We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Traditional Project Management approaches often struggle to keep up with today’s rapidly evolving requirements and market demands. This is where Agile Project Management comes into play.
Agile Project Management is a flexible and iterative approach to managing projects, emphasizing adaptability, collaboration, and continuous improvement. Agile is not just a buzzword but a powerful methodology that has revolutionised how projects are planned, executed, and delivered.
It is evident from the 16th State of Agile Survey Report, which reported that 80% of organisations are using Agile as their predominant approach to derive digital transformation.
So, is it time for you too to implement this methodology for effective Project Management (PM)? If yes, don’t know what it is? How to implement it? What are its key components? Worry no more. Read this blog to learn about Agile Project Management’s key concepts and benefits. Also, explore its best practices to harness the power of Agile and drive success.
Table of Contents
1) What is Agile Project Management?
2) How to become an Agile Project Manager?
3) Understanding Agile principles
4) Different Agile Project Management techniques?
5) Implementing Agile in your organisation
6) Advantages of Agile Project Management
7) Limitations of Agile Project Management
8) Agile Project Manager roles and responsibilities
9) Agile vs traditional Project Management
10) Conclusion
What is Agile Project Management?
Are you looking for a comprehensive Project Management methodology to derive success in your organisation? If yes, then Agile Methodology can prove a game changer for you. But what is Agile Project Management? Let’s find out. Here’s the Agile Project Management definition:
Agile Project Management is a flexible and iterative approach to managing projects, emphasising adaptability, collaboration, and continuous improvement. It originated in the software development industry but has since expanded to various sectors and industries, including marketing, product development, and construction.
Unlike traditional PM methodologies that follow a linear and sequential process, Agile embraces change and uncertainty as inherent aspects of the project. It acknowledges that customer requirements can evolve, market conditions can shift, and unforeseen challenges can arise during the project lifecycle.
It further provides a framework that enables teams to respond and adapt effectively to these changes, ultimately delivering value to customers and stakeholders. At the heart of this methodology lies four core values outlined in the Agile Manifesto:
a) Individuals and interactions over processes and tools: Agile emphasises the importance of collaboration and effective communication among team members. It recognises that empowered individuals working together can achieve better outcomes than relying solely on rigid processes and tools.
b) Working software (or deliverables) over comprehensive documentation: It encourages teams to create working prototypes, software, or other deliverables that customers can test and validate.
c) Customer collaboration over contract negotiation: By involving customers early and frequently, teams can gather feedback and understand evolving requirements. They can also ensure that the project delivers value that aligns with customer needs.
d) Responding to change over following a plan: It also encourages teams to embrace change and adapt their approaches accordingly. This flexibility allows for course corrections, continual learning, and optimisation of project outcomes.
How to become an Agile Project Manager?
If you are an Agile Project Manager, your duties go beyond the usual Project Management tasks. Your primary function is facilitating communication and collaboration within the Agile team to ensure effectiveness. Your responsibility includes guiding the team through the project lifecycle, removing hindrances and improving processes to boost efficiency and productivity.
As an Agile Project Manager, your adaptability to changing requirements and promoting a culture of continuous improvement is essential for your career growth. Let us go over some aspects that are important in becoming an Agile Project Manager.
Essential Skills required for an Agile Project Manager
To become a successful Agile Project Manager, you need to incorporate a unique blend of skills that complement Agile principles. Let us explore certain attributes:
a) Effective communication: As an Agile Project Manager, it's essential to have strong communication skills. You must clearly explain project goals, requirements, and status updates to all stakeholders. Furthermore, being a good listener helps you better understand your team members' needs and worries, which can encourage a more cooperative work environment.
b) Adaptability and flexibility: Agile projects require adaptability, flexibility, and quick decision-making. As an Agile Project Manager, embracing change and navigating uncertainties is essential to keep the project on track.
c) Collaborative approach: Agile methodologies centre around collaboration, teamwork, open communication, trust, and respect. A successful Agile Project Manager must possess these essential attributes.
Gaining relevant experience and knowledge
Familiarise yourself with Agile methodologies: To become an Agile Project Manager, it is crucial to have a firm grasp of Agile methodologies and their implementation. A good starting point is to get familiar with widely used Agile frameworks such as Scrum, Kanban, and Lean. Study their fundamental principles, practices, and ceremonies. Learn the roles and responsibilities of Agile team members and how they work together to achieve project success. Understanding each approach will help you tailor your methods to the specific project needs.
Seek Project Management certifications: Obtaining Agile Project Management certifications is valuable and validates expertise, demonstrating commitment to the field. Consider pursuing certifications such as Scrum Master Certification or PMI Agile Certified Practitioner (PMI-ACP). These certifications enhance your knowledge of Agile principles and practices and make you more marketable to potential employers. They provide a structured learning path and often require you to gain practical experience working on Agile projects.
Hands-on experience through internships or volunteer work: Looking for opportunities to work as an intern or volunteer in organisations that embrace Agile methodologies is an effective way to gain practical experience in Agile Project Management. Collaborating with Agile teams will give you firsthand exposure to Agile practices, project dynamics, and challenges in an Agile environment. This experience will enhance your skills and offer practical insights into applying Agile principles.
Understanding Agile principles
Agile is rooted in a set of guiding principles that shape its philosophy and practices. These principles, outlined in the Manifesto, serve as a compass for Agile teams, helping them navigate complex projects and deliver value to customers efficiently. Now, let's explore its key Agile Project Management principles and gain a deeper understanding of their significance:
a) Consumer satisfaction through early and continuous delivery of valuable software
b) Adapting changing requirements, even at the latter part of the development process
c) Frequently deliver working software, with a preference for a short period
d) Collaboration between stakeholders and developers throughout the project
e) Build projects around inspired individuals, giving them the atmosphere and support they need
f) Face-to-face communication is the most effective and efficient method of conveying information
g) Working software or solutions as the primary measure of progress
h) Sustainable development, ensuring a constant speed
i) Constant attention to good design and technical excellence
j) Eliminating waste
k) Self-organising teams with the power to make decisions
i) Regular reflection on ways to become more effective and adjusting behaviour accordingly
Different Agile Project Management techniques?
This PM methodology is not a one-size-fits-all approach. It encompasses various methodologies, each with its own set of practices and frameworks. These methodologies provide teams with guidelines and structures to effectively plan, execute, and deliver projects using Agile principles. The following are some popular methodologies:
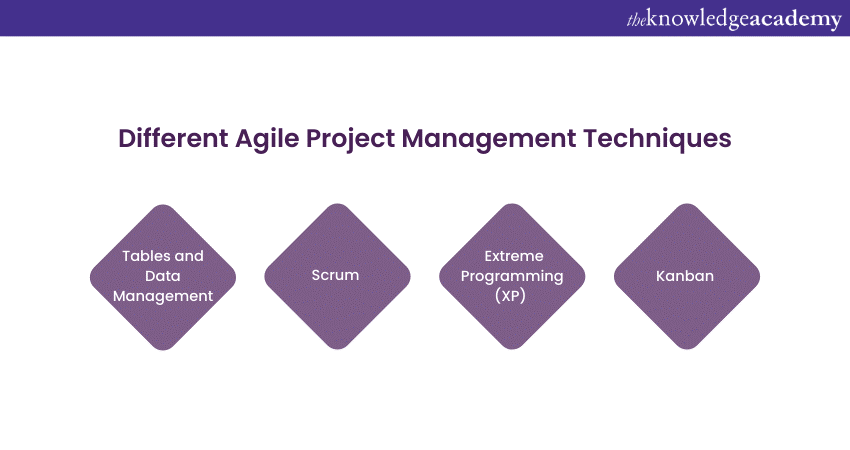
Scrum
Scrum is one of the most widely adopted methodologies. It focuses on delivering value incrementally through short iterations called sprints. The Scrum framework consists of predefined roles, such as Scrum Master, Product Owner, and Development Team. It also involves specific ceremonies like Daily Stand-ups, Sprint Planning, Sprint Review, and Sprint Retrospective.
Kanban
Kanban is a visual Agile methodology that emphasises workflow visualisation and limiting Work In Progress (WIP). Kanban provides a visual representation of the project’s status using Kanban Boards, which represents the workflow, with tasks moving from one column to another as work progresses. Therefore, it promotes flexibility and encourages teams to focus on completing existing work before starting new tasks.
Lean
Lean manufacturing principles inspire this methodology and focus on eliminating waste and maximising customer value. Lean emphasises continuous improvement, just-in-time delivery, and value stream mapping.
It also encourages teams to identify and eliminate non-value-added activities, streamline processes, and improve efficiency. As a result, teams can deliver projects faster, minimise resource waste, and enhance overall outcomes.
Extreme Programming (XP)
Extreme Programming (XP) is another Agile methodology emphasising close collaboration, continuous feedback, and high-quality software development practices. It incorporates practices such as test-driven development, pair programming, frequent releases, and continuous integration.
Further, XP fosters a strong customer focus, promotes team communication, and ensures the delivery of high-quality software products through rigorous testing and refactoring.
These are just a few examples of Agile Project Management. Each methodology has its strengths and suitability for different project scenarios. Choosing the right methodology based on the project’s characteristics, team dynamics, and organisational context is important.
Leap Agile excellence and accelerate your career growth. Join our Agile Training today!
Implementing Agile in your organisation
Implementing Agile across organisations requires a systematic approach to ensure a successful transition. The implementation process typically involves several key phases, each with its own set of activities and objectives. So, let’s explore the various phases of Agile PM implementation:
Phase 1: Assessment and planning
In this initial phase, the Agile Coach and teams require to do the following:
a) Assessing organisation's readiness for Agile adoption
b) Evaluating factors, including organisational structure, culture, and existing PM practices.
c) Identifying the project(s) suitability for Agile methodologies and defining the desired outcomes.
d) Developing a comprehensive implementation plan that outlines the goals, timelines, and resources required for the Agile Transformation.
Phase 2: Education and training
Education and training play a vital role in Agile Implementation. It involves the following:
a) Providing training sessions and workshops to all relevant stakeholders, including Project Managers, team members, and executives.
b) Educating them about Agile principles, methodologies, and the benefits of adopting the methodology.
c) Training regarding Agile roles and responsibilities, its ceremonies, and tools and techniques.
Phase 3: Pilot project execution
Next is the execution phase, where the strategies made in previous phases are implemented. This phase involves:
a) Selecting a small-scale pilot project to test Agile practices in a real-world scenario
b) Implementing Agile principles, frameworks, and practices in the pilot project
c) Allowing teams to gain hands-on experience and identify areas for improvement
d) Monitoring the progress of the pilot project closely and collecting feedback from the team
Phase 4: Scaling Agile
Once the pilot project is successful, it’s time to scale Agile Project Management across the organisation. It means that the teams engage in the following:
a) Identifying other projects or teams that can benefit from Agile methodologies and gradually introducing Agile practices to them
b) Providing support and guidance to these teams during the transition, ensuring they understand the Agile principles
c) Adapting Agile practices to specific projects
d) Encouraging collaboration, knowledge sharing, and continuous learning across teams
Phase 5: Continuous improvement and adaptation
This PM methodology is an iterative and adaptive approach. This phase focuses on continuous improvement and adaptation. This involves:
a) Conducting regular retrospectives and feedback sessions to evaluate the effectiveness of Agile practices
b) Identifying areas for refinement
c) Encouraging teams to share lessons learned and best practices
d) Emphasising the importance of embracing change
e) Experimenting with new approaches
f) Promoting a culture of improvement and continuous learning
Advantages of Agile Project Management
Agile Project Management approach offers several advantages, such as:
--alt= “What is Agile Project Management? Understanding the Fundamentals”--
(Image suggestion) : Add
in centre. Add “Bold Pointers”- ALL.
a) Greater freedom: Agile Project Management allows designers to focus on their strengths when working on models.
b) Efficient use of resources: This approach enables swift deployment with minimal waste, making the most available resources.
c) Greater adaptability and flexibility: Developers can easily adjust to new requirements and make necessary changes.
d) Quick detection of issues: This allows for prompt resolution of problems and better management of projects.
e) Improved collaboration with users: Agile Project Management promotes collaboration, resulting in products that more effectively meet their needs.
f) Distinctions from other Project Management approaches: Unlike traditional methods like Waterfall, Agile Project Management does not require clearly defined goals and processes at the beginning of development.
Learn how to implement Agile practices with our Certified Professional In Agile Project Management (CPAPM) Course.
Limitations of Agile Project Management
Agile Project Management has certain advantages. However, there are some potential drawbacks to consider, such as:
a) Inconsistent results: As there are minimal predefined courses of action at the start of a project, it can sometimes go off track.
b) Difficulties in measuring progress: Off-track projects may lead to less predictable outcomes, making it harder to measure progress.
c) Time constraints: Agile Management relies on making quick decisions. Therefore, it may only be suitable for organisations that take a short time to analyse issues.
d) Communication challenges: Collaboration between teams or end-users must continuously create the best possible product. This can pose communication challenges.
Agile Project Manager roles and responsibilities
Agile Project Manager’s roles and responsibilities include the following:
a) Assistance: The Agile Project Manager assists the team in achieving quality performance, holding teams accountable for their work, removing obstacles, and mentoring less experienced team members.
b) Defined scope of projects: The Agile Project Manager establishes the project’s schedule and scope while balancing this with timely and regular value deliveries and organising and leading working and project status meetings.
c) Delivery: The Agile Project Manager is responsible for providing outstanding business value projects to the users.
d) Extended Support: The Agile Project Manager supports the product owner in managing communications with stakeholders, managing customer expectations for deliverables, and implementing an effective project governance system.
e) Teamwork: The Agile Project Manager empowers the team through team-building techniques, ensuring each team member makes a meaningful contribution and is fully engaged in the project.
Agile vs traditional Project Management
Let us look at some differences between these management approaches:
|
Agile Project Management |
Traditional Project Management |
|
The development approach is iterative and incremental |
The development approach is sequential and linear |
|
Flexibility and adaptability are of significance |
Planning and execution according to a predefined plan is of significance |
|
The primary focus is on customer satisfaction |
Delivering defined project goals and objectives is prioritised |
|
Project completion is in sprints or iterations. |
Project completion is in defined phases. |
|
Changes and improvements throughout the project are encouraged |
Strict process for change management with limited scope for change once a phase is completed. |
|
Involves high customer involvement, and customer collaboration is continuous. |
Customer involvement is limited after initial project requirements gathering. |
Conclusion
Agile Project Management has revolutionised the way projects are executed, delivering numerous benefits to organisations across various industries. By embracing Agile principles and implementing its methodologies, organisations can gain a competitive edge, deliver high-quality products and services, and foster a culture of continuous learning and improvement.
Propel your Project Management career forward with our comprehensive Agile Project Management Foundation & Practitioner (AgilePM®) Course.
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming Project Management Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Agile Project Management Foundation (AgilePM®)
Agile Project Management Foundation (AgilePM®)
Mon 13th May 2024
Mon 20th May 2024
Tue 28th May 2024
Mon 3rd Jun 2024
Mon 10th Jun 2024
Sat 15th Jun 2024
Mon 17th Jun 2024
Mon 24th Jun 2024
Mon 1st Jul 2024
Mon 8th Jul 2024
Sat 13th Jul 2024
Mon 15th Jul 2024
Mon 22nd Jul 2024
Mon 29th Jul 2024
Sat 3rd Aug 2024
Mon 5th Aug 2024
Mon 12th Aug 2024
Mon 19th Aug 2024
Tue 27th Aug 2024
Mon 2nd Sep 2024
Sat 7th Sep 2024
Mon 9th Sep 2024
Mon 16th Sep 2024
Mon 23rd Sep 2024
Mon 30th Sep 2024
Sat 5th Oct 2024
Mon 7th Oct 2024
Mon 14th Oct 2024
Mon 21st Oct 2024
Mon 28th Oct 2024
Sat 2nd Nov 2024
Mon 4th Nov 2024
Mon 11th Nov 2024
Mon 18th Nov 2024
Mon 25th Nov 2024
Mon 2nd Dec 2024
Mon 9th Dec 2024
Sat 14th Dec 2024
Mon 16th Dec 2024
Mon 6th Jan 2025
Mon 13th Jan 2025
Mon 20th Jan 2025
Mon 27th Jan 2025
Mon 3rd Feb 2025
Mon 10th Feb 2025
Mon 17th Feb 2025
Mon 24th Feb 2025
Mon 3rd Mar 2025
Mon 10th Mar 2025
Mon 17th Mar 2025
Mon 24th Mar 2025
Mon 31st Mar 2025
Mon 7th Apr 2025
Mon 14th Apr 2025
Tue 22nd Apr 2025
Mon 28th Apr 2025
Tue 6th May 2025
Mon 12th May 2025
Mon 19th May 2025
Tue 27th May 2025
Mon 2nd Jun 2025
Mon 9th Jun 2025
Mon 16th Jun 2025
Mon 23rd Jun 2025
Mon 30th Jun 2025
Mon 7th Jul 2025
Mon 14th Jul 2025
Mon 21st Jul 2025
Mon 28th Jul 2025
Mon 4th Aug 2025
Mon 11th Aug 2025
Mon 18th Aug 2025
Mon 25th Aug 2025
Mon 1st Sep 2025
Mon 8th Sep 2025
Mon 15th Sep 2025
Mon 22nd Sep 2025
Mon 29th Sep 2025
Mon 6th Oct 2025
Mon 13th Oct 2025
Mon 20th Oct 2025
Mon 27th Oct 2025
Mon 3rd Nov 2025
Mon 10th Nov 2025
Mon 17th Nov 2025
Mon 24th Nov 2025
Mon 1st Dec 2025
Mon 8th Dec 2025
Mon 15th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


