We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
A Network is a system of interconnected devices that can communicate and share data over a medium, such as a cable, a wireless signal, or a satellite. Networks are essential for various purposes, such as communication, collaboration, education, entertainment, and business. However, there are multiple Types of Networks and not all are the same; they differ in size, scope, topology, architecture, functionality and the protocols they use.
If you want to learn about the different Types of Networks and how they work, you have come to the right place. In this blog, you will learn about various Types of Networks in detail and provide you with some examples and applications of each type. Read ahead to learn more!
Table of Contents
1) What is a Network?
2) 10 Types of Networks
a) Local Area Network (LAN)
b) Personal Area Network (PAN)
c) Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN)
d) Wide Area Network (WAN)
e) Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
f) Campus Area Network (CAN)
g) Virtual Private Network (VPN)
h) Enterprise Private Network (EPN)
i) Storage Area Network (SAN)
j) Passive Optical Local Area Network (POLAN)
3) Conclusion
What is a Network?
A Computer Network constitutes a cohesive ensemble of interconnected computers and peripheral devices, facilitating the seamless exchange of data and hardware resources. Its primary function is fostering efficient communication, allowing devices within the network to share information and resources. This collaborative framework enhances storage efficiency by enabling centralised data storage and retrieval.
Information sharing across a Computer Network streamlines communication and fosters collaboration among users. Resources, including printers, scanners, and storage devices, become easily accessible, optimising their utilisation. Moreover, Computer Networks promote timely communication, ensuring that information reaches its destination promptly.
10 Types of Networks
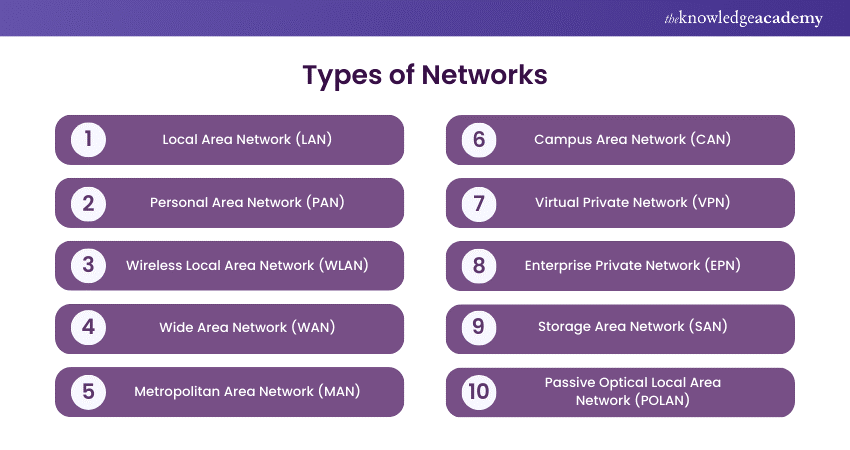
Here are the 10 most common Computer Network Types used in the industry:
1) Local Area Network (LAN)
A Local Area Network (LAN) connects devices and computers within a limited geographic area, such as a home, office, or campus. Utilising Ethernet cables or wireless technology, LANs facilitate fast data transfer and resource sharing. They are fundamental for file sharing, printing, and collaborative projects in office environments, fostering a cohesive digital environment. The following are some features of this Type of Network:
1) High data transfer rates: LANs provide fast data transfer rates, ensuring quick communication between connected devices.
2) Resource sharing: LANs enable sharing of resources such as printers, files, and applications among connected devices.
3) Scalability: LANs can quickly scale to accommodate additional devices and users within the defined geographic area.
4) Low cost: LAN implementations are cost-effective and suitable for small to medium-sized environments.
5) Easy installation: LANs are relatively easy to install and set up, contributing to their widespread adoption in various settings.
2) Personal Area Network (PAN)
A Personal Area Network links devices within an individual's workspace, typically covering a range of a few meters. PANs often use wireless technologies like Bluetooth or USB connections, enabling seamless communication between personal devices such as smartphones, laptops, and wearable gadgets. The following are some features of this Type of Network:
a) Wireless connectivity: PANs often rely on wireless technologies like Bluetooth, providing convenient, cable-free connections.
b) Device interconnectivity: PANs seamlessly connect personal devices, fostering an integrated digital ecosystem.
c) Mobility: PANs support mobility, allowing users to move within the network range while maintaining connectivity.
d) Low power consumption: Many PAN devices operate with low power consumption, extending battery life for portable devices.
e) Simple configuration: PANs typically have straightforward setup processes, enhancing user accessibility.
Unlock the realm of VPN with our VPN Training – Sign up today!
3) Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN)
A Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) employs wireless technology, allowing devices to connect without physical cables. This flexibility enhances mobility, making WLANs prevalent in homes, offices, and public spaces. Wi-Fi routers enable multiple devices to access the internet concurrently, emphasising convenience and eliminating the need for extensive cabling. The following are some features of this Type of Network:
a) Flexibility and mobility: WLANs offer flexibility and mobility, allowing devices to connect without physical constraints.
b) Easy expansion: WLANs can be easily expanded by adding access points to accommodate growing device numbers.
c) Remote access: WLANs enable remote access to the network, facilitating connectivity from different locations.
d) Scalability: WLANs can scale to support many devices, making them suitable for diverse environments.
e) Cost-effective infrastructure: WLANs reduce the need for extensive cabling, resulting in cost-effective infrastructure.
4) Wide Area Network (WAN)
A Wide Area Network (WAN) spans large geographical areas, connecting Local Area Networks (LANs) across cities, countries, or continents. To enable global communication, WANs use various technologies, including public and private networks. They are crucial for multinational corporations, providing a framework for efficient data transfer and communication between distant locations. The following are some features of this Network Type:
a) Global connectivity: WANs provide international connectivity, linking geographically dispersed locations.
b) Versatility: WANs support various communication technologies, including leased lines, satellite links, and MPLS.
c) Centralised management: WANs often have centralised management, allowing efficient oversight of network resources.
d) Wide range of services: WANs offer a broad range of services, including data transfer, voice communication, and multimedia streaming.
e) Reliability: WANs are designed to ensure consistent connectivity across vast distances.
Explore the skills needed for CloudFare with our CloudFare Training – Sign up today!
5) Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
A Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) covers a city or a large campus, serving as an intermediary between Local Area Networks (LANs) and Wide Area Networks (WANs). MANs offer high-speed connectivity within a specific geographic region, supporting organisations with multiple offices or campuses nearby. The following are some features of this Network Type:
a) High-speed connectivity: MANs deliver high-speed connectivity within a city or large campus, enhancing data transfer efficiency.
b) Interconnectivity: MANs interconnect multiple LANs, fostering seamless communication among organisational units.
c) Centralised management: MANs often have centralised management, simplifying the oversight of network resources.
d) Scalability: MANs can scale to accommodate the network requirements of growing urban areas or expanding campuses.
e) Cost-effective solutions: MANs provide cost-effective solutions for organisations operating within a specific metropolitan region.
6) Campus Area Network (CAN)
A Campus Area Network (CAN) interconnects multiple Local Area Networks (LANs) within a specific campus or enterprise. CANs facilitate efficient data exchange among different departments, promoting seamless communication and resource sharing within the campus environment. The following are some features of this Type of Network:
a) Interdepartmental communication: CANs facilitate efficient communication and resource sharing among different departments within a campus.
b) Resource optimisation: CANs optimise resource usage, ensuring that computing and storage resources are efficiently distributed.
c) Scalability: CANs can scale to accommodate the evolving needs of a growing campus environment.
d) Security: CANs often incorporate security measures to protect sensitive data and ensure network integrity.
e) High-speed connectivity: CANs deliver high-speed connectivity within the campus, supporting data-intensive applications.
7) Virtual Private Network (VPN)
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) creates a secure, encrypted network over the internet, enabling secure remote access to a private network. VPNs are essential for remote work, allowing users to connect to their organisation's network securely from any location with internet access. The following are some features of VPN:
a) Secure data transmission: VPNs use encryption protocols to secure data transmission over public networks.
b) Remote access: VPNs enable secure remote access to an organisation's private network, supporting telecommuting and mobile work.
c) Cost-effective connectivity: VPNs provide a cost-effective alternative to dedicated private networks, especially for remote locations.
d) Privacy: VPNs ensure privacy by masking the user's IP address, enhancing online anonymity.
e) Global connectivity: VPNs offer global connectivity, allowing users to access the private network from different locations.
Stay at the forefront of IT skills and fundamentals with our IT Fundamentals Training – Join today!
8) Enterprise Private Network (EPN)
An Enterprise Private Network (EPN) caters to a specific enterprise, linking its branches, offices, or facilities. EPNs facilitate streamlined communication and resource sharing among different locations within a single organisation, promoting efficiency and cohesion. The following are some features of EPN:
a) Interconnected branches: EPNs interconnect various branches, facilitating seamless communication and resource sharing.
b) Centralised administration: EPNs often have centralised administration, ensuring uniformity in network management across different locations.
c) Scalability: EPNs can scale to support additional branches or facilities as an organisation expands.
d) Secure communication: EPNs prioritise security, implementing measures to protect sensitive data and ensure safe communication.
e) Enhanced collaboration: EPNs improve branch collaboration, supporting joint projects and efficient communication.
9) Storage Area Network (SAN)
A Storage Area Network (SAN) is dedicated to efficient data storage and retrieval. It separates storage resources from the main network, providing a centralised and scalable solution for managing and accessing large volumes of data. SANs are crucial for enterprises with extensive storage needs, enhancing data management and accessibility. The following are some features of this Type of Network:
a) Centralised storage: SANs provide centralised storage solutions, enabling efficient management and data accessibility.
b) High performance: SANs offer high-speed data transfer, supporting data-intensive applications and large-scale storage needs.
c) Scalability: SANs can scale to accommodate growing storage requirements, making them suitable for enterprises with expanding data volumes.
d) Data protection: SANs often include data protection features such as backup and recovery mechanisms to safeguard critical information.
e) Simplified management: SANs simplify data management by centralising storage resources and streamlining administration.
10) Passive Optical Local Area Network (POLAN)
A Passive Optical Local Area Network (POLAN) employs passive optical technology for high-speed data transmission within a local area. POLANs use fibre optics to enhance connectivity and bandwidth, making them suitable for environments where high-performance data transfer is critical, such as businesses, campuses, or extensive facilities. The following are some features of this Type of Network:
a) High bandwidth: POLANs utilise passive optical technology, providing high-bandwidth connectivity for data-intensive applications.
b) Scalability: POLANs can scale to support increased bandwidth requirements, making them adaptable to growing network demands.
c) Reduced cable complexity: POLANs reduce cable complexity by leveraging fibre optics, simplifying network infrastructure.
d) Energy efficiency: POLANs often boast energy-efficient designs, contributing to reduced power consumption and operational costs.
e) Future-proofing: POLANs incorporate advanced optical technology, positioning them as a future-proof solution for evolving network requirements.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the diverse Types of Networks is crucial in navigating the digital realm. From LANs to WANs, each network type plays a vital role. Embrace the knowledge gained and confidently traverse the dynamic world of connectivity, armed with insights into the various types of networks.
Gain insights into Networking with our Introduction to Networking Training – Join today!
Frequently Asked Questions

A Local Area Network (LAN) is confined to a limited geographic area, like an office, while a Wide Area Network (WAN) spans larger distances, connecting LANs across cities or countries. LANs are ideal for localised communication, while WANs facilitate broader connectivity on a global scale.

Hybrid Networks integrate diverse network types, merging Local Area Networks (LANs), Wide Area Networks (WANs), or cloud-based networks. This synergy optimises performance, balancing the efficiency of LANs for local tasks and the expansive reach of WANs for broader connectivity, creating a versatile and robust network infrastructure.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various IT Support and Solution Trainings, including Introduction to Networking Training and Security Management, Planning and Asset Protection Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Importance of CCNA.
Our IT Infrastructure and Networking blogs covers a range of topics related to Computer Networks, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Networking skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming IT Infrastructure & Networking Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Introduction to Networking Training
Introduction to Networking Training
Fri 14th Jun 2024
Fri 12th Jul 2024
Fri 30th Aug 2024
Fri 13th Sep 2024
Fri 18th Oct 2024
Fri 29th Nov 2024
Fri 13th Dec 2024







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


