We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Ethereum (ETH) is a decentralised global software platform powered by Blockchain technology Using Blockchain results in the establishment of a peer-to-peer network which safely executes and verifies the application codes. These are also known as smart contracts. Ethereum Blockchain enables the participants to perform different transactions with one another without the need for any central authority.
Ethereum allows users to make transactions and earn interest on their holdings, store Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs), perform trading of cryptocurrencies, play games, use on social media platforms, and many more activities.
The launch of Ethereum in 2015 became the world’s first project that expanded Blockchain use cases. It introduced new and unique technologies allowing users to create digital tokens and self-sustaining applications. This led to the development of Decentralised Finance (DeFi), Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs), GameFi, and NFTs. Today there are more than 117.5 million Ethereum coins in circulation.
Ethereum is a decentralised blockchain network powered by Ether. Learn more about the Ethereum blockchain, including its Use cases, features, and more.
Table of Contents
1) What is Ethereum?
2) History of Ethereum
3) How does Ethereum Work?
4) What is Ethereum 2.0 (Eth2)?
5) How to buy Ethereum?
6) Use cases of the Ethereum Blockchain
7) Why should you use Ethereum?
8) Ethereum Features
9) The Future of Ethereum
10) Conclusion
What is Ethereum?
Ethereum is the second most popular cryptocurrency, just behind Bitcoin. It is a form of cryptocurrency or digital currency and is solely present online. The Ethereum blockchain is a platform based on individual units known as ‘Ether’. It works on a decentralised computer network or distributed ledger (commonly known as blockchain) and manages and tracks the currency.
Blockchain is made up of nodes which are the volunteer computers used to mine coins. Ether tokens are produced from these nodes, and the mining process creates cryptography. The currency is based on the cryptography design. Since mining demands using a computer’s resources and puts intense pressure on the computer, the miners are rewarded with Ether.
Ethereum is perceived to be similar to Bitcoin. However, unlike Bitcoin, the Ethereum blockchain was not created as digital money.
Learn how bitcoins work and how to secure bitcoins. Register for our Bitcoin and Cryptocurrency Course now!
History of Ethereum
Ethereum was born as a result of a whitepaper published by Vitalik Buterin in 2013. Cofounders Gavin Wood, Jeffrey Wilcke, Charles Hoskinson, and others, alongside Buterin, tried to raise money in Ether to fund the present and future projects of Ethereum.
Ethereum was a brainchild created as a solution to the imperfections of Bitcoin. By doing so, it also sanctioned the development of Decentralised Applications (DApp). With DApp development going on, different platforms could not operate together in the Blockchains sector. The creation of Ethereum was intended to connect them. Ethereum was a brainchild created as a solution to the imperfections of Bitcoin. Buterin believed that how DApps run and connections needed to be merged to sustain adoption.
Ethereum came into existence as Ethereum 1.0. One of the interesting features of Ethereum is that a central body does not control it. Instead, the people in the Ethereum community get to make individual decisions within Dapps. The rules are hardcoded into the network for blockchain developers to enforce their own rules.
An interesting development in the history of Ethereum was the Decentralised Autonomous Organisation (DAO). Launched in 2016, this organisation was in charge of voting for any wanted changes in the network and proposals. They smartly avoided a single authority figure and instead relied on a group of people that could vote for changes.
One of the darkest times Ethereum faced was when the DAO faced a significant security threat. A hacker stole £33 million; after this incident, Ethereum was voted to be upgraded to a new network. This "hard fork" ended the journey of 'Ethereum Classic' and helped the new fork – Ethereum – exist.
Want to learn about Blockchain - Join Blockchain Training Course today!
How Does Ethereum Work?
Similar to Bitcoin, a network in Ethereum resides on nearly thousands of computer systems worldwide. The credit for the network's operation and existence goes to the users involved as 'nodes' instead of a centralised server. This turns the network into a decentralised kind and is very resistant to external attacks. As a result, the network does not go down, which means that other nodes will remain functional despite any one system or 'node' failing.
Amidst the network of Ethereum is the Ethereum Virtual Machine or 'EVM', which is a computer run by the decentralised system. Every existing node on the network holds a copy of that computer, which means that any and all exchanges must be verified so that all nodes can make updates to their copies of the EVM. These exchanges are also considered 'transactions' and contained within blocks existing on the Ethereum Blockchain.
These blocks do not get to go on the network before confirmation or validation from the miners, providing transaction history. Verifying transactions through mining is known as the Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus method. Every block has a unique identification code of 64 digits. Miners are required to obtain that code and prove that it is unique. The computer power invested in this process is a testament to their work. When that proof gets verified, miners get paid in ETH.
The way they get paid is another story altogether. Every transaction is accompanied by a sum called 'gas'. Whoever initiates the payment has to pay the gas, which is the same thing paid to miners. The objective of gas is to limit the actions a user can perform per transaction and avoid network spam.
There is a limit to the gas that a block can hold, as this differs with transaction type and amounts. Thus, depending on network activity, the price of gas can get a bit high for some users. Due to this, users are always on the run to be the first to validate transactions. As a result, the network gets busy and boosts fees higher than before.
Cryptocurrency is required to link with Ethereum. It is stored in blockchain wallets that are connected to Dapps. Using them, the users can do whatever they like, whether lending money or playing games. Cryptocurrency acts as data here, allowing users free browsing and anonymous interactions. This points to how non-discriminatory the DApps are. For instance, no banking Dapp can be rejected because of race or financial condition of the user. The users are in control, which is one feature that associates Ethereum with the word "the future of web interaction."
Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and many more are based on blockchain technology. Learn the structure and mechanisms of blockchain with the Blockchain Training course!
What is Ethereum 2.0 (Eth2)?
Ethereum 2.0 has been created as a complete shift from the Ethereum system, where-in the upgrade takes place from the PoW model to the Proof-of-Stake (PoS). The new release overcomes a majority of the former's technical obstacles. Ethereum and Ethereum 2.0, also referred to by the Ethereum Foundation as 'ETH 1.0' and 'ETH2', are known as the execution and consensus layer accordingly.
Blockchain awareness has been growing steadily nowadays and welcoming more and more users. This can result in higher network activity, high transaction fees, and slow validation time. Sometimes, the cost can exceed 50% of the transaction amounts. Although the Dapp developers are working to make it more accessible for mainstream adoption, these issues are one of the many reasons why we require Ethereum 2.0.
It is to be noted that Ethereum 2.0 has been materialising over time and is anything but a one-time event. It is characterised by introducing two essential features – the Beacon Chain and PoS consensus algorithm.
The traditional Ethereum model is evolving by trying to interconnect with one of the first features of Ethereum 2.0 - the Beacon Chain. It helps to add any necessary changes needed for future upgrades. One of these changes is known as Shard Chains. Sharding is the process of branching transactions amongst various smaller Blockchain networks. They help in clearing any network blocks.
The second important feature is the Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus algorithm. It is known for offering a more accessible and quicker form of Blockchain consensus. The PoS feature uses validators instead of miners. Validators act as nodes, as they are the users who perform various tasks like storing the Ethereum Blockchain, validating transactions, and more.
Any form of unique and heavy hardware is not required in PoS the way it is required in cryptocurrency mining. The fact that any user with sufficient funds and a device can participate increases its accessibility and hence appeal. As validators grow, so do the blocks that get validated. This ensures network growth and helps decentralise Ethereum more.
Preparing for an interview? Refer to these Blockchain Interview Questions and Answers to boost your preparation.
How to buy Ethereum
Cryptocurrencies cannot be purchased from regular brokerage sites on the internet. You can buy cryptocurrency only from a cryptocurrency trading platform. Depending on the type of trader you are, you can access several different cryptocurrency exchanges present today. This can include a simple dashboard and sometimes a difficult one.
The four basic steps to follow to buy Ethereum are:
1) Choose a cryptocurrency exchange
2) Fund your account
3) Order your Ethereum
4) Store Ethereum
Once you choose a cryptocurrency exchange, the next step is to open an account. This will involve sharing your personal information and then identity verification. After verification, you have to connect your bank account or debit card to fund your account. Then you purchase Ethereum so that you can invest.
After filling in your account, you can enter the money you wish to exchange for Ethereum. Factoring in the pricing of the Ethereum and your desired amount, you might buy a single Ethereum currency's shares.
Use cases of the Ethereum Blockchain
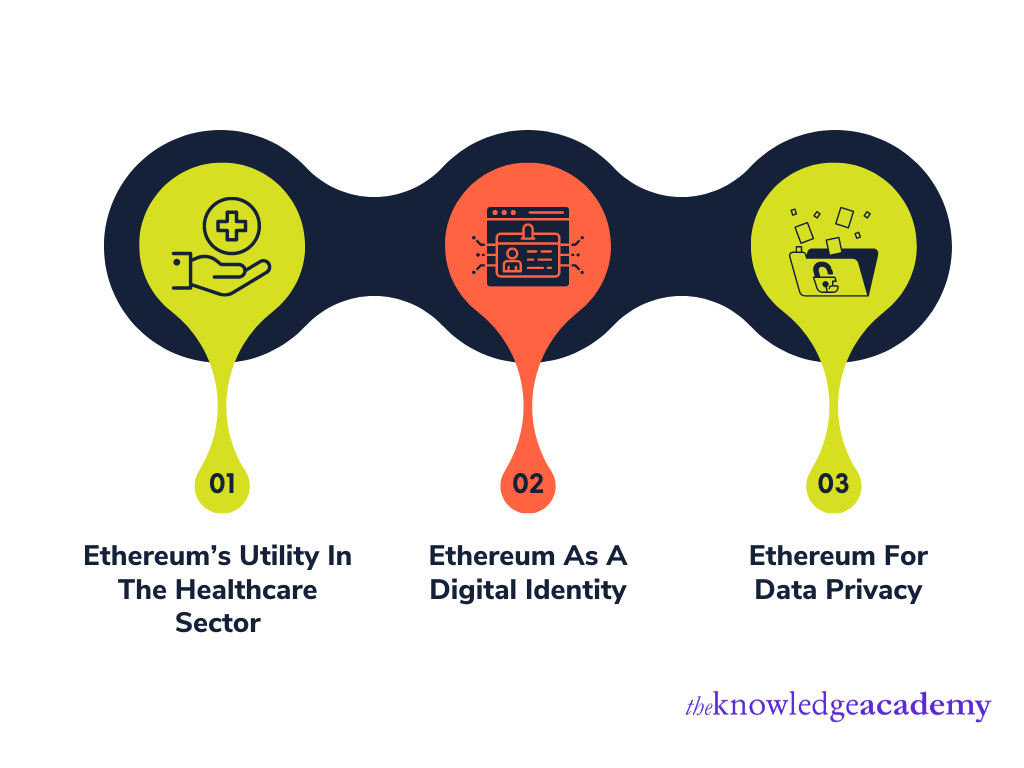
Ethereum is becoming a common part of every person’s life, mainly due to the increasing use of cryptocurrencies. Here are a few of the use cases of Ethereum in modern life.
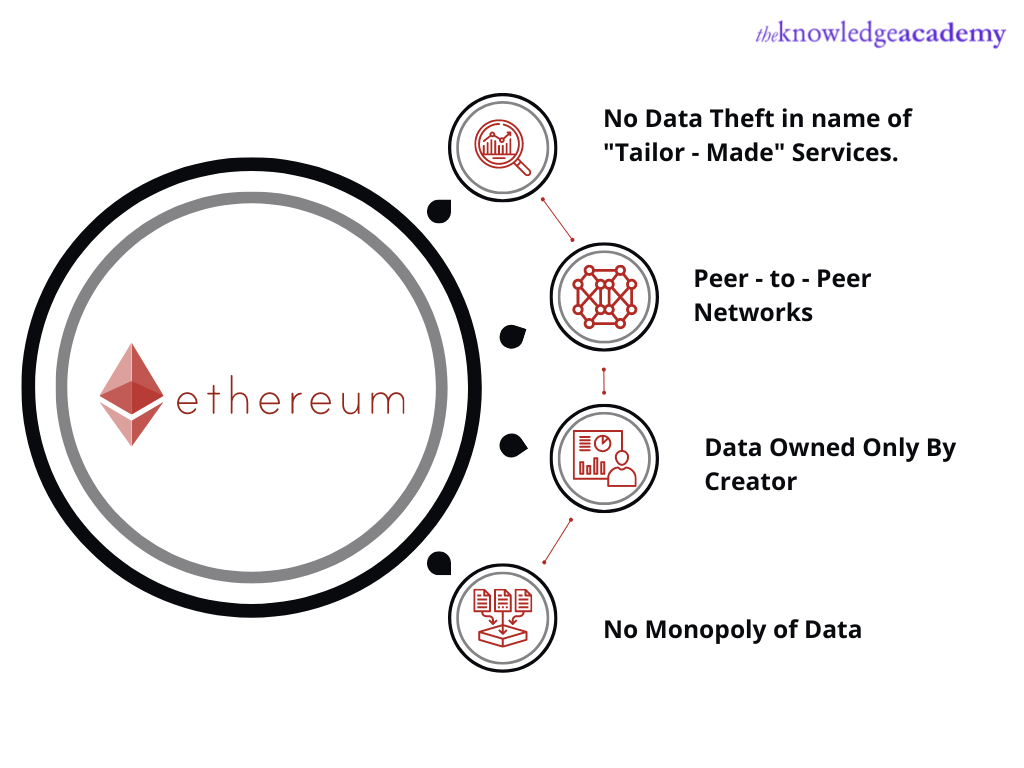
Ethereum’s utility in the healthcare sector – Hospitals and doctors keep a record of their patients. However, it becomes difficult for patients to share this information if they change locations. Currently, there is no centralised system where such data can be stored, accessed, and used. However, the use of Ethereum can change this and share such information with medical professionals, enabling them to monitor health closely.
Ethereum as a digital identity – Ethereum can be used to check the authenticity of identity-related documents such as passports, licenses, and others online.
Due to increasing risks on the internet, governments cannot verify a person's identity online. But Ethereum can change all that and present the authorities with a fast and reliable method to check the identity of people online.
Ethereum for Data privacy – Modern-day companies and even search engines are storing users' personal data to make billions of profits. However, Ethereum’s Blockchain technology can be used to make such data collection a difficult task. Ethereum platforms log every time search engines store and use the user's data. It also makes these logs publicly accessible, enabling the users to see if companies are using their data.
Learn how to create and deploy your tokens with the Ethereum Developer Training course.
Why should you use Ethereum?
As discussed above, the use cases of Ethereum are increasing, making it an integral part of everyday modern life. Here are a few reasons that explain why you should use Ethereum.
Quicker and Cheaper cross border payment
With stablecoins such as Tether and US Coin (USDC), based on Ethereum, cross-border payments have become quicker and cheaper. Global payment systems can be made stable and affordable with Ethereum Blockchain.
Quick help in the time of need
In times of emergency, such as the current Russia-Ukraine war, cryptocurrencies such as Ethereum have emerged as a means for the Ukrainians to not only stay connected with the outside world but also gain access to quick and reliable money.
Ethereum Features
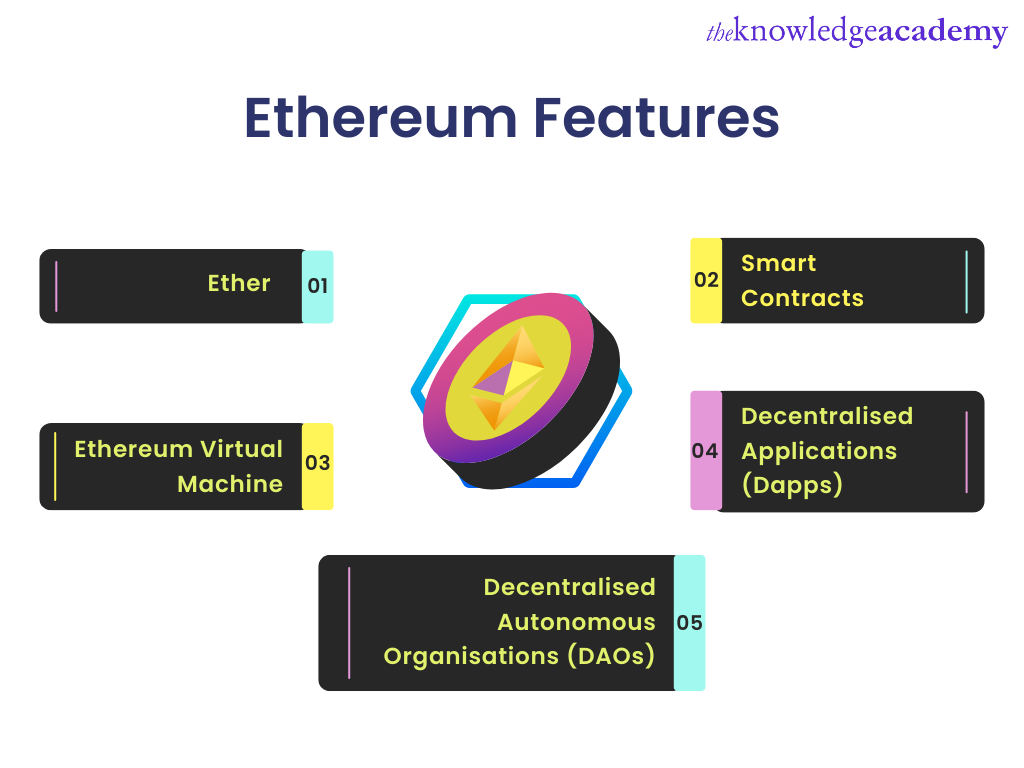
Before exploring the world of Ethereum in detail, it is necessary to understand a few of its basic terms and concepts. Here is a list of some of the key features of Ethereum:
1) Ether
2) Smart Contracts
3) Ethereum Virtual Machine
4) Decentralised Applications (Dapps)
5) Decentralised Autonomous Organisations (DAOs)
Ether
Ethereum's cryptocurrency is known as Ether (ETH). The computational resources and transaction fees that occur on the network are paid using Ether. It is a peer-to-peer currency, which is also used to buy gas. Any transaction on the Ethereum network is made using gas. In order to run transactions on the network, you need gas, which can be acquired by paying in Ether.
Smart Contracts
Smart Contracts, like regular contracts, contain mutually decided rules and regulations to assist the exchange of assets between two parties. The asset could be money, property, or even digital assets. Any user on the Ethereum network can create these contracts.
One of its essential features of it is the rigidness of the contracts. Once contracts are developed, they cannot in any way or form be changed. The transactions done over a finalised smart contract will be registered permanently. If the contract happens to be modified in the future, the transactions associated with the initial contract will remain unaffected.
Smart Contract executions are decentralised, as a centralised authority is not present. Instead of a central authority, processes like verification are handled by anonymous parties in the network. Using Smart Contracts has a lot of benefits. It provides a safe environment for transparent transactions and secures the identities of either party. Both the sender and receiver accounts are notified upon the successful completion of transactions.
Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM)
Ethereum Virtual Machines (EVMs) provide the underlying software or foundation that helps decode Smart Contracts and allows users to interact with them. Smart Contracts written in Solidity language are understood using EVMs.
EVM works in a sandbox environment – isolated virtual machines where potentially unsafe codes can be executed without affecting the rest of the network. It allows the testing of Smart Contracts multiple times until you can verify them. If you are content with its performance, you can position it on Ethereum's main network.
Decentralised Applications (Dapps)
Logging into a typical blockchain application requires an Application Programming Interface (API) to access the centrally hosted data. On the other hand, Decentralised Applications use smart contract-based API to collect your desired data from the Blockchain network.
This Blockchain network is decentralised, where all transactions that occur in the network are verified by miners using the smart contract. The software for Dapp does not rely on a centralised authority and, as a result, provides a direct link between end-users and Dapp providers. When open-source applications use public Blockchain-based tokens to run, it is considered a Dapp. They rely on these tokens as fuel to function.
Decentralised Autonomous Organisations (DAOs)
The DAO is a decentralised organisation that collectively votes to introduce or remove necessary changes to the network. The organisation consists of a designated group of people that function on a democratic basis. The regulations in a smart contract command DAOs, and they use the contracts for decision-making.
The DAO has an efficient and concise voting process. This starts with funding the Dapp so that it can execute. A token is provided to each member that represents the share percentage of that person in the DAO. These tokens are used to vote in the organisation, and the maximum votes lead to a decision.
The Future of Ethereum
The developers of Ethereum have been able to guarantee the rising popularity of the Ethereum Blockchain by creating decentralised finance projects and NFTs with it. The new applications have spiked network traffic, attracting more developers to Ethereum.
Unfortunately, these factors are insufficient to provide a hassle-free future for Ethereum. One of the significant drawbacks is the lag in technological upgradation. This puts Ethereum at a disadvantage amongst its competitors and the ever-growing crypto world. In addition, the recent uprise of Bitcoin might also affect the significance of Ethereum.
Conclusion
After reading this blog, we hope you can understand Ethereum Blockchain and its uses in modern life. Cryptocurrencies like Ethereum have become a means for people to earn passive income and take the most advantage of the market situation. You, too, can learn about Ethereum Blockchain and other cryptocurrencies to enhance your career and earning potential.
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming Programming & DevOps Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Blockchain Training Course
Blockchain Training Course
Thu 11th Jul 2024
Thu 19th Dec 2024







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


