We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

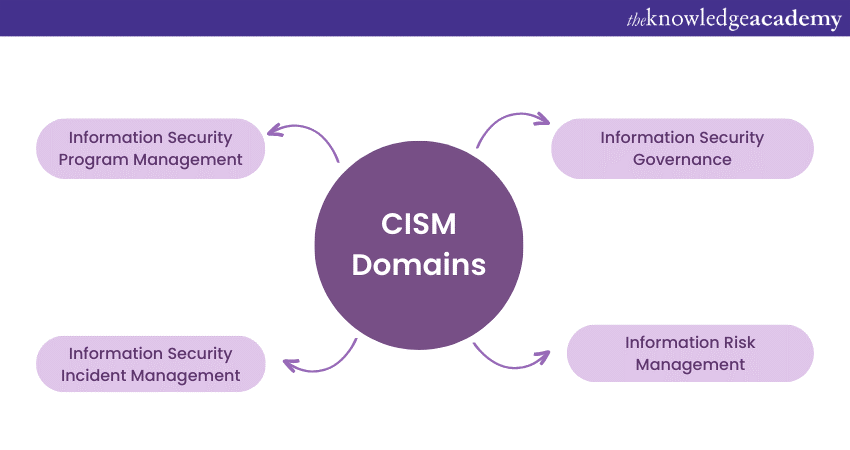
Types of CISM domains refer to the four key areas of expertise that the Certified Information Security Manager (CISM) certification covers. These domains are essential for professionals who are responsible for managing, designing, and overseeing information security systems and processes within an organisation.
Each domain covers a specific aspect of information security management and is critical for ensuring the security and protection of sensitive data. This certification helps to enhance the credibility of professionals in the field of information security management and prepares them for leadership roles in the industry. In this blog, you will learn, what is CISM and the different types of CISM domains required for the certification exam. Continue reading about cisa vs cism and learn more!
Table of Contents
1) What are the Domains included in CISM?
2) Topics covered in CISM Domains
3) CISM job Domains
4) Conclusion
What are the Domains included in CISM?
The CISM exam includes 150 multiple-choice questions with a time duration of four hours. The four functional areas in which candidates are assessed. The main domains included in CISM are:
Domain 1: Information Security governance
The first domain of the CISM exam focuses on assessing candidates' competence in developing, maintaining, and managing information security governance structure. It examines their ability to create and implement effective frameworks that govern the overall security of an organisation's information assets.
Demonstrate skills: Within this domain, candidates are required to demonstrate their understanding of various aspects. They must be able to identify and comprehend the pertinent contractual and regulatory CISM requirements that have an impact on the enterprise. This includes recognising legal obligations, industry standards, and compliance mandates that influence Information Security practices.
Organisational hierarchy: Candidates need to describe how enterprise structure, culture, and leadership influence the performance of an organisation's information security strategy. They should have a grasp of how organisational hierarchies, communication channels, and management styles can either support or hinder the effectiveness of security initiatives.

Assessment of Information Security strategy: Another important aspect covered in this domain is the measurement of the impact of an information security strategy on enterprise risk management. Candidates must demonstrate their ability to evaluate and quantify the potential risks associated with information security, as well as the effectiveness of the implemented security measures in mitigating those risks.
Integrating security measures: Candidates will be tested on their capability to align the information security program with the operational objectives of other business functions. This involves integrating security measures into the overall business operations and ensuring that security goals are in line with the organisation's strategic objectives.
Develop and utilise metrics: Lastly, candidates can expect questions related to security metrics, which involve the effective measurement and assessment of security performance. They should understand how to develop and utilise metrics that provide a periodic and quantitative evaluation of security effectiveness, enabling organisations to track progress, identify areas for improvement, and take the right steps to deal effectively with the Information Security procedure.
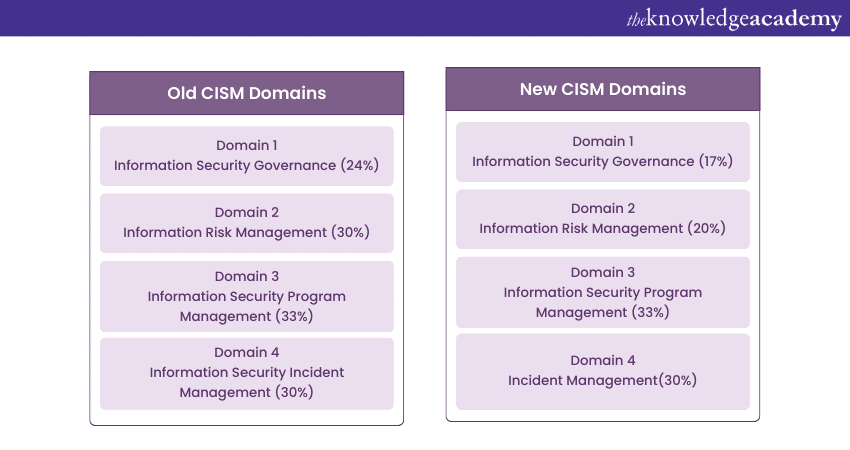
Total number of questions covered: 25
Domain 2: Information security risk management
The second domain of the CISM exam focuses on information risk management, which is crucial for organisations to effectively identify and address potential risks. This domain introduces several important concepts such as exposures, vulnerabilities, threats, impacts, and various recovery-related metrics like Recovery Time Objective (RTO) and Recovery Point Objective (RPO).
Understanding these concepts allows individuals to assess the risks faced by an organisation and take appropriate actions. By calculating and evaluating possible risks, one can determine whether to avoid, transfer, accept, or mitigate them. This strategic approach helps save time for both the individual and their team, ultimately demonstrating their value and benefit to the organisation.
Total number of questions covered: 30
Learn about the various important steps that go into information security governance. Register right away for our CISM Certified Information Security Manager Training!
Domain 3: Information Security Program Development and Management (ISPDM)
The third domain within ISPDM focuses on security program and management. Its primary objective is to configure effective strategies and implement them in a manner that considers cost-effectiveness. Furthermore, it is crucial to align these strategies with the desired goals and outcomes of the company. There are several challenges associated with ISPDM, namely:
a) People: Dealing with personnel-related issues and ensuring their cooperation and adherence to security measures.
b) Processes: establishing efficient processes to manage security programs and ensure their effectiveness.
c) Policy Issues: Addressing policy-related challenges and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
d) Program Objectives: Aligning the security program with the organisation's objectives and continuously monitoring its progress.
Ethical and legal considerations play a vital role in ISPDM, encompassing aspects such as regulatory requirements and personnel obligations. It is essential to calculate and manage risks effectively to achieve favourable outcomes. By effectively addressing potential risks, a better overall outcome can be attained.
Total questions covered: 50
Domain 4: Information Security Incident Management (ISIM)
The final domain focuses on preparedness for handling Information Security incidents. This domain deals with managing problems that are unplanned. Candidates are required to outline the necessary procedures and prerequisites for developing an incident response plan. Furthermore, attention should be given to methodologies for categorising or classifying incidents, as well as how the response plan is to be thoroughly tested and evaluated.
Incident Management encompasses the operational aspect, which involves the continuous management of reported incidents. Candidates must provide a description of the methods and processes employed to assess, investigate, and effectively contain an incident. Moreover, it is vital to comprehend the relationship between incident response, business continuity, and the impact on the overall business. One of the primary objectives of this domain is to ensure that candidates can promptly identify and contain incidents while addressing their existing causes.
Total questions covered: 45
How to sustain your CISM certification?
It's critical that you earn 120 hours of CPE over the course of three years to keep your CISM® certification active. A minimum of 20 hours must be put in on a yearly basis and submitted to ISACA, the industry's governing body. Before renewing the certification for the current year, it is crucial to make sure that the prerequisites for the prior year have been met. It is necessary to stay informed and compliant with the annual CPE audits conducted by the governing body. Additionally, you must report your CPE hours earned every three years, with at least 20 hours per year, and pay the appropriate fee of £69 for non-members or £36 for members.
You are also expected to abide by the Professional Ethics Code established by ISACA as a CISM certified professional. Maintaining your certification and preserving the standards of the profession depend on you adhering to these rules.
You can take part in information security management-related conferences, seminars, training sessions, or webinars to earn CPE hours. You can also obtain CPE hours by participating in peer-reviewed publications, writing papers, or reading books. Making sure that the selected tasks fit within the CISM job practice areas is essential.
The four CISM job practice areas include:
a) Information Security Governance
b) Information Risk Management
c) Information Security Program Management d) Information Security Incident Management
Conclusion
The four CISM domains cover a broad range of skills and knowledge required for effective Information Security management. After becoming CISM certified and gaining expertise in these domains, individuals can enhance their knowledge and skills in information security management, which can lead to career growth opportunities in the field of CISM or CRISC. Consequently, the CISM domains provide a comprehensive framework for advancing one's career in Information Security management. For further preparation and insight, explore our blog to discover essential CISM interview questions.
Become proficient in Information Security Management with our CISM Training. Sign up today!
Frequently Asked Questions

Primavera was founded in 1983, specialising in project management software. Acquired by Oracle in 2008, it evolved to become a leading tool for managing complex projects across various industries.

Primavera is not an ERP system; it is a Project Management software designed for planning, scheduling, and managing complex projects. However, it can be integrated with ERP systems to enhance project and resource management.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various CISM Course, including Certified Information Security Manager (CISM) Training, Certified Data Protection Officer (CDPO) Course and Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control (CRISC) Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into CISM or CRISC: A Complete Comparision.
Our IT Security & Data Protection Blogs cover a range of topics related to CISM, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your network security skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming IT Security & Data Protection Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 CISM Certified Information Security Manager
CISM Certified Information Security Manager
Sat 3rd Aug 2024, Sun 4th Aug 2024
Mon 12th Aug 2024
Mon 9th Sep 2024
Mon 14th Oct 2024
Sat 9th Nov 2024, Sun 10th Nov 2024
Mon 11th Nov 2024
Mon 9th Dec 2024
Mon 6th Jan 2025
Mon 3rd Feb 2025
Mon 3rd Mar 2025
Mon 14th Apr 2025
Tue 6th May 2025
Mon 2nd Jun 2025
Mon 7th Jul 2025
Mon 4th Aug 2025
Mon 1st Sep 2025
Mon 6th Oct 2025
Mon 3rd Nov 2025
Mon 1st Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


