We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

ISO 14001 Version 2004 vs 2015: This comparison sheds light on the changes and improvements in Environmental Management practices between the two versions. ISO 14001:2004 and ISO 14001:2015 are two versions of the international standard for Environmental Management Systems (EMS). Both the 2004 and 2015 versions help organisations improve environmental performance, compliance, stakeholder engagement, and sustainable development.
According to NSAI, ISO 14001 has been widely embraced as the preferred model for Environmental Management by industrial companies, service organisations, utilities, and public bodies in more than 150 countries globally emphasises the integration of ISO 14001 Risks and Opportunities. By adopting the updated version, organisations can enhance environmental performance and contribute to a greener future. Read this blog to uncover the differences between ISO 14001 Version 2004 vs 2015 and their impact on optimising your organisation's Environmental Management practices.
Table of Contents
1) Overview of 14001:2004
2) Overview of ISO 14001:2015
3) Key Differences between ISO 14001:2004 and 2015
4) Similarities between ISO 14001 Version 2004 and 2015
5) ISO 14001 2004 benefits
6) ISO 14001 2015 benefits
7) Conclusion
Overview of ISO 14001:2004
ISO 14001:2004 is a globally recognised standard for Environmental Management. It assists organisations in effectively managing their environmental responsibilities. This version focuses on compliance with regulations and minimising negative impacts. By implementing ISO 14001:2004, organisations can improve their environmental performance, reduce risks, and demonstrate their commitment to sustainability.
It offers a framework for identifying and controlling environmental aspects, resulting in better resource management and a smaller environmental footprint with ISO 14001 Document Control. Compliance with ISO 14001:2004 enables organisations to enhance their reputation, gain a competitive edge, and contribute to a greener future.

Overview of ISO 14001:2015
ISO 14001:2015 takes a comprehensive approach, considering the entire ISO 14001 Life Cycle of products and services. It helps organisations identify ways to be more sustainable, like using resources efficiently and preventing pollution. The standard emphasises leadership involvement and engaging stakeholders, which means getting everyone on board with environmental responsibility.
ISO 14001:2015 is designed to be easily integrated with other management system standards. By adopting it, organisations can improve their environmental performance, reduce risks, and show their dedication to sustainable practices.
Understand the ISO 14001 structure efficiently with our ISO 14001 Internal Auditor Course. Join now!
Key Differences between ISO 14001:2004 and 2015
ISO 14001 helps organisations identify and manage environmental impacts, comply with regulations, ISO 14001, including the ISO 14001 Context of the organisation enhance performance, and promote sustainability with the aid of ISO 14001 Software to streamline and optimize environmental management processes.
ISO 14001:2004 was the previous version, while ISO 14001:2015 introduced significant updates to align with current environmental challenges and practices. Exploring the following differences between these versions will shed light on the transition and enhanced features of ISO 14001:2015: ensuring effective ISO 14001 Compliance
Organisational context
ISO 14001:2004:
a) Focuses on understanding the organisation's environmental aspects and impacts.
b) Does not explicitly address the organisational context.
ISO 14001:2015:
a) Requires organisations to identify internal and external issues that impact their Environmental Management.
b) Considers the organisational context, including its social, cultural, and economic aspects.
Needs and expectations of interested parties
ISO 14001:2004:
a) Does not explicitly emphasise identifying and addressing the needs and expectations of interested parties.
ISO 14001:2015:
a) Requires organisations to identify and understand the needs and expectations of interested parties.
b) Encourages organisations to engage with stakeholders and address their concerns.
Leadership and commitment
ISO 14001:2004:
a) Focuses on the establishment of an Environmental Management system without specific emphasis on leadership and commitment.
ISO 14001:2015:
a) Emphasises leadership engagement and commitment to Environmental Management.
b) Requires top management to demonstrate leadership in establishing and integrating Environmental Management practices.
Life cycle perspective
ISO 14001:2004:
a) Does not explicitly require organisations to consider the entire life cycle of products and services.
ISO 14001:2015:
a) Encourages organisations to adopt a life cycle perspective when identifying environmental aspects and impacts.
b) Considers all stages of a product or service, from raw material acquisition to end-of-life disposal.
Environmental performance
ISO 14001:2004:
a) Focuses on monitoring and measuring environmental performance without specific guidance on improvement.
ISO 14001:2015:
a) Requires organisations to set objectives and targets for improving their environmental performance.
b) Emphasises proactive initiatives to enhance environmental performance and achieve sustainable outcomes.
Communications
ISO 14001:2004:
a) Does not explicitly emphasise communication of environmental performance or engagement with stakeholders.
ISO 14001:2015:
a) Requires organisations to establish a communication process for internal and external stakeholders.
b) Emphasises the importance of transparent and effective communication regarding environmental performance and management efforts.
Similarities between ISO 14001 version 2004 and 2015
While ISO 14001:2015 introduces updates and enhancements, organisations familiar with ISO 14001:2004 will find many similarities when transitioning to the newer version. The similarities include:
a) Both versions focus on establishing an effective system to manage environmental aspects and impacts.
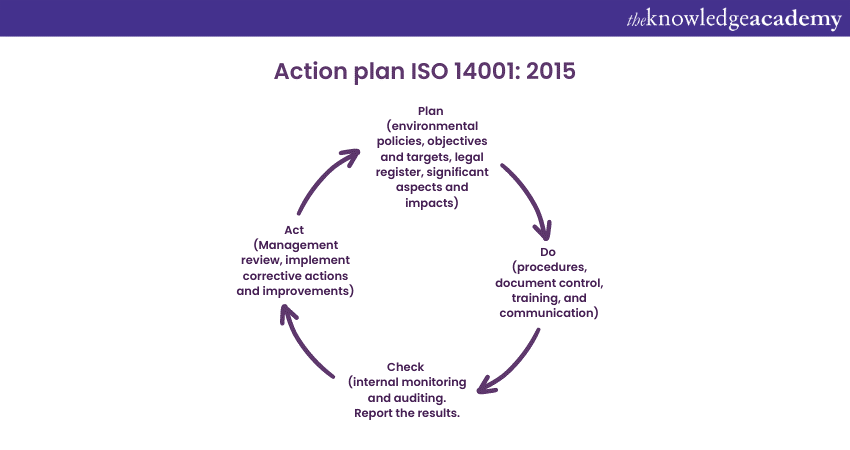
b) Both versions use the Plan-Do-Check-Act cycle for continuous improvement in environmental performance.
c) Both versions require organisations to have an environmental policy showing their commitment to environmental protection and improvement.
d) Both versions emphasise compliance with applicable environmental regulations.
e) Both versions require setting specific goals to improve environmental performance.
f) Both versions emphasise providing training and ensuring employees have the necessary skills for Environmental Management.
g) Both versions require maintaining documented information related to the EMS.
h) Both versions require periodic reviews by top management to assess the EMS's effectiveness.
i) Both versions promote an ongoing commitment to improving environmental performance.
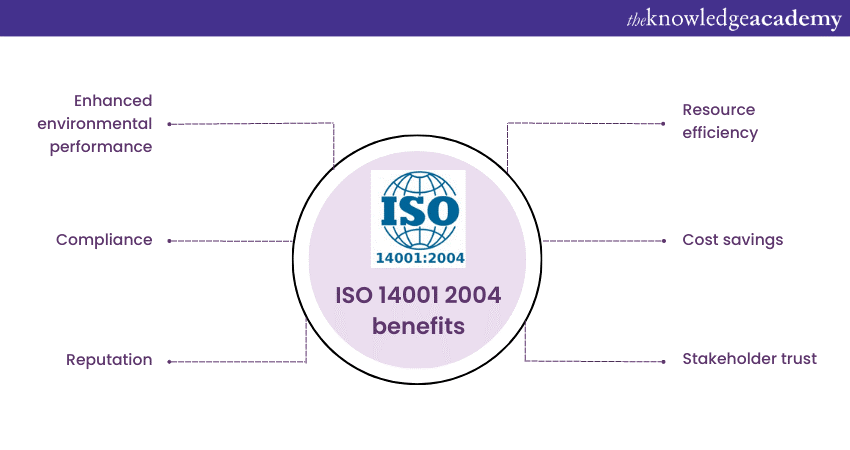
ISO 14001 2004 benefits
ISO 14001:2004 offers several unique benefits for organisations striving to improve their Environmental Management practices. By implementing ISO 14001:2004, organisations can:
a) Enhance environmental performance and minimise their impact on the environment.
b) Improve resource efficiency and reduce waste generation.
c) Comply with environmental regulations and avoid penalties or legal issues.
d) Boost their reputation by demonstrating commitment to environmental responsibility.
e) Gain a competitive edge by meeting customer expectations for sustainable practices.
f) Increase employee engagement and morale by fostering a culture of environmental awareness.
g) Identify and mitigate environmental risks, minimising potential incidents or accidents.
h) Achieve cost savings through improved energy efficiency and waste management.
i) Enhance stakeholder trust and build strong relationships with customers, suppliers, and the community.
j) Foster innovation and creativity in finding sustainable solutions.
Learn the fundamental principles of Environmental Management with our ISO 14001 Lead Implementer Course. Sign up now!
ISO 14001 2015 benefits
ISO 14001:2015 brings a fresh set of unique benefits for organisations committed to Environmental Management and sustainability. By adopting ISO 14001:2015, organisations can:
a) Foster a holistic approach to Environmental Management by considering the overall life cycle of products and services, from procurement to disposal.
b) Improve stakeholder engagement by actively involving interested parties in environmental decision-making processes.
c) Strengthen leadership and commitment to environmental sustainability throughout the organisation, driving a culture of responsibility.
d) Enhance strategic decision-making by aligning Environmental Management with the organisation's overall business objectives.
e) Improve communication and transparency by effectively sharing environmental performance information with internal and external stakeholders.
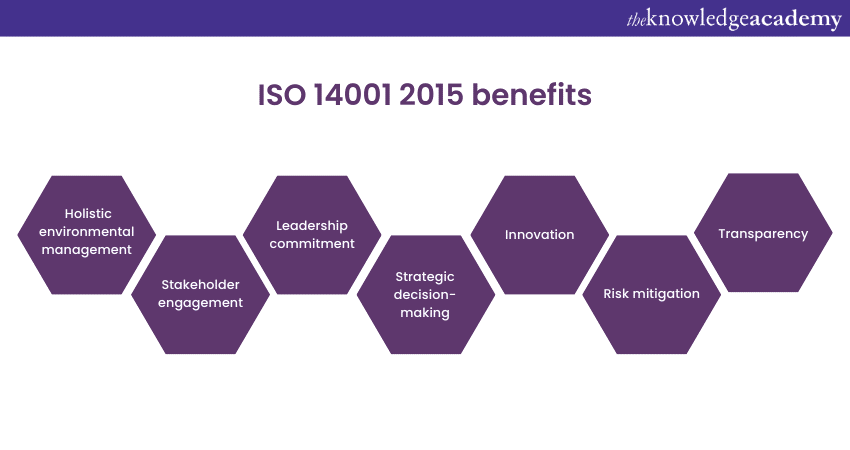
f) Promote innovation and creativity in finding sustainable solutions, encouraging organisations to explore new approaches and technologies.
g) Ensure compliance with environmental regulations and minimise the risk of penalties or legal issues.
h) Drive continual improvement in environmental performance by setting measurable objectives and targets.
i) Enhance reputation and brand value by demonstrating a proactive and forward-thinking approach to environmental responsibility.
Achieve long-term cost savings through resource efficiency, waste reduction, and energy conservation.
Conclusion
We hope this blog gave you an overview of ISO 14001 Version 2004 vs 2015. ISO 14001:2004 and ISO 14001:2015 empower organisations to improve Environmental Management, drive innovation, and demonstrate commitment to sustainability. They offer a competitive edge, engage stakeholders, and contribute to a sustainable future. Adopting ISO 14001 signifies responsibility and drives positive change.
Master our ISO 14001 Training for sustainable Environmental Management. Join now to make a difference!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming Health & Safety Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 ISO 14001 Foundation Certification
ISO 14001 Foundation Certification
Mon 17th Jun 2024
Mon 21st Oct 2024







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


