the latest developments to ensure your chosen operating system meets your expectations and future demands. Carefully understanding the differences between Unix vs Linux is important to be able to decide which one to chose.
Level up your Unix administration skills. Join our Administrating UNIX Systems course and gain the knowledge needed to excel in administrating UNIX systems. Register now and unlock new opportunities!
Conclusion
In this blog, we compared Unix vs Linux and explored their architecture, user interface, software availability, performance, and system requirements. Considering individual needs and preferences is crucial when choosing between the two. Whether you prioritise stability, customisation, or community support, selecting the right operating system depends on finding the best fit for your requirements.
Our Linux Training can help you start your journey with the Linux OS! Try it today!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming IT Infrastructure & Networking Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 LINUX Fundamentals Course
LINUX Fundamentals Course
Thu 16th May 2024
Thu 12th Sep 2024
Thu 14th Nov 2024







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


