We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Technology has reshaped various aspects of our lives, and the Healthcare sector is no exception. Imagine a scenario where Healthcare providers can instantly access crucial patient information from anywhere or where intricate medical images can be swiftly analysed to deliver accurate diagnoses. This is precisely where the concept of Cloud Computing in Healthcare steps in. Cloud Computing uses the internet for storing and accessing data and applications, ushering in a remarkable transformation within the Healthcare industry.
According to Statista, Cloud Computing is forecasted to reach 480 billion GBP by 2023. Healthcare is among the prominent applications of Cloud Computing. In this blog, we will explore Cloud Computing in Healthcare, its significance, benefits, applications, and innovations, along with challenges and considerations.
Table of Contents
1) Understanding Cloud Computing in Healthcare
2) Applications of Cloud Computing in Healthcare
3) Security and privacy concerns
4) Cloud service models in Healthcare
5) Cloud deployment models in Healthcare
6) Choosing the right model for Healthcare institutions
7) Future trends and innovations
8) Challenges and considerations
9) Conclusion
Understanding Cloud Computing in Healthcare
Cloud Computing is a transformative technological approach that has significantly impacted various industries, including Healthcare. It involves the delivery of computing resources—such as storage, processing power, and software—over the internet. Instead of relying on local servers or devices, it also allows organisations to access and utilise these resources remotely, providing a dynamic and flexible infrastructure
Importance of Cloud Computing in Healthcare
Cloud Computing addresses critical challenges that the Healthcare sector faces, such as the need for efficient data management, streamlined communication, and rapid access to patient information. It facilitates seamless collaboration among Healthcare professionals, enabling them to work together on a patient's diagnosis and treatment plan regardless of their physical location.
Additionally, Cloud Computing's role in telemedicine and remote patient monitoring is noteworthy. As the world becomes more interconnected, cloud-based platforms empower Healthcare providers to deliver consultations remotely, enhancing patient care accessibility and convenience. Remote patient monitoring devices can transmit real-time health data to cloud servers, allowing Healthcare teams to track patient well-being and intervene promptly when necessary.
Benefits of Cloud Computing in Healthcare
The benefits of cloud computing are that it offers enhanced data storage and accessibility. Patient records, medical images, and test results can be stored securely in the cloud, and accessible to authorised professionals whenever needed. This immediate access to comprehensive patient histories supports well-informed decision-making, leading to more accurate diagnoses and tailored treatment plans.
Cost efficiency is another significant advantage. It eliminates the need for extensive on-site infrastructure, reducing the associated expenses. Healthcare institutions can pay for the resources they use, scaling up or down as demands fluctuate, thus optimising resource allocation.
Embrace the future of Healthcare with Cloud Computing – unlock innovation, efficiency, and patient-centric solutions today!
Applications of Cloud Computing in Healthcare
Cloud Computing's transformative capabilities have found a multitude of applications within the Healthcare sector, revolutionising how medical services are delivered, managed, and improved.
Electronic Health Records (EHRs) and Electronic Medical Records (EMRs)
One of the foremost applications is the storage and management of EHRs and EMRs. Cloud-based systems securely store patient data, ensuring authorised Healthcare providers have instant access to comprehensive medical histories. This accessibility streamlines patient care by allowing quick and accurate decision-making, regardless of the provider's physical location.
Telemedicine and remote patient monitoring
Cloud Computing plays a crucial role in telemedicine, enabling remote consultations between patients and Healthcare professionals. Additionally, it facilitates the remote monitoring of patients' health conditions through wearable devices that transmit real-time data to cloud servers. This capability not only enhances patient convenience but also enables proactive interventions based on accurate, up-to-date information.
Medical imaging and diagnostics
The cloud has revolutionised medical imaging by enabling the storage, sharing, and analysis of intricate images such as X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans. Healthcare providers can access these images remotely, enabling faster consultations and expert opinions. Furthermore, cloud-powered diagnostic tools harness the processing power required for complex image analysis, aiding in accurate diagnoses.
Research and data analysis
Cloud Computing empowers medical researchers by providing the computational resources necessary for analysing vast datasets efficiently. Researchers can collaborate on projects regardless of their geographical locations, advancing medical discoveries and treatments. The cloud's scalability allows researchers to handle significant data volumes without the need for extensive on-premises infrastructure.
Security and privacy concerns
While Cloud Computing offers numerous advantages in Healthcare, it also raises security and privacy concerns that must be meticulously addressed to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of sensitive patient data.
Data security in the Cloud
The security of patient information is paramount, and entrusting this data to third-party cloud service providers requires stringent security measures. Cloud systems must implement robust encryption techniques to safeguard data both during transmission and storage. Multi-factor authentication protocols add a layer of protection, ensuring only authorised personnel can access patient records.
Regulatory compliance (HIPAA, GDPR, etc.)
Healthcare operates within regulations, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union. Cloud solutions must comply with these regulations, ensuring patient rights are respected, and data breaches are prevented. This entails strict adherence to data handling, storage, and transmission standards.
Mitigating security risks
Cloud providers must implement comprehensive security protocols to mitigate potential risks. Regular security audits, vulnerability assessments, and intrusion detection systems are essential components of a proactive security strategy. Rapid response mechanisms should be in place to address any breach promptly and minimise potential damages.
User education and awareness
Healthcare professionals and staff must be well-informed about best practices in data security. Training sessions should emphasise the importance of strong passwords, responsible data sharing, and the identification of potential phishing attempts.
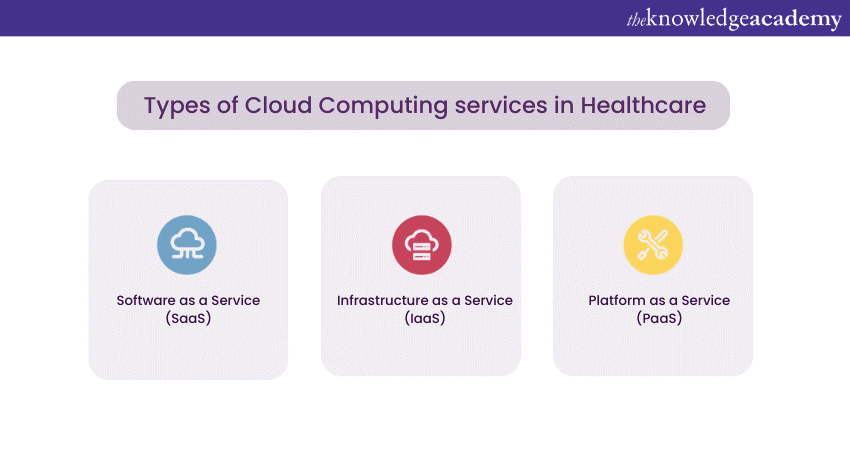
Cloud service models in Healthcare
Cloud Computing offers different service models that cater to the needs of Healthcare organisations, providing flexibility and scalability while optimising resource utilisation and costs.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS forms the fundamental building blocks of computing infrastructure over the cloud. In Healthcare, this translates to the availability of virtualised resources such as servers, storage, and networking. Healthcare institutions can scale their Information Technology (IT) resources up or down as needed, eliminating the need for extensive on-premises hardware. This flexibility is particularly valuable during peak workloads or when launching new applications.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS provides a platform to create, launch, and oversee applications, relieving them of concerns about the underlying infrastructure. In Healthcare, this model enables the creation of customised applications that address specific clinical or administrative needs. Developers can focus on functionality rather than infrastructure management, accelerating the deployment of innovative solutions.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS offers ready-to-use software applications over the cloud. Healthcare institutions can utilise Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems, practice management software, and telehealth platforms without the hassle of local installations and maintenance. SaaS SaaS solutions streamline workflows, enhance collaboration, and provide regular updates, ensuring that healthcare professionals work with updated Cloud Computing Tools.
Comparison and use cases
Choosing the appropriate service model depends on the specific requirements of the Healthcare organisation. Smaller clinics might benefit from SaaS applications due to their ease of use and lower upfront costs. Larger hospitals might opt for IaaS and PaaS solutions to accommodate their complex and varied IT needs, enabling them to tailor applications precisely.
Elevate your skills with our Cloud Computing Training and unlock a world of limitless technological possibilities.
Cloud deployment models in Healthcare
Cloud Computing offers various deployment models, each with distinct advantages and considerations, allowing Healthcare institutions to tailor their cloud strategies to their specific requirements and preferences.
Public cloud
Third-party providers host public clouds, furnishing shared resources accessible via the internet. In Healthcare, this model provides cost-effective scalability and reduces maintenance burdens. Smaller Healthcare organisations, clinics, and startups can leverage public clouds to access advanced technology without hefty upfront investments.
Private cloud
Private clouds are exclusively designated for a single organisation, offering heightened control and elevated security measures. This model suits Healthcare institutions with stringent data privacy and compliance requirements, like larger hospitals or research organisations. It offers better customisation and can be located on-site or hosted by a third-party provider.
Hybrid cloud
Hybrid clouds are the combination of both Private cloud and Public cloud components, allowing Healthcare organisations to balance performance and cost-efficiency. Sensitive patient data can reside in the Private cloud, while less sensitive applications take advantage of the Public cloud's scalability. Hybrid models are suitable for Healthcare institutions aiming to optimise resource allocation while adhering to regulatory standards.
Community cloud
Community clouds are shared among organisations with similar interests and concerns. In Healthcare, this model can serve regional Healthcare networks or collaborations among research institutions. Shared resources enable cost-sharing and facilitate data exchange while maintaining the required levels of security and compliance.
Choosing the right model for Healthcare institutions
Selecting the appropriate deployment model hinges on factors such as data sensitivity, scalability needs, and budget constraints. Healthcare organisations should conduct a thorough assessment of their IT requirements and consult with cloud experts to determine the most fitting model.
Elevate your skills with Linux OpenStack Administration Training and master the art of cloud management.
Future trends and innovations
The future of Cloud Computing in Healthcare is brimming with promising trends and innovative advancements that have the potential to reshape the industry, enhance patient care, and revolutionise the way Healthcare is delivered.
AI and Machine Learning in Cloud-Based Healthcare
AI and ML are poised to make a profound impact on Healthcare. Cloud Computing furnishes the essential computational capacity to handle extensive Healthcare data, generating insights for tailor-made treatment strategies, disease forecasting, and advancements in pharmaceutical discovery. AI-powered algorithms can rapidly identify patterns in medical images, aiding in faster and more accurate diagnoses.
Edge computing for real-time applications
Edge computing is set to transform Healthcare by bringing computation closer to the data source, minimising latency, and enabling real-time decision-making. In emergency situations or remote patient monitoring, edge devices can process critical data on-site, sending only relevant insights to the cloud. This approach improves response times and reduces the strain on network bandwidth.
Interoperability and standardisation
Cloud Computing paves the way for improved interoperability among various Healthcare systems and providers. By integrating Electronic Health Records (EHRs) and medical data across platforms, patients can experience seamless care transitions. Standardisation efforts are gaining momentum, ensuring that data formats and communication protocols are universally understood, allowing different systems to communicate effectively.
Elevate your tech expertise with our Microservices Architecture Training and master the future of Agile, scalable software development!
Challenges and considerations
While Cloud Computing offers immense benefits to Healthcare, it also presents notable challenges and considerations that must be addressed to ensure a smooth and secure implementation.
Integration with existing systems
Integrating cloud solutions with existing on-premises systems can be complex. Legacy systems may not be immediately compatible with cloud platforms, requiring careful planning and potentially necessitating system upgrades or replacements. Ensuring seamless data flow between old and new systems is crucial to maintaining operational efficiency.
Data migration and portability
Transferring large volumes of sensitive patient data to the cloud demands meticulous planning and execution. Data migration involves preserving data integrity, security, and maintaining compliance with regulations such as HIPAA. Ensuring minimal disruption during migration and guaranteeing data portability between different cloud providers are essential considerations.
Vendor lock-In
Choosing a specific cloud provider can lead to vendor lock-in, where it becomes challenging to switch to a different provider due to proprietary technologies or data formats. Healthcare institutions need to carefully evaluate vendor agreements and strategies for mitigating vendor lock-in risks, such as using open standards and portable data formats.
Conclusion
Cloud Computing in Healthcare Industry helps doctors access patient data, enables remote care, and boosts research. With careful planning, we can overcome challenges and embrace a brighter, patient-focused future in Healthcare.
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming Cloud Computing Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Cloud Computing Training
Cloud Computing Training
Thu 15th Aug 2024
Thu 5th Dec 2024







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


