We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Mastering the CCSP domains will help you gain the expertise needed to secure cloud environments, protect sensitive data, and ensure compliance with industry standards. According to ISC official website, by obtaining the CCSP, you can prove that you possess the technical skills and aptitude required to successfully plan, oversee, and safeguard data, apps, and infrastructure in the cloud.
Becoming a Certified Cloud Security Professional (CCSP) can be a highly rewarding endeavour, and equip you with the skills and knowledge necessary to excel in the field of cloud security. In this blog, we will delve into the six CCSP Domains, explore their key concepts, and discuss their significance in securing cloud-based systems.
Table of Contents
1) All about CCSP Certification
2) Six types of CCSP Domains
a) Domain 1: Cloud Concepts, architecture and design
b) Domain 2: Cloud Data Security
c) Domain 3: Cloud platform infrastructure security
d) Domain 4: Cloud application security
e) Domain 5: Cloud security operations
f) Domain 6: Legal, risk and compliance
3) Conclusion
All about CCSP Certification
The CCSP Certification is a renowned security certification designed for experienced professionals in the field of cloud security. It is recognised globally as a benchmark for cloud security expertise. Offered by the International Information System Security Certification Consortium (ISC)2, a non-profit organisation dedicated to cybersecurity education and certification, the CCSP is part of a comprehensive range of certifications provided by (ISC)2.
The CCSP Certification addresses the unique challenges associated with cloud security and validates an individual's proficiency in designing, implementing, and managing secure cloud environments. Acquiring these skills bolsters your prospects and propels your CCSP Career into a new stratosphere. It was officially introduced at the RSA Conference in 2015 and has gained significant popularity in the market ever since its inception. As the adoption of cloud technology continues to grow, the CCSP certification remains relevant and valuable for professionals seeking to enhance their cloud security capabilities and advance their careers in this rapidly evolving field.

Six types of CCSP Domains
Each area of knowledge and expertise covered by the CCSP certification is referred to as a CCSP domain. The CCSP Common Body of Knowledge (CBK) is divided into six domains that cover various aspects of cloud security. Here are the CCSP Domains:
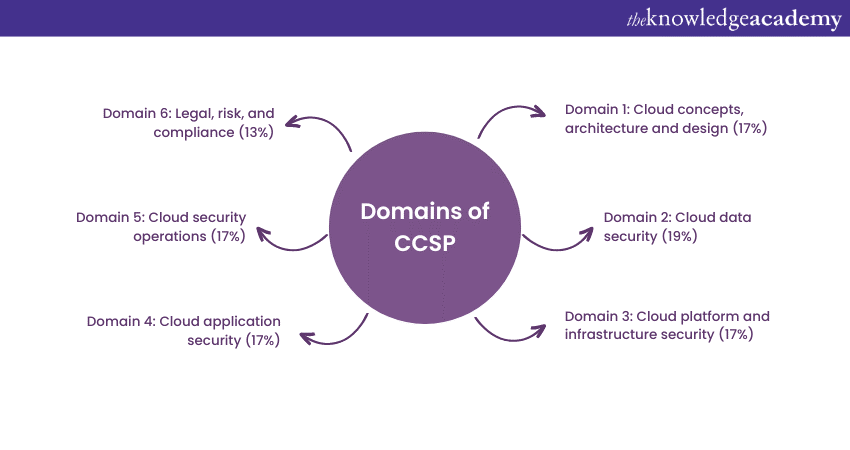
CCSP Domain 1: Cloud Concepts, architecture and design
Weightage: 17%
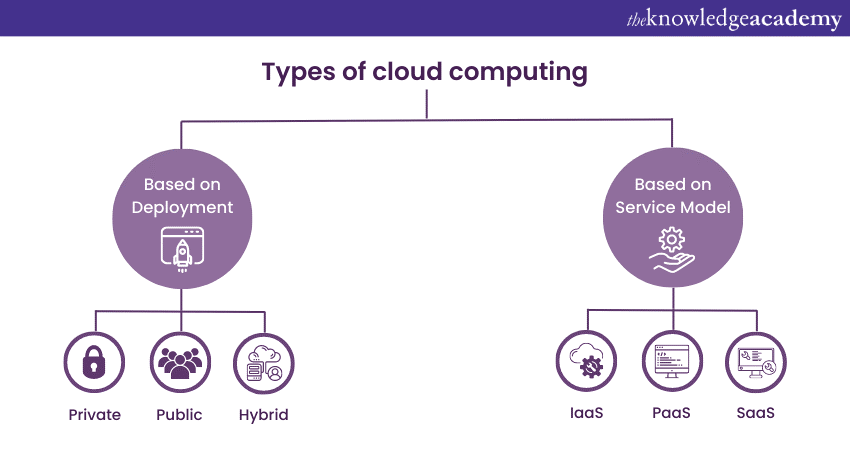
In CCSP Domain 1, we explore the essential concepts, architecture, and design principles of cloud computing. Cloud computing lets users access and utilise computing resources over the internet, offering flexibility and cost-effectiveness. This knowledge is essential for effectively securing cloud environments, ensuring data and service confidentiality, integrity, and availability. This domain covers different cloud service models which include:
a) Software as a Service (SaaS): SaaS provides ready-to-use software
b) Platform as a Service (PaaS): PaaS offers a platform for application development
c) Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): IaaS offers virtualised computing resources
CCSP Domain 1 provides a strong foundation in cloud computing concepts, architecture, and design. It familiarises you with different service and deployment models, virtualisation technologies, and the components of a cloud infrastructure. The ISO/IEC 17788 lays a foundation for these components.
Cloud concepts, architecture and design cover the following:
a) Basics of cloud computing: It covers the essential elements of cloud computing, such as on-demand self-service, widespread network access, multitenancy, quick elasticity and scalability, resource pooling, and measured service. It measures the level of understanding that candidates have related to elements of cloud computing.
b) Cloud reference architecture: This talks about cloud computing operations, cloud service types and cloud deployment models. The roles of these cloud computing activities are included in the standard ISO/IEC 17789. IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS are the major elements of this section.
c) Cloud computing security concepts: This section includes:
1) Cryptography and key management
2) Access control
3) Data and media sanitisation
4) Network security
5) Virtualisation security
6) Common threats
c) Secure Cloud Computing Design Principles: This area covers cloud secure data lifecycle, cloud based Disaster Recovery (DR) and Business Continuity (BC) planning, cost benefit analysis, functional security requirements and security considerations for different cloud categories.
d) Evaluate Cloud Service Providers: This section requires using reliable methods for certificate verification. For example, Cloud customers do not oversee the entire cloud environment, therefore it is suggested to verify operations provided by a cloud provider.
Domain 2: Cloud Data Security
Weightage: 19%
Data security in the cloud is the main topic of "Cloud Data Security." It addresses issues including database protection, application security, data lifecycle management, data classification, protecting sensitive data, secure storage, and legal compliance. The focus of the domain is on putting security mechanisms in place to guarantee data availability, confidentiality, and integrity in cloud settings. This section covers:
a) Understanding cloud data concepts:
Domain 2 of the CCSP certification covers key concepts related to cloud data security. It includes understanding and implementing practices for data classification, data lifecycle management, data rights management, data retention and destruction, data privacy, data anonymisation and pseudonymisation, data sovereignty, and data loss prevention.
This domain focuses on ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data in cloud environments while complying with legal and regulatory requirements. It emphasises the need to protect sensitive data, manage data throughout its lifecycle, enforce access controls, and implement measures to prevent data breaches and unauthorised disclosure.
b) Designing and implementing cloud data storage architectures:
This includes different types of cloud storage services covering all components of cloud storage. The cloud storage services include storage types like long-term, ephemeral and raw disk. These storages are applied with IaaS, PaaS and SaaS.
c) Designing and applying data security strategies
This section covers the following topics:
1) Encryption and key management
2) Hashing
3) Masking
4) Tokenisation
5) Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
6) Data Obfuscation
7) Data de-identification and new cryptography-related technologies
d) Implementing data discovery: This section introduces a range of possible enterprise collaborations made possible by data and analytics sharing. This involves two kinds of data discovery techniques like:
a) Structured data
b) Unstructured data
e) Implementing data classification: This explains in detail about data classification methods. It involves mapping, labeling data and protecting sensitive data.
f) Designing and implementing Information Rights Management (IRM): This section deals with evaluating technology to handle user accessibility related to various types of data. It spans around objectives like data rights, provisioning, access models and handling appropriate tools such as issuing and cancellation of certificates.
Advance your career options in cloud computing by registering in our CCSP Certified Cloud Security Professional Training course today!
Domain 3: Cloud platform infrastructure security
Weightage: 17%
Domain 3 primarily focuses on cloud infrastructure security. It assesses a candidate's aptitude based on how well they manage risk assessments, establish and implement cloud security protocols, and incorporate cloud computing into their organisation's BC/DR plan. This section includes:
a) Understand cloud infrastructure components: This includes virtualisation, network architecture, storage systems, compute resources, and security controls. It's important to grasp the basic elements that make cloud services possible, such as virtual machines, networks, storage, and access controls. This knowledge is essential for designing and securing cloud environments effectively.
b) Designing a secure data centre: It focuses on creating a safe and protected environment for data. This involves implementing security measures like access controls, monitoring systems, firewalls, and backup solutions. The goal is to ensure that data is kept confidential, unaltered, and available when needed. It also covers physical security measures to protect the data centre from unauthorised access.
c) Evaluate risks related to cloud infrastructure: It includes identifying and understanding potential threats and problems that could impact the security and functioning of cloud environments. This helps to reduce risks, implement effective security measures, and comply with standards and regulations. The goal is to protect the cloud infrastructure from potential vulnerabilities and ensure a secure environment for data and services.
d) Implement plan security controls: It involves creating a strong security framework that includes access controls, network security, data protection, physical security, and incident response planning. The goal is to design a comprehensive and effective security system that safeguards the data center and ensures the continuity of business operations.
e) Organise DR and BC: DR ensures IT system and data recovery after disasters, while BC sustains critical business operations during disruptions, enabling continuity and trust. It includes risk assessments, backups, alternate sites, incident response, and testing.
Domain 4: Cloud application security
Weightage: 17%
Domain 4 explores the various security challenges in cloud computing applications. Candidates' understanding of the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC), cloud software assurance, and finding the right combination of cloud computing technology and identity management solutions are assessed in this domain. This section includes:
a) Encourage application security awareness and training: Encourage the development of training and public awareness campaigns to inform individuals about the significance of application security. This promotes informed decision making among professionals to meet the needs for cloud computing.
b) Understanding the Secure Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) Process: Recognise and describe the steps involved in creating software while implementing security controls at every stage.
c) Put the SDLC to use: Put security measures into place at each stage of software development to produce applications that are more reliable and secure. This discusses about the STRIDE and DREAD models and how to apply them in cloud settings.
d) Put Cloud software assurance and validation to use: Use methods like vulnerability assessments and security audits to make sure that cloud software is secure and reliable. It includes two types of testing: Static Application Security testing (SAST) and Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST). SAST is a white box testing approach. It checks at the code to look for software problems and vulnerabilities like SQL injection. On the other hand, DAST is a black box testing technique that scans a programme as it operates to look for flaws that a hacker might use against it.
e) Implement verified secure software: Choose and deploy software applications that have undergone rigorous security testing and evaluation. It is also implemented on applications which are commercial, open-source, and community sourced.
f) Understanding cloud application architecture: Understand how cloud applications are designed, deployed, and managed in a distributed and scalable environment. This part also talks about the most common technologies of cloud computing. For example, Extensible Markup Language (XML), Web Application Firewalls (WAFs) and application virtualisation all come under this approach.
g) Creating appropriate Identity and Access Management (IAM) solutions: Create effective solutions to manage user identities, authentication, authorisation, and access controls in the cloud. It also covers topics like Federated Identity Management to manage system access within the organisation.
Domain 5: Cloud security operations
Weightage: 17%
Domain 5 revolves around issues related to cloud computing services. It primarily focuses on network infrastructure management and cloud service security experts. The subject of this domain includes Identity and Access Management (IAM) in cloud systems. It involves being aware of and putting into practise efficient methods for managing user identities, authenticating users, limiting access to resources, and enforcing security regulations. IAM minimises the risk of unauthorised access and data breaches in cloud systems by ensuring that only authorised users can access cloud resources.
a) Create and implement physical and logical infrastructure for cloud environments: This includes setting up the physical and virtual components required for cloud environments. It deals with data center planning including physical and logical layers applied in various technologies.
b) Manage the physical and logical infrastructure for cloud environments: This talks about how to manage physical and logical infrastructure for cloud environments. It monitors the ongoing management of infrastructure in cloud environments. It involves implementing best practices for system administration, conducting regular maintenance, ensuring compliance with security policies, and keeping up with technology updates and patches to maintain a secure and efficient infrastructure.
c) Operate the physical and logical infrastructure for cloud environments: This discusses the operation of physical and logical infrastructure for cloud environments. It focuses on managing and maintaining the physical and virtual components of the cloud environment. It involves tasks such as monitoring system performance, ensuring availability, managing capacity, and addressing any operational issues that may arise.
d) Put operational controls and standards in place: It sets up operational controls and abides by standards set by the industry for efficient and legal operations. Setting protocols, rules, and policies for operational tasks like change management, incident response, access controls, and disaster recovery are all included in this section.
e) Support digital forensics: This focuses on providing support for digital forensics activities in cloud environments. It involves preserving and analysing digital records in the event of security incidents or legal investigations. This includes following proper forensic procedures, collecting and analysing data, and collaborating with relevant stakeholders to support investigations.
f) Maintain contact with important parties: It focuses on streamlined communication with stakeholders considering it to be the most important part of operations. This involves establishing clear channels of communication with stakeholders, such as clients, vendors, and internal teams. It includes sharing information, addressing concerns, coordinating activities, and ensuring that all parties involved are informed and aligned with the cloud environment's operations and security requirements.
g) Controlling security operations: This deals with managing the day-to-day security operations in cloud environments. It involves tasks such as monitoring security events, conducting security assessments and audits, implementing security controls, managing incidents, and enforcing security policies. The goal is to maintain a secure and resilient cloud environment by promptly identifying and mitigating security risks and threats.
Domain 6: Legal, risk and compliance
Weightage: 13%
Domain 6 includes comprehending and addressing legal requirements, evaluating and managing cloud service-related risks, and guaranteeing compliance with suitable laws and professional standards. Professionals in this field gain knowledge of how to negotiate the legal system, recognise and reduce risks, and put in place efficient compliance controls to safeguard data and privacy in the cloud. It includes the following topics:
a) Legal requirements and unique risks within the cloud environment: Identify and communicate the specific laws and regulations that apply to cloud computing, as well as the potential risks that are unique to this environment, such as data breaches or unauthorised access. This area addresses the legal restrictions imposed by numerous countries as well as specific legal dangers associated with cloud computing.
b) Privacy issues: This section will help you learn about issues with cloud privacy, such as how to handle, store, and safeguard personal data. comprehending consent laws, adopting proper safeguards, and comprehending privacy regulations. This section goes in-depth on the idea of eDiscovery and digital forensics as they relate to cloud computing.
c) Audit process, methodologies, and required adaptations for a cloud environment: This topic will help you understand the audit procedures and methodologies used to assess security and compliance in the cloud. It identifies the necessary adjustments and considerations when conducting audits in a cloud-based environment, such as assessing cloud provider controls and ensuring data integrity.
d) Implications of cloud to enterprise risk management: This area of study will help you determine the impact of cloud computing on an organisation's risk management practices. It evaluates the risks associated with adopting cloud services, such as potential disruptions, data loss, or vendor lock-in, and develop strategies to mitigate and manage these risks effectively. It includes four stages of risk management framing, assessing, responding, and monitoring.
e) Outsourcing and cloud contract design: This topic talks about the considerations and best practices for outsourcing cloud services and designing appropriate contracts. This involves understanding Service-level Agreements (SLAs), data ownership and retention, disaster recovery plans, and other contractual aspects to ensure that the cloud service meets the organisation's needs and complies with legal requirements.
Conclusion
We hope this blog gives you enough insights on CCSP Domains. By understanding and mastering these domains, people can make sure that cloud systems are safe and that important data is protected. This is important because a lot of our information and services are stored in the cloud nowadays. So, by learning about and applying the CCSP Domains, we can make sure that our cloud systems are trustworthy and our data is secure.
Learn how to conduct risk assessments of existing and proposed cloud-based environment with our CCSP Training Course today. Sign up now!
Frequently Asked Questions

Mastering CCSP domains has propelled careers by enhancing professionals' expertise in cloud security. Individuals adept in domains like Cloud Data Security, Architecture, and Legal/Compliance gain a competitive edge in the dynamic tech landscape. They navigate complex cloud environments, ensuring data confidentiality and compliance, increasing employer and client trust.
Mastery in Identity and Access Management secures cloud resources, bolstering cybersecurity. Proficiency in Security Operations guarantees swift threat responses, fostering a resilient cloud infrastructure. CCSP mastery empowers professionals to safeguard organisations in the evolving digital realm, unlocking new opportunities and career advancements.

Successfully preparing for the CCSP certification involves a structured approach. Begin by thoroughly understanding each domain—Security and Risk Management, Asset Security, Security Architecture and Engineering, Communication and Network Security, Identity and Access Management, Security Assessment and Testing, and Security Operations. Utilise official study materials, practice exams, and real-world scenarios to reinforce concepts. Engage in hands-on labs to apply theoretical knowledge. Join study groups or forums for collaborative learning. Regularly assess progress and focus on weaker areas. Prioritise time management and maintain a consistent study schedule. Lastly, simulate exam conditions to build confidence. This holistic strategy ensures comprehensive preparation across all CCSP domains.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
Upcoming IT Security & Data Protection Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 CCSP Certified Cloud Security Professional
CCSP Certified Cloud Security Professional
Sat 27th Jul 2024, Sun 28th Jul 2024
Tue 27th Aug 2024
Sat 26th Oct 2024, Sun 27th Oct 2024
Mon 25th Nov 2024
Mon 20th Jan 2025
Mon 24th Mar 2025
Mon 23rd Jun 2025
Mon 29th Sep 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


