We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
The financial landscape has seen a massive revolution with the emergence of Cryptocurrency. As with any groundbreaking technology, understanding the Pros and Cons of Cryptocurrency is essential for individuals, businesses, and regulators alike.
According to a 2023 Statista report, the value of Cryptocurrency is projected to cross 30 billion GBP, and the user volume is expected to cross 950 million GBP by 2027. Cryptocurrencies offer incredible opportunities, and they also present their challenges. Explore this blog on the Pros and Cons of Cryptocurrency to learn about its benefits & risks. Find its potential for financial growth while viewing its volatility.
Table of Contents
1) A brief overview of Cryptocurrency
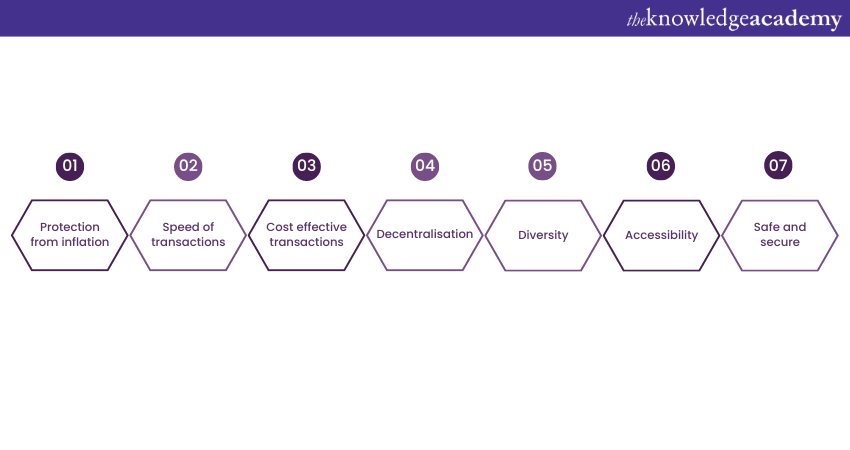
2) Advantages of Cryptocurrency
a) Protection from inflation
b) Speed of transactions
c) Cost effective transactions
d) Decentralisation
e) Diversity
f) Accessibility
g) Safe and secure
h) Transparency
i) Effortless currency exchange
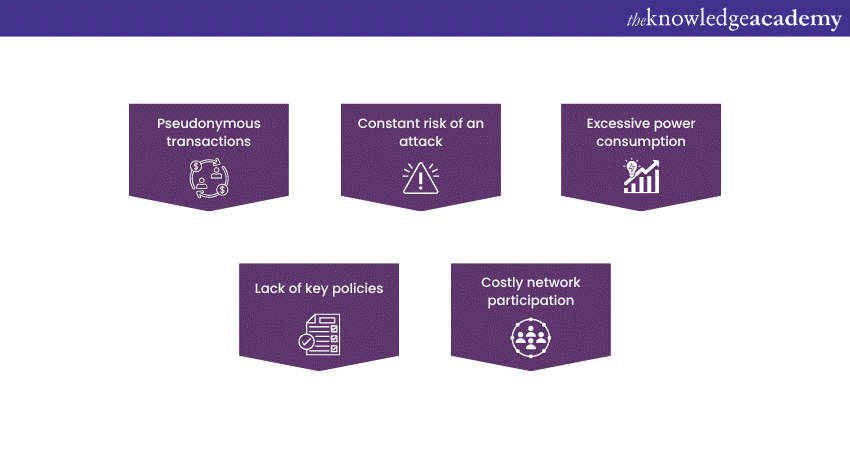
3) Disadvantages of Cryptocurrency
a) Pseudonymous transactions
b) Constant risk of an attack
c) Excessive power consumption
d) Lack of key policies
e) Costly network participation
4) Conclusion
A brief overview of Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrency represents a groundbreaking form of digital currency that operates independently from a central bank. Utilising blockchain technology provides a secure and transparent way to conduct transactions.
Additionally, each transaction is recorded in a public ledger called a blockchain, which is virtually impossible to alter or forge. Originating with the creation of Bitcoin in 2008, the world of Cryptocurrency has expanded to include thousands of different digital currencies. The decentralised nature of Cryptocurrency enables global accessibility, generally with lower transaction fees compared to traditional banking systems.
However, it also brings challenges, such as price volatility and regulatory concerns. Cryptocurrencies are seen by many as the future of finance, but they remain a complex and evolving field that requires understanding and caution.

Advantages of Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrency offers pros such as enhanced security, global accessibility, transparency, and low transaction costs. However, it is not without cons, including significant price volatility, a lack of regulation, technical barriers for some users, and potential misuse. These factors are the Pros and Cons of Cryptocurrency that collectively shape the risk and reward profile of digital currency investments.
Here are the advantages of Cryptocurrency described in detail as shown below:
Protection from inflation
Protection from inflation is a key advantage of certain assets, including some cryptocurrencies. Inflation erodes the value of money, meaning that over time, a given amount of money will purchase fewer goods and services. Assets that are resistant to inflation maintain their value even as the general price level rises.
Additionally, Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin have a capped supply, meaning that there's a maximum number of coins that can ever exist. This scarcity can create a hedge against inflation, as the value is not diluted by an ever-increasing supply, unlike traditional fiat currencies, where governments can print more money, leading to inflation.
Speed of transactions
The speed of transactions refers to how quickly a financial operation, such as a payment or transfer, can be completed. In traditional banking, international transactions might take several days due to various checks and processes.
Now with cryptocurrencies, the speed of transactions is often remarkably faster. Utilising decentralised Blockchain technology, cryptocurrencies can process transactions in minutes or even seconds. This rapidity enables immediate global transfers without the need for intermediaries or prolonged waiting periods.
However, the speed might vary depending on the Cryptocurrency used and network congestion at the time of the transaction, making the actual timeframes subject to fluctuation.
Cost-effective transactions
Cost-effective transactions refer to the financial efficiency achieved by reducing or minimising fees associated with transferring money or making payments. Traditional banking systems often involve multiple intermediaries, each adding their own fees, making the overall transaction expensive.
Furthermore, Cryptocurrencies, by contrast, offer a decentralised platform, eliminating the need for many middlemen. This can significantly reduce transaction costs, making them more affordable for both individuals and businesses.
Such cost-effective transactions are especially beneficial for international transfers, where traditional banking fees can be exorbitant. By streamlining the process and cutting unnecessary costs, cryptocurrencies enhance financial accessibility and efficiency.
Decentralisation
Decentralisation is a core principle in various systems, particularly in the context of cryptocurrencies. It means that no single entity, like a government or central bank, has control over the entire network. Instead, control is distributed among multiple participants or nodes.
Now, in a decentralised system, each transaction is verified by a network of nodes rather than a central authority. This ensures that no single point of failure exists, enhancing the security and resilience of the system.
Moreover, decentralisation promotes transparency accessibility and often reduces costs, but it also brings challenges, including potential coordination difficulties and regulatory complexities.
Acquire a solid understanding of how to trade Cryptocurrency by signing up for the Cryptocurrency Trading Training now!
Diversity
Diversity refers to the wide variety of distinct characteristics, ideas, or elements within a group or system. In a societal context, diversity often pertains to the inclusion and acceptance of individuals from different ethnicities, genders, ages, religions, disabilities, and socioeconomic backgrounds.
Additionally, embracing diversity leads to a richer, more creative, and empathetic environment, as varied perspectives contribute to innovation and problem-solving. In the world of investments or portfolio management, diversity can mean holding a mix of different assets reducing risk through spreading exposure. Diversity, whether in society or finance, represents strength, flexibility, and resilience, fostering growth and harmony.
Accessibility
Accessibility refers to the convenience with which people can access and use a service, product, or information, regardless of any physical, financial, or technical barriers they may face. In the context of technology and online platforms, accessibility often involves creating interfaces that can be used by everyone, including those with disabilities.
Now for cryptocurrencies, accessibility means that anyone having an internet connection and a digital wallet can participate in transactions, without the need for a traditional banking relationship.
More importantly, this can empower individuals in remote or underserved areas, allowing them to engage with the global economy in ways that were previously impossible. Accessibility fosters inclusivity and equal opportunity.
Safe and secure
Safety and security refer to the protection of information, assets, or systems against potential threats and unauthorised access. In the context of technology and finance, including cryptocurrencies, it embodies robust measures to guard against hacking, fraud, or misuse.
Additionally, utilising advanced cryptographic techniques, many cryptocurrencies offer high levels of security. The underlying blockchain technology ensures that once a transaction is recorded, it cannot be altered, providing a permanent and tamper-proof record.
However, safety and security are often reliant on user practices, such as keeping private keys confidential. While technologies can provide robust protection, user awareness and responsible practices are vital for maintaining a safe and secure environment.
Transparency
Transparency refers to the quality of being clear, open, and honest in all types of communication, dealings, or operations. In a business or financial context, transparency means providing complete, accurate, and timely information to all stakeholders, allowing them to make informed decisions.
Now, in the world of Cryptocurrency, transparency is facilitated through the use of blockchain technology, where all transactions are recorded on a public ledger. This ledger can be viewed by anyone, ensuring that activities are openly documented and verifiable.
More importantly, transparency builds trust, as it holds parties accountable and helps prevent fraudulent or unethical behaviour, fostering confidence in the system or organisation.
Privacy
Privacy refers to the rights of individuals that allow them to keep their personal information and activities confidential and secure from unauthorised access or disclosure. In today's digital age, privacy is a growing concern, especially in financial transactions.
Furthermore, in the context of cryptocurrencies, privacy is a double-edged sword. On one hand, transactions are recorded on a public ledger, ensuring transparency. On the other hand, the identities of the parties involved are often obscured and represented only by cryptographic addresses.
This, more importantly, ensures a level of anonymity, allowing users to conduct transactions without revealing personal details. Privacy in cryptocurrencies is valued by many but also raises concerns regarding the potential misuse of illicit activities.
Effortless currency exchange
Effortless currency exchange refers to the seamless and easy conversion of one currency into another. In traditional banking, currency exchange might involve complex procedures, fees, and sometimes delays.
Additionally, with cryptocurrencies, the process can be notably streamlined. Many platforms and digital wallets allow users to effortlessly exchange various cryptocurrencies or convert them into fiat currencies in real-time. This can be done from anywhere in the world with just a few clicks, often at competitive exchange rates.
Moreover, the ease and efficiency of Cryptocurrency exchange make it an attractive option for travellers, international businesses, and anyone needing to handle multiple currencies with minimal fuss.
Gain more knowledge about blockchain technology by signing up for the Ethereum Developer Training now!
Disadvantages of Cryptocurrency
The cons of Cryptocurrency include its significant price volatility, making investments risky. Lack of regulation can lead to potential fraud or misuse. The complexity of the technology may deter some users, and energy consumption in mining some cryptocurrencies raises environmental concerns. These factors contribute to a more cautious approach by some investors and regulators.
Here are the disadvantages of Cryptocurrency described in detail as shown below:
Pseudonymous transactions
Pseudonymous transactions refer to a method where parties are identified by pseudonyms rather than personal information. In the context of cryptocurrencies, users transact with alphanumeric addresses not directly linked to their real-world identities.
Now, this provides a level of privacy and anonymity, yet all transactions are still recorded on the public blockchain. While pseudonymous transactions offer privacy benefits, they can also be associated with concerns regarding potential misuse of illicit activities.
Constant risk of an attack
The constant risk of an attack in the context of cryptocurrencies refers to the perpetual threat posed by hackers and malicious entities attempting to exploit vulnerabilities within a system. Even with advanced Cyber-security measures, no system is entirely immune.
Moreover, cyberattacks can lead to the theft of assets, loss of personal information, or even a compromised network. Vigilance, regular updates, and adherence to best practices are essential to mitigate these risks, but the potential for an attack always remains a concern.
Excessive power consumption
Excessive power consumption in Cryptocurrency refers to the enormous amount of energy required by certain mining processes, notably Bitcoin. Mining involves complex calculations requiring significant computational power.
Now, in some instances, the energy consumed can rival that of entire countries. This has raised environmental concerns, particularly if the energy comes from non-renewable sources. Efforts are being made within the industry to reduce this consumption, but it remains a significant issue and a core argument against the widespread adoption of some cryptocurrencies.
Learn about various Cryptocurrencies and deploy private blockchains by signing up for the Blockchain Training Course now!
Lack of key policies
The lack of key policies in Cryptocurrency refers to the absence of standardised regulations and guidelines that govern the usage and trading of digital currencies. This regulatory vacuum can create uncertainty and inconsistency, posing challenges for investors, users, and authorities.
Moreover, the absence of clear policies may lead to unethical practices, fraud, or misuse of cryptocurrencies. It underscores the need for coherent regulations that provide protection while still fostering innovation within the rapidly evolving world of digital currencies.
Costly network participation
Costly network participation in Cryptocurrency refers to the significant investment required to become a miner or operate a full node within certain blockchain networks. The hardware, electricity, and ongoing maintenance can be expensive, especially in competitive mining environments like Bitcoin.
More importantly, these high costs can deter individual participation and lead to the centralisation of mining power in the hands of a few large entities. It's an aspect that challenges the ideal of decentralised control and inclusivity within some Cryptocurrency systems.
Conclusion
The Pros and Cons of Cryptocurrency paint a complex picture of a revolutionary financial system. While offering benefits like decentralisation, security, and accessibility, it also poses challenges including volatility, risk of attack, and regulatory ambiguity. A thoughtful consideration of the advantages and disadvantages is essential for anyone engaging in the dynamic world of digital currency.
Learn about how bitcoins work and their applications, by signing up for our Bitcoin and Cryptocurrency course now!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming Advanced Technology Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Cryptocurrency Trading Training
Cryptocurrency Trading Training
Fri 10th May 2024
Fri 9th Aug 2024
Fri 8th Nov 2024







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


