We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Understanding the differences between Mortgages and Loans is crucial for making informed financial decisions. Whether you're considering purchasing a property or need funds for other purposes, knowing the key distinctions between Mortgage vs Loan can help you navigate the borrowing landscape more effectively. In this blog, we will explore the fundamental disparities between Mortgages and Loans. While both involve borrowing money, Mortgages specifically pertain to financing real estate purchases, while Loans encompass a broader range of borrowing options.
In this blog on Mortgage vs Loan, we will explore factors such as collateral requirements, interest rates, Loan amounts, repayment terms, and purpose, aiming to equip you with the knowledge needed to make the right borrowing choice for your unique circumstances.
Table of Contents
1) What is Mortgage?
2) What is a loan?
3) Difference between Mortgage and Loan?
4) Mortgage vs Loan: Collateral requirement
5) Mortgage vs Loan: Interest rates
6) Mortgage vs Loan: Loan amounts and repayment terms
7) What are the types of Mortgages?
8) What are the types of Loans?
9) Conclusion
What is Mortgage?
A mortgage is a type of Loan that is secured by your home or property. When you take out a mortgage, the lender registers a lien on your home or property, which means that if you fail to make your payments, the lender has the legal right to seize and sell your property. This is known as foreclosure.
Mortgages are normally used to purchase or refinance a home or property. Since homes can be quite expensive, most borrowers need more cash to pay for them outright. Lenders consider multiple factors when approving a Mortgage, including your credit score, income, and debt-to-income ratio. They will also usually require an appraisal to determine the value of the property, which will impact how much they can lend you. Mortgages can also be used to access the equity in your home for other purposes.
What is a Loan?
Loans are financial agreements between two parties, where the creditor provides money to the borrower in exchange for repayment of the borrowed principal amount with interest. The borrower agrees to repay the debt as per the lender's terms.
Multiple types of Loans, such as term Loans and revolving Loans, can be used for commercial or personal purposes and can be secured or unsecured. Each type of Loan has its advantages and disadvantages and is used in different financing scenarios.
When you borrow money, you must repay it with interest over time. In the case of a term Loan, you need to pay off the borrowed amount over a specific period of time with fixed payments. With a revolving Loan, you can withdraw money within a certain credit limit and make additional withdrawals as you make repayments.
Difference between Mortgage and Loan?
Let us look at few differences between Mortgage and Loan:
a) A Loan is fundamentally lending money to someone who requires it. People often borrow money from the bank, acting as a lender. In the case of mortgages, the borrower procures a Loan using their property as collateral. Mortgages are considered safer alternatives to loan as they are backed by certain collateral.
b) The Loan is secured through Mortgage Loans, which have a comparatively low probability of default when compared to other Loans. This is due to the low Loan-to-value ratio, which is an important factor in Mortgage Loans. It is an industry benchmark for Mortgage Loans to have a property value of two times. Additionally, Mortgage Loans have a fixed repayment timeline and a reduced risk of default than other Loans.
c) The crucial difference between a Loan and a Mortgage is that a Mortgage is secured and has compulsory payments, while Loans are often unsecured and more flexible.
d) Mortgage Loans are obtained by offering a property that is worth more than the amount of money an individual needs to borrow. In case the borrower fails to make the principal or interest payments on the Mortgage Loan, the banks or financial institutions have the right to take over and sell the property in the open market. This enables them to recover the remaining money owed or try to sell the property at its fair market value.
Embark on a rewarding journey in Mortgage advice, gain industry knowledge, and become a certified Mortgage professional with our comprehensive CeMAP Training.
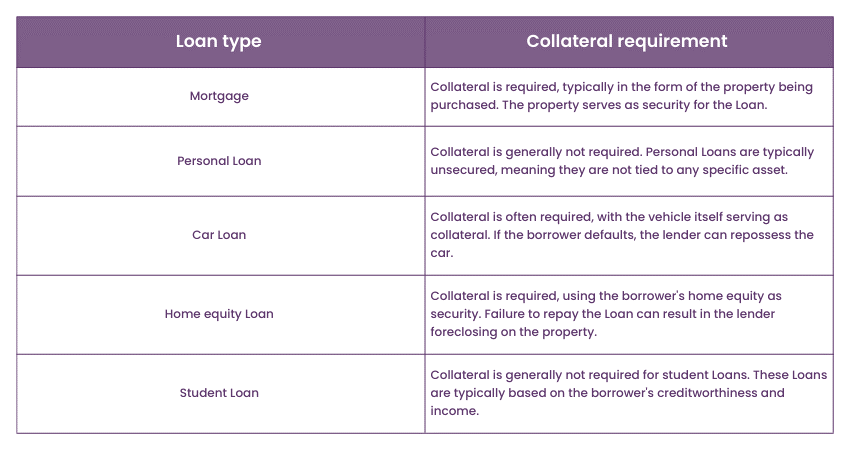
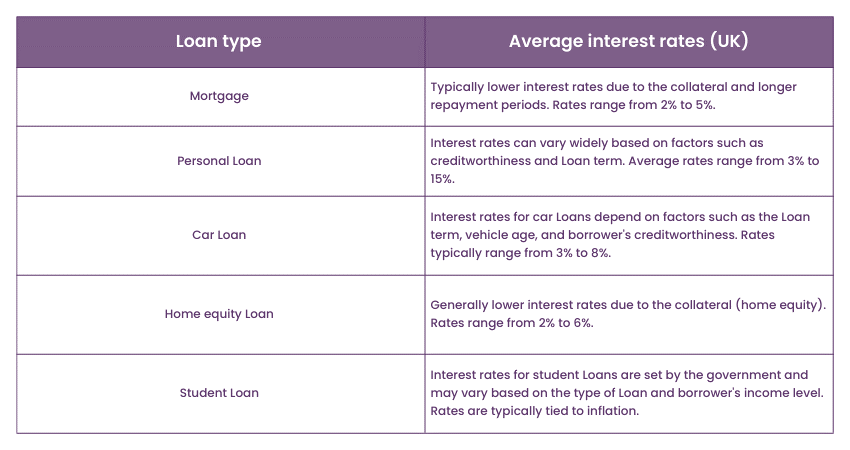
Mortgage vs Loan: Collateral requirement
One of the key differences between Mortgages and Loans lies in the collateral requirement. A Mortgage is a secured Loan, meaning it is backed by the property being purchased. The property itself serves as collateral, providing security to the lender. If the borrower fails to repay the Loan, the lender can repossess and sell the property to recover the outstanding debt. This collateral requirement offers reassurance to the lender, as they have a tangible asset that can be used to mitigate their risk.
The collateral requirement associated with Mortgages often leads to lower interest rates compared to unsecured Loans. Since the lender has the security of the property, they are willing to offer more favourable terms to borrowers. This is because the risk of default is relatively lower due to the property acting as a safeguard.
On the other hand, Loans may or may not require collateral, depending on the type and purpose of the Loan. Some Loans, such as car Loans or home equity Loans, may be secured by the specific asset being financed. In these cases, if the borrower defaults, the lender can repossess the asset to recover their losses. However, many Loans, especially personal Loans or credit cards, are unsecured and do not require collateral. These Loans rely on the borrower's creditworthiness and income as the basis for approval, and they often come with higher interest rates to compensate for the increased risk borne by the lender.
It’s important to note that the collateral requirement can significantly impact the terms and conditions of the Loan. Collateral provides security for the lender and can offer borrowers more favourable terms, such as lower interest rates and longer repayment periods. Understanding the collateral requirement of a Loan or Mortgage is essential for borrowers to evaluate their options and make informed financial decisions.
Mortgage vs Loan: Interest rates
Interest rates are another important factor that distinguishes Mortgages from Loans. When it comes to Mortgages, interest rates tend to be lower compared to many other types of Loans. This is primarily due to the collateral provided by the property and the longer repayment periods associated with Mortgages.
Mortgage interest rates are often fixed, meaning they remain constant throughout the repayment period. This stability provides borrowers with predictability in their monthly payments, allowing them to budget more effectively. Lower interest rates on Mortgages can lead to substantial savings throughout the Loan's lifespan.
On the other hand, Loans can have varying interest rates depending on the type and terms of the Loan. Some Loans, like personal Loans or credit card debt, typically come with higher interest rates compared to Mortgages. Unsecured Loans, which lack collateral, carry higher risks for lenders, thus resulting in higher interest rates to compensate for that risk. Furthermore, certain Loans, such as student Loans, may have fixed or variable interest rates. The borrower's monthly payments may change due to market conditions, which can cause variable interest rates to fluctuate.
It’s important for borrowers to consider the impact of interest rates when deciding between a Mortgage and a Loan. Lower interest rates on Mortgages can make homeownership more affordable and enable borrowers to build equity in their property. Conversely, higher interest rates on Loans can increase the overall cost of borrowing and affect the borrower's ability to repay the debt in a timely manner.
Before committing to any Loan or Mortgage, it is crucial to carefully evaluate the interest rates, understand the terms and conditions, and consider the long-term financial implications. Comparing interest rates across different lenders and Loan products can help borrowers secure the most favourable terms and save money over the course of the borrowing period.
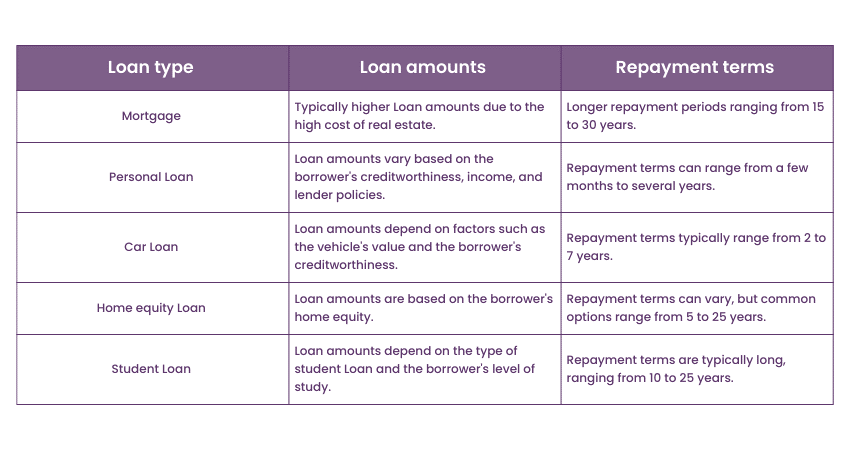
Mortgage vs Loan: Loan amounts and repayment terms
Loan amounts and repayment terms differ between Mortgages and other types of Loans. Mortgages typically involve larger Loan amounts due to the high cost of real estate. The amount borrowed is determined by the property's value and the borrower's financial profile. These substantial Loan amounts enable individuals to purchase homes and properties that might otherwise be unaffordable without long-term financing.
Repayment terms for Mortgages are generally longer compared to other Loans. It is common for Mortgage repayment periods to range from 15 to 30 years, providing borrowers with an extended timeframe to repay the Loan. The extended repayment period allows for smaller monthly instalments, making homeownership more manageable for borrowers. However, it’s important to note that longer repayment terms can result in higher total interest payments over the life of the Loan.
In contrast, Loans other than Mortgages can vary widely in terms of Loan amounts and repayment terms. Loans may be obtained for various purposes such as education, car purchases, or debt consolidation. The Loan amounts for these purposes are typically smaller compared to Mortgages. Repayment terms for Loans can vary from a few months to several years, depending on the lender, the borrower's creditworthiness, and the purpose of the Loan. Shorter repayment terms may be suitable for individuals who prefer to repay their debts quickly or have a specific timeframe in mind.
When considering Loan amounts and repayment terms, borrowers should carefully assess their financial situation, needs, and preferences. Understanding the affordability of monthly payments and the overall cost of borrowing is essential. It is advisable to compare Loan offers from different lenders, evaluate the repayment terms, and choose an option that aligns with one's financial goals and capabilities.
What are the types of Mortgages?
There are multiple types of Mortgages that depend upon various factors such as rate of interest and duration of term. Let us look at a few of them to gain clarity:
Fixed-rate Mortgages
The majority of home Loans are fixed-rate Mortgages. These are large Loans that require repayment over a long period of time, typically 10 to 50 years or earlier if possible. Fixed-rate Mortgages have a predetermined rate of interest, which can only be modified by refinancing the Loan. Payments remain constant throughout the lifetime of the Loan, and borrowers can pay extra amounts to reduce the Loan's term. In these Loan programs, repayment of the Loan goes first towards the interest, then towards paying down the principal.
FHA Mortgage Loans
The U.S. Federal Housing Administration (FHA) offers insurance for Mortgage Loans given by FHA-approved lenders to high-risk borrowers. These Loans are not provided by the government but rather by independent institutions such as banks; the government only insures a certain amount of the Loan. FHA Loans are typically given to first-time homebuyers who have a low to moderate income and who cannot make a 20% down payment. They are also available to those with a poor credit history or a history of bankruptcy. It is important to note that while FHA Loans allow high-risk borrowers to purchase a home without a 20% down payment, they do require private Mortgage insurance.
VA Loans for veterans
VA Loans operate similarly to FHA Loans, where the government does not directly lend money but rather insures or guarantees a Loan given by another lender. If a veteran defaults on their Loan, the government repays the lender at least 25% of the Loan amount.
VA Loans offer a range of benefits, including the fact that veterans are not required to make any down payments or carry private Mortgage insurance (PMI). Due to their military service, some veterans may have limited civilian work experience and income, making them high-risk borrowers who could be declined for conventional Mortgage Loans.
There are several types of Mortgages available in the market, such as interest-only Mortgages, adjustable-rate Mortgages (ARM), and reverse Mortgages, among others. However, fixed-rate Mortgages remain the most popular type of Mortgage. Among the fixed-rate Mortgages, 30-year fixed-rate programs are the most commonly used option.
Unlock your full potential in Mortgage advice, advance through all levels of expertise, and achieve your CeMAP Level 1, 2, and 3 certifications with our comprehensive training.
What are the types of Loans?
Let us look at a few types of Loans to gain clarity on which are suitable for your needs:
Open-end vs closed-end Loans
There are two primary types of Loan credit: Open-end credit, also known as revolving credit and closed-end credit. Open-end credit can be borrowed repeatedly, like a credit card, having a limit that can be used indefinitely as long as the borrower pays off the card monthly and does not exceed the limit. Each time the card balance is paid down to zero, the borrower can access the full credit limit again.
When someone borrows a fixed amount of money with the agreement to pay it back in full on a later date, it's known as closed-end credit or a term Loan. However, if the borrower has already paid back a portion of the Loan, it doesn't mean that they can borrow that amount again. For instance, if a person has a closed-end Mortgage Loan of 150,000 and has already paid back 70,000, they can't borrow another 70,000 from the same Loan. Instead, they would have to apply for a new Loan if they need more credit.
Secured vs. Unsecured
Loans can be simplified into two types: Secured loan and unsecured loan. Unsecured Loans are not supported by any collateral, which means that lenders cannot claim any asset to recover their losses in the event of a borrower's default. The approval of unsecured Loan applications is based on the borrower's income, credit history, and credit score. As unsecured Loans pose a higher risk to lenders, they usually come with a higher interest rate and a smaller amount compared to secured Loans. Examples of unsecured Loans are personal Loans, bank overdrafts, and credit cards.
Secured Loans, also referred to as collateral Loans, are Loans that are backed by assets, such as Mortgages and auto Loans. These Loans mandate the borrower to put up an asset as collateral in order to receive cash. Although secured Loans often offer higher amounts of money to borrowers at lower interest rates, they are considered less risky for lenders. The terms of the Loan agreement decide if lenders may have the right to take partial or full possession of the asset if the borrower fails to repay the Loan.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the key differences between Mortgages and Loans, and comparing Mortgage vs Loan options, is essential for making informed financial decisions. Mortgage life cycle are specifically designed for financing real estate purchases, with the property serving as collateral and offering lower interest rates. Loans, on the other hand, provide flexibility for various purposes but may come with higher interest rates and shorter repayment terms. By evaluating factors such as collateral requirements, interest rates, Loan amounts, repayment terms, and purpose, individuals can make the right borrowing choice based on their specific needs and financial goals. Responsible borrowing, coupled with careful consideration of these Mortgage vs Loan differences, is crucial in achieving long-term financial success.
Embark on a rewarding career in financial advice, acquire in-depth knowledge and skills, and earn your Diploma for Financial Advisers (DipFA) through our specialised DipFA Training.
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 CeMAP Course (Level 1,2 and 3)
CeMAP Course (Level 1,2 and 3)
Mon 20th May 2024
Mon 22nd Jul 2024
Mon 18th Nov 2024







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


