We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
In today's interconnected world, the need for robust Ethical Hacking and Cyber Security practices has become increasingly vital. Both Cybersecurity and Ethical Hacking are crucial in protecting our digital landscape from malicious activities. While they share a common goal of securing computer systems and networks, there are fundamental differences between these two domains.
If you wish to understand a detailed comparison of Cybersecurity, Ethical Hacking, their differences and how both fields are related, this blog is just for you. Keep reading this Ethical Hacking and Cyber Security to learn the key differences between Cybersecurity and Ethical Hacking.
Table of Contents
1) Ethical Hacking vs Cyber Security: Overview
2) Roles of Cyber Security and Ethical Hacking
3) What Is the Difference Between Ethical Hacking and Cyber Security?
a) Objectives and approaches
b) Legal implications
c) Skills and expertise
4) Conclusion
Ethical Hacking vs Cyber Security: Overview
Cyber Security protects computer systems, networks, and data from unauthorised access, theft, and damage. It ensures information confidentiality, integrity, and availability through hardware and software safeguards, policies, and protocols.
The importance of Cyber Security is higher than ever, as it protects individuals, businesses, and organisations from countless cybercrimes, such as data breaches, malware infections, hacking attempts, and identity theft. Cybersecurity helps maintain trust and confidence in digital transactions and ensures the smooth functioning of critical services. Key Cybersecurity concepts include authentication, encryption, intrusion detection, firewalls, and vulnerability management.
They often use Intrusion Detection and Prevention systems (IDPS) to monitor traffic on network for suspicious activities and prevent unauthorised access. Firewalls and network security mechanisms act as barriers against external threats. Risk assessment and vulnerability management involve identifying potential weaknesses and implementing measures to mitigate them.
Ethical Hacking, also referred to as white-hat hacking or penetration testing is a legitimate practice that involves intentionally exploiting vulnerabilities in computer systems to identify potential security weaknesses. Ethical Hackers, also called penetration testers, utilise their skills and knowledge to assess an organisation's security posture.
Ethical Hacking professionals operate within legal boundaries and adhere to a strict code of ethics. There are usually five kinds of Ethical Hacking professions under the White hat Ethical Hacking category:
1) White box Ethical Hacking: Knowledge about the inner working of a system
2) Black box Ethical Hacking: No knowledge about the inner mechanisms.
3) Grey box Ethical Hacking: Partial knowledge about inner mechanism.
4) Red team Ethical Hacking: Ethical hacking game of replicating a cyber-attack.
5) Blue team Ethical Hacking: Ethical hacking game of repelling a cyber-attack.
The ethics behind Ethical Hacking revolve around obtaining proper authorisation before performing any hacking activities. Ethical Hacking professionals ensure that their actions do not cause harm or disrupt critical services. Their primary objective is to enhance security by identifying weaknesses and providing recommendations for improvement.
Try our Ethical Hacking Training and learn to legally bypass the security of systems!
Roles of Cyber Security and Ethical Hacking
Cyber Security and Ethical Hacking professionals together to protect systems and networks. They identify vulnerabilities, implement preventive measures, respond to incidents, identify weaknesses, evaluate security posture, and provide recommendations for enhancing security. Their efforts create a more secure digital environment for individuals and organisations.
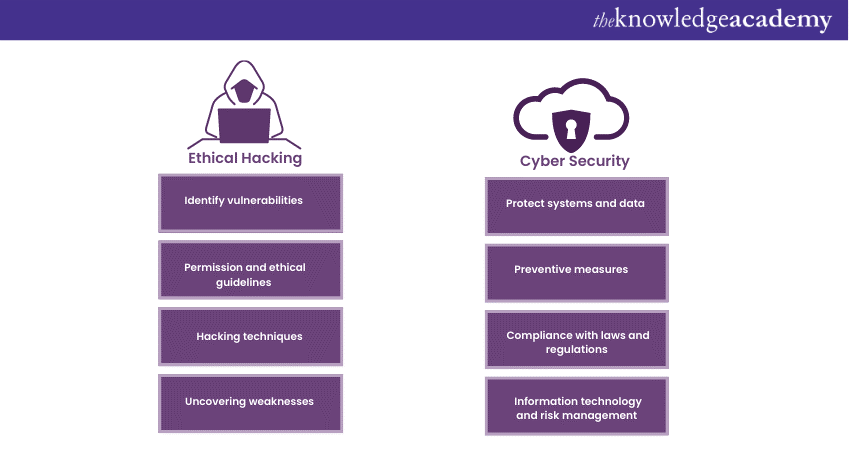
Identifying vulnerabilities and threats
Cyber Security professionals analyse systems and networks to identify vulnerabilities and potential threats. These professionals make use of specialised tools and methods to assess security weaknesses and determine potential attack vectors. This proactive approach helps organisations stay ahead of cyber threats.
Implementing preventive measures
Cyber Security experts implement preventive measures to safeguard systems and data. This includes deploying firewalls, antivirus software, intrusion detection systems, and secure coding practices. These measures mitigate the risk of unauthorised access, data breaches, and other cyber threats.
Incident response and recovery
When a Cyber Security incident occurs, professionals respond swiftly to detect, contain, and mitigate the impact. They investigate and analyse incidents, identify root causes, and take suitable countermeasures to prevent future occurrences. They also focus on recovering compromised systems and restoring data integrity.
Identifying system weaknesses
Ethical Hacking professionals systematically identify system weaknesses and vulnerabilities. Through security assessments and penetration testing, they simulate real-world attacks to find potential entry points for malicious actors. Their findings provide valuable insights for organisations to strengthen their security defences.
Evaluating security posture
Cyber Security experts evaluate an organisation's security posture by assessing policies, procedures, and technical controls. They identify areas for improvement, such as access controls, network configurations, and employee awareness. Regular evaluations help organisations proactively address vulnerabilities.
Recommendations for enhancing security
Based on their assessments, Cyber Security professionals provide actionable recommendations. These may include patching vulnerabilities, implementing stronger access controls, network segmentation, and employee training programs. By implementing these recommendations, organisations can enhance their security measures.
Learn the basics of Ethical Hacking with the Ethical Hacking Professional Course!
What is the difference between Ethical Hacking and Cyber Security?
Cyber Security protects systems and data from cyber threats, while Ethical Hacking aims to identify vulnerabilities through controlled simulated attacks. Compliance with regulations and laws of local governing body is crucial in both fields, but Ethical Hacking requires explicit permission. Here are some differences that will allow you to effectively leverage cybersecurity and Ethical Hacking to enhance their security posture.
Objectives and approaches
Cybersecurity and Ethical Hacking have distinct objectives and approaches. Cybersecurity protects computer systems, networks, and data from unauthorised access, theft, and damage. Its primary goal is to ensure information confidentiality, integrity, and availability. These professionals employ preventive measures like firewalls, encryption, and access controls to secure systems and mitigate cyber threats.
On the other hand, Ethical Hacking, also known as penetration testing, aims to identify security vulnerabilities by simulating real-world attacks. Ethical Hacking professionals adopt the mindset of potential attackers to discover weaknesses that could be exploited. Their objective is to enhance security by uncovering vulnerabilities and providing recommendations for improvement. Ethical Hacking involves a proactive and controlled approach to ensure the security of systems.
Legal implications
Another significant difference between cybersecurity and Ethical Hacking lies in the legal implications. Cyber Security professionals operate within the legal framework, adhering to laws and regulations governing data protection and privacy. Their activities focus on defensive measures to protect systems and data from malicious actors. Compliance with legal requirements has high value in the field of cybersecurity.
Ethical Hacking, although conducted with consent and authorisation, can pose legal challenges if not executed properly. Ethical hackers must obtain permission from system owners before conducting penetration testing or vulnerability assessments. They must also adhere to ethical guidelines and ensure their actions do not cause harm or disruption. Complying with the laws is crucial to avoid legal consequences.
Skills and expertise
Cyber Security and Ethical Hacking demand different skill sets and expertise. Cybersecurity professionals possess a broad understanding of Information Technology (IT), network security, risk management, and compliance. They know security frameworks, encryption protocols, and incident response procedures. Strong foundation of analytical and problem-solving skills is essential in identifying vulnerabilities and implementing appropriate controls.
Ethical Hacking professionals, on the other hand, require technical expertise in various hacking techniques, tools, and methodologies. They must have in-depth knowledge of system vulnerabilities, network protocols, and attack vectors. They continuously update their skills to stay abreast of emerging threats and vulnerabilities.

Conclusion
Ethical Hacking and Cyber Security are distinct but interconnected disciplines. While Cyber Security safeguards systems and data from threats, Ethical Hacking identifies vulnerabilities. Both play critical roles in maintaining a secure digital environment, ensuring information confidentiality, integrity, and availability. Together, they contribute to strengthening overall security defences.
Try our Mastering Metasploit Framework Course and use Metasploit in penetration testing!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming IT Security & Data Protection Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Ethical Hacking and Penetration Testing Training
Ethical Hacking and Penetration Testing Training
Fri 14th Jun 2024
Fri 20th Sep 2024
Fri 13th Dec 2024







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


