We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Businesses in various sectors are increasingly acknowledging the importance of reducing their environmental footprint and implementing sustainable measures. However, many individuals continue to face challenges incorporating Environmental Management Systems (EMS) due to unfamiliarity with sustainable methods. Understanding the ISO 14001 Life Cycle can significantly help businesses overcome these challenges and effectively implement sustainable practices.
The ISO 14001 Life Cycle serves as a strong mechanism for promoting positive transformation within a company. By adopting this method, companies can discover chances for enhancement, minimise environmental damage, and improve their overall sustainability initiatives.
Are you prepared to enhance your organisation's environmental responsibility to a higher level? Delve into this blog to explore the ISO 14001 Life Cycle and evaluations. Learn how to integrate sustainability into the core of your operations.
Table of Contents
1) What is Life Cycle Perspective?
2) Why Consider Life Cycle Perspective?
3) Key Phases of the Life Cycle Perspective
4) Benefits of Life Cycle Perspective
5) Implementing the 14001 Life Cycle
6) Conclusion
What is Life Cycle Perspective?
The concept of "Life Cycle Perspective" involves companies aiming for ISO 14001 Certification considering the complete lifecycle of their products or services in efforts to minimise their environmental footprint. This perspective is crucial for developing an effective Environmental Management System, and the use of ISO 14001 Software can greatly assist in managing this process.
Comprehending and using the Life Cycle approach helps firms find chances to reduce waste and improve sustainability during the product's entire lifecycle. Normally, a product or service goes through five stages in its lifecycle, which we will explore in the upcoming sections.
By considering each stage, utilising ISO 14001 Software, and understanding the Context of ISO 14001, companies can develop more comprehensive strategies for reducing their overall environmental impact.

Why Consider Life Cycle Perspective?
Life Cycle perspective means thinking about all the stages it goes through, from being made to being used and eventually disposed of. This is important because some of the ways a product or service can harm the environment occur during this period. By looking at the whole Life Cycle, a company can figure out how much control it has over these stages which is crucial for ISO 14001 Compliance. This also helps them make choices that are better for the environment.
Companies and its employees who work in design, sales, and finance make a lot of choices about how to improve customer satisfaction. They have to think about things like
a) Making customers happy
b) Ensuring quality
c) Being innovative
d) Keeping things safe
e) Keeping costs down
When they think about the whole Life Cycle, they also consider how these choices will affect the environment and the community. For example, when designing appliances like washing machines and refrigerators, they can choose to use the following:
a) Recycled materials
b) Avoid harmful substances
c) Use less water and energy
d) Design them to last a long time
All of these decisions are made during product design and can significantly impact on the environment.
Key Phases of the Life Cycle Perspective
The Life Cycle, as embraced by ISO 14001:2015, encompasses various interconnected stages that span from extracting the raw materials to disposing of the products. Understanding these stages is crucial for organisations seeking to manage their environmental impacts and promote sustainability effectively. So, let’s explore each stage in more detail:
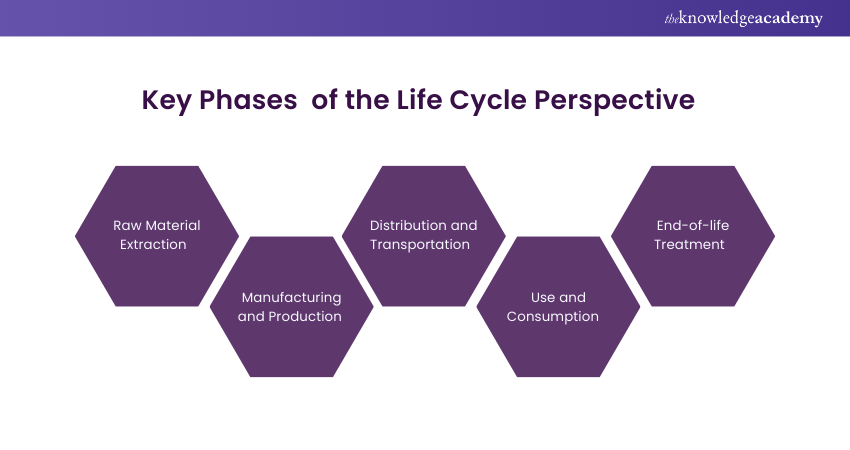
1) Raw Material Extraction
This stage involves extracting and acquiring natural resources, such as minerals, metals, or timber. It encompasses activities such as mining, logging, and farming. Extraction practices can have significant environmental implications, including habitat destruction, soil erosion, and depletion of natural resources.
2) Manufacturing and Production
Once the raw materials are obtained, they undergo manufacturing and production processes. This stage involves transforming the raw materials into finished products through various industrial processes. It includes activities
a) Refining,
b) Processing,
c) Assembling
d) Packaging.
Manufacturing can result in emissions, waste generation, and energy consumption, which must be carefully managed.
3) Distribution and Transportation
After manufacturing, the products are distributed and transported to reach consumers or end-users. This stage involves activities like packaging, warehousing, Logistics, and transportation. Distribution processes contribute to greenhouse gas emissions, energy consumption, and waste generation, particularly concerning packaging materials and transportation fuel.
4) Use and Consumption
Once the products reach consumers, they are used and consumed in various ways. This stage encompasses the product's operational life, including activities such as usage, maintenance, and repair. Energy consumption, emissions, and waste generation can occur during this stage, depending on the nature of the product and how it is used.
5) End-of-life Treatment
The final stage of the Life Cycle is the end-of-life treatment of products. It includes disposal, recycling, or reuse options. Depending on the product, it may be discarded as waste, recycled into new products, or repurposed for alternative uses. Proper management of end-of-life treatment is critical to minimise the environmental impact associated with waste disposal and promote resource efficiency through recycling and circular economy practices.
Master Environmental Management with our ISO 14001 Foundation Certification – Register now!
Benefits of Life Cycle Perspective
Let’s explore some of the advantages of Life Cycle Perspective and how it manages and define business processes:
The successful integration of a Life Cycle Perspective into an environmental management system depends on commitment across all organisational levels and functions. Strengthening this perspective necessitates systematic management and a clear definition of processes and their interactions. The organisation should regularly review documentation, especially when changes occur in processes, products, or systems, using the plan-do-check-act approach.
Implementing the 14001 Life Cycle
Implementing ISO 14001:2015 with the perspective of the Life Cycle is a proactive approach that enables organisations to effectively manage their environmental impacts and promote sustainability throughout all the stages of the Life Cycle. Here are key steps to successfully implement ISO 14001:2015 Life Cycle:
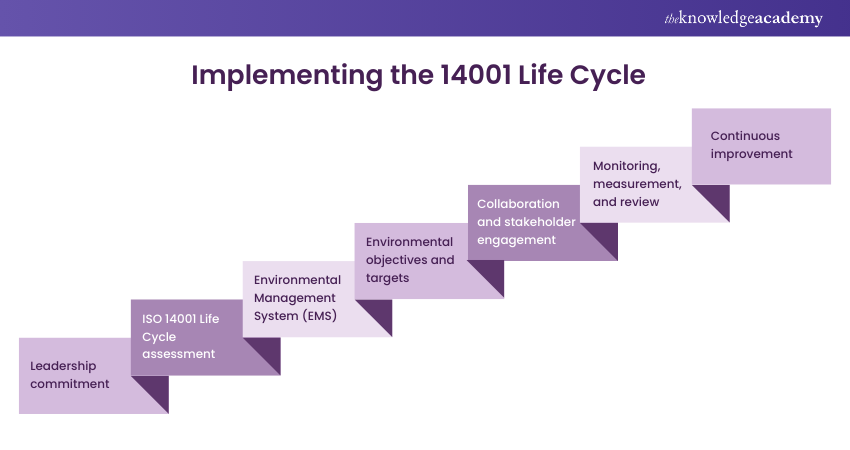
1) Leadership Commitment
Leaders should establish environmental policies, allocate necessary resources, and set clear objectives and targets aligning with the Life Cycle's perspective. By demonstrating leadership commitment, organisations can create a culture of environmental responsibility and engage employees at all levels.
2) ISO 14001 Life Cycle Assessment
Conduct a comprehensive assessment to identify the environmental aspects and impacts associated with each stage of the Life Cycle. This assessment will help prioritise actions, set meaningful objectives, and develop strategies to mitigate negative environmental impacts. It involves the following activities to ensure a thorough understanding of the Life Cycle and its potential environmental effects:
a) Gathering data
b) Analysing processes
c) Involving relevant Stakeholders
3) Environmental Management System (EMS)
Establish an effective EMS based on ISO 14001 requirements. Develop procedures and processes to address the identified environmental concepts and impacts throughout the Life Cycle. This includes the following:
a) Defining roles and responsibilities
b) Establishing communication channels
c) Implementing training programs to ensure employees understand their environmental obligations
Learn to develop and implement EMS with our ISO 14001 Lead Implementer Course – Sign up today!
4) Environmental Objectives and Targets
Set environmental objectives and targets that measure, achieve, and align with the organisation’s environmental policy and legal requirements. Also, focus on improving performance at different Life Cycle stages, such as reducing resource consumption, minimising waste generation, and promoting eco-friendly practices. Additionally, review and update objectives regularly to reflect changing circumstances and opportunities for improvement.
5) Collaboration and Stakeholder Engagement
Foster partnerships, share knowledge and collaborate on environmental initiatives. Also, involve stakeholders in Decision-Making Processes and seek their input on environmental improvements. By building strong relationships, organisations can enhance sustainability practices and promote positive environmental outcomes.
6) Monitoring, Measurement, and Review
Use relevant indicators and metrics to evaluate progress towards objectives and targets. Further, review and analyse data regularly to identify trends, Reciprocal Easement Agreements (REAS) for improvement, and potential ISO 14001 Risks and Opportunities as Additionally, conduct and management reviews to ensure the effectiveness of the EMS and compliance with ISO 14001 requirements, demonstrating ongoing commitment to meet requirements
7) Continuous Improvement
Embrace a culture of continuous improvement by encouraging innovation, creativity, and learning. It involves the following activities:
a) Continuously seeking opportunities to enhance environmental performance
b) Involving employees in generating ideas
c) Implementing best practices
d) Driving sustainability initiatives
e) Regularly communicating progress and achievements to motivate and engage stakeholders
Conclusion
Adopting the ISO 14001 Life Cycle offers companies a strong structure for methodically controlling environmental effects. By choosing this strategy, businesses can show their dedication to being environmentally responsible while also improving their efficiency and reputation. Taking a proactive approach promotes sustainability in the long run, encourages innovative environmental practices, and nurtures trust with stakeholders. In the end, it enables organisations to have a major impact on building a more sustainable and resilient future.
Unlock the potential of sustainable business practices with our ISO 14001 Certification - Join now!
Frequently Asked Questions

Clause 6.1.2 of ISO 14001 details the Life Cycle Perspective, highlighting the evaluation of environmental impacts at each phase of a product’s Life Cycle. This includes stages from raw material extraction to disposal. This method ensures thorough sustainability management.

By adopting a Life Cycle Perspective, companies can pinpoint and mitigate environmental and social impacts throughout a product’s entire lifespan, fostering more sustainable practices and bolstering corporate responsibility.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various ISO 14001 Courses, including the ISO 14001 Foundation Certification, ISO 14001 Lead Auditor Course, and ISO 14001 Internal Auditor Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into ISO 14001 Risks and Opportunities.
Our Health & Safety Blogs cover a range of topics related to ISO 14001, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Health & Safety skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Health & Safety Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 ISO 14001 Foundation Certification
ISO 14001 Foundation Certification
Mon 6th Jan 2025
Mon 7th Apr 2025
Mon 4th Aug 2025
Mon 3rd Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


