We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Cloud technology has revolutionised the way how we store, access, and manage data in today's technology-driven world. But What is Cloud Computing? In this blog, we will explore and dive into the concept, significance, and increasing adoption of cloud computation by businesses and individuals, setting the stage for a complete overview.
Throughout this comprehensive overview, we will delve into the core principles of cloud technology, discuss its various types and deployment models, and highlight the benefits it offers., Additionally, we will address security and privacy concerns, examine potential challenges and risks, explore future trends, and present real-world case studies. In this blog, you will learn about What is Cloud Computing and how primarily providing hosted services over the internet works.
Table of Contents
1) Understanding Cloud Computing
2) Benefits of Cloud Computing
3) Types of Cloud Services
4) Security and Privacy in the Cloud
5) Challenges and Risks of Cloud Computing
6) Conclusion
Understanding Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is a revolutionary concept that has transformed the way how we store, access, and utilise computing resources. It involves the computing services, such as servers, storage, databases, and software, over the Internet. The concept of cloud computation has evolved over time, driven by advancements in technology and the increasing demand for scalable and flexible computing solutions.
One of the key characteristics of cloud technology is on-demand self-service. Users can access and provision computing resources, such as virtual machines or storage, without the need for human intervention from the service provider. This allows for greater autonomy and agility in managing computing resources, as users have direct control over their provisioning.
Broad network access is another crucial characteristic of cloud computing. It allows users to access their applications, data, and services from anywhere, using various devices connected to the internet. This accessibility promotes collaboration and facilitates remote work, as individuals and teams can easily share and work on resources regardless of their physical location.
Resource pooling is an essential aspect of cloud technology. Cloud service providers consolidate computing resources, such as servers and storage devices, into a shared pool that multiple users can draw upon. This pooling of resources allows for efficient utilisation, as the resources can be dynamically allocated and reallocated based on demand. It also enables economies of scale, benefiting both the providers and consumers in terms of cost-effectiveness.
Rapid elasticity is a key characteristic that allows cloud computing resources to be scaled up or down quickly based on demand. Users can dynamically adjust their resource allocation to meet changing workload requirements, ensuring optimal performance and avoiding overprovisioning or underutilisation. This elasticity is particularly valuable for organisations with fluctuating computing needs.
Cloud computing services are typically offered on a measured service basis. Users are billed for their resources they consume, allowing for cost transparency and flexibility. This pay-as-you-go model ensures that organisations only pay for the resources they use, optimising their expenses and allowing for cost-effective scalability.
Cloud computing deployment models provide different options for organisations based on their needs and requirements.
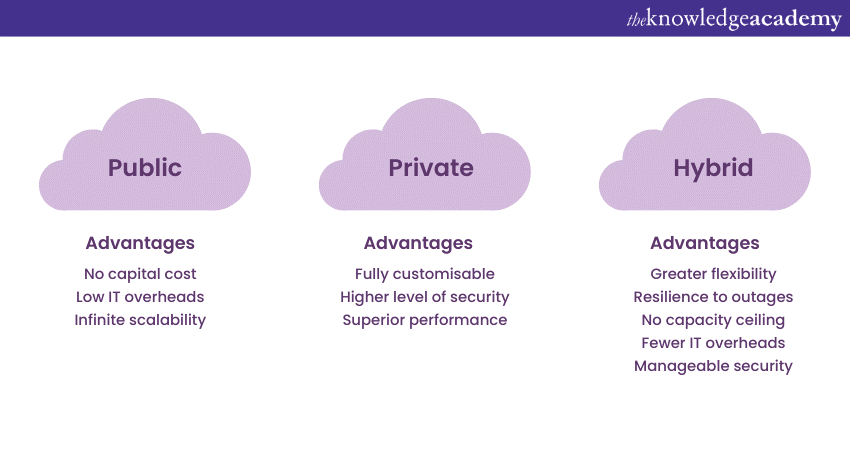
Public: These cloud services are offered by third-party internet vendors and are accessible to anyone.
Private: On the other hand, this cloud infrastructure, on the other hand, is dedicated to a single organisation and can be hosted on-premises or by a service provider.
Hybrid: This cloud service combines both public and private cloud environments, allowing organisations to leverage both benefits.
Community: This cloud service is a shared infrastructure that serves a specific community or industry, providing shared resources and services.
Understanding the concept and characteristics of cloud computation, as well as the different deployment models, is crucial for organisations and individuals looking to harness the power of this technology. By leveraging cloud computing, businesses can achieve scalability, flexibility, cost savings, and improved collaboration.
Learn the details of different Cloud services with our Cloud Computing Courses!
Benefits of cloud computing
Cloud computing offers numerous advantages for businesses and individuals alike. It enables organisations to achieve cost savings, scalability, and flexibility, while individuals benefit from easy access to data, convenience, and reduced hardware requirements.
Cost savings for businesses
Cloud computing eliminates the need for upfront infrastructure costs. Instead of investing in expensive hardware or data centers, businesses can leverage cloud services and pay for the computing resources they consume on a pay-as-you-go basis. This flexible pricing model allows for greater cost efficiency, as organisations only pay for the resources they use. Additionally, businesses can reduce with hardware maintenance and upgrade expense, as these responsibilities are shifted to the cloud service provider.
Scalability and flexibility
One of the significant benefits of cloud technology is its ability to scale computing resources based on demand. Businesses can easily scale their resources to accommodate fluctuations in workload. This flexibility ensures that organisations can handle peak workloads without experiencing any performance issues, while avoiding unnecessary expenses during periods of low demand. Cloud computing provides the ability to adapt quickly to changing business needs.
Enhanced collaboration and productivity
Cloud computing fosters enhanced collaboration and productivity within organisations. Teams can seamlessly share and collaborate on documents and projects in real-time through cloud-based tools and applications. This promotes efficient communication and improves workflow efficiency, enabling teams to work together regardless of their physical location. Remote work capabilities are greatly enhanced, allowing teams to collaborate effectively, even when geographically dispersed.
Easy access to data for individuals
For individuals, cloud computing offers easy access to data from anywhere, at any time. By leveraging cloud storage services, individuals can store their files and data in the cloud and access them using any device with an internet connection. This eliminates the need for carrying physical storage devices and provides the convenience of accessing files on the go. Whether at home, in the office, or on the road, individuals can easily retrieve and work with their data.
Convenience for individuals
Cloud computing brings convenience to individuals by offering cloud-based applications and services. Users can access software and applications directly through web browsers, eliminating the need for installation and updates on individual devices. This provides a hassle-free experience and a seamless user interface. Individuals can utilise their preferred applications and software without the burden of managing and maintaining them on their own devices.
Reduced hardware requirements for individuals
Cloud computing reduces hardware requirements for individuals. Instead of relying on powerful personal computers, individuals can leverage the processing power and storage capabilities of cloud servers. This allows for the use of lightweight devices such as laptops or even mobile devices, without sacrificing performance or storage capacity. Individuals can enjoy the benefits of cloud technology without the need for high-end hardware.
Types of cloud services
Cloud computing offers an extensive services to cater to different needs and requirements. There are three main types of cloud services: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS).
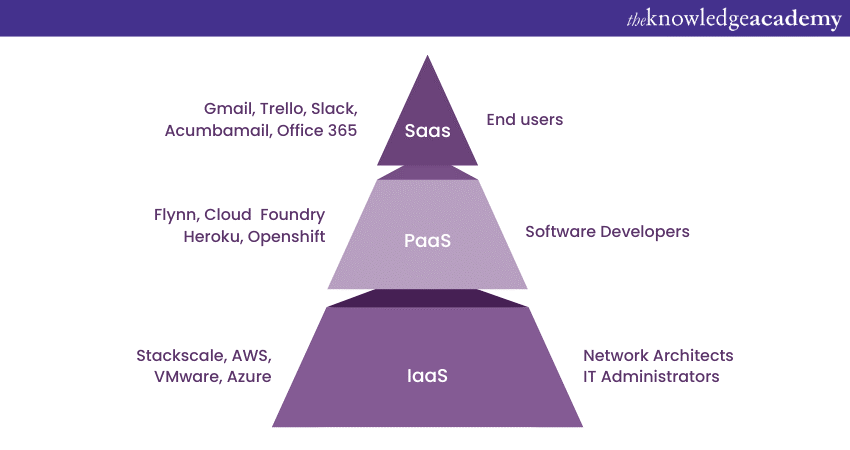
Infrastructure as a Service
IaaS provides virtualised computing resources over the internet. With IaaS, businesses can access and manage virtualised infrastructure elements such as virtual machines, storage, and networking resources. This gives organisations greater control and flexibility over their IT infrastructure without the need to invest in physical hardware. Examples of IaaS providers include Amason Web Services (AWS) with their Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2), Microsoft Azure's Virtual Machines, and Google Cloud Platform's Compute Engine.
Platform as a Service
PaaS offers a complete development and deployment environment in the cloud. PaaS providers offer a platform that includes infrastructure, operating systems, development tools, and runtime environments, providing room for developers to focus on building applications without eliminating the need to manage the underlying infrastructure. Popular PaaS providers include Heroku, Google App Engine, and Microsoft Azure's App Service.
Software as a Service
SaaS delivers software applications over the internet, accessible through a web browser or a client application. SaaS removes the requirement for organisations to install and maintain software on individual devices, as the software is centrally primarily hosted and managed by the service provider. Examples of SaaS offerings include customer relationships management tools like Salesforce, productivity suites like Google Workspace (formerly G Suite), and collaboration tools like Slack and Microsoft 365.
Learn to handle cloud infrastructure and virtual machines with Cloud Computing Training!
Security and privacy in the cloud
Cloud computing has revolutionised the way organisations store, process, and manage data. However, concerns regarding data security, privacy, and compliance are critical considerations when adopting cloud services.
Data security
Cloud service providers have a responsibility to implement robust security measures to protect customer data. They invest in state-of-the-art infrastructure, encryption technologies, and access controls to safeguard data from unauthorised access, data breaches, and cyber threats. It is crucial for customers to assess the security practices of cloud service providers, such as data encryption at rest and in transit, regular standard security audits, and compliance with to industry standards and regulations in the industry like ISO 27001 or GDPR.
However, customers also have a role to play in ensuring data security. They must implement appropriate access controls, strong authentication mechanisms, and regularly update their systems and applications to mitigate vulnerabilities. It is essential imperant to follow security best practices, including using complex and unique passwords, enabling multi-factor authentication, and regularly monitoring and auditing access to sensitive data.
Data privacy
Data privacy is another significant concern when storing data in the cloud. Cloud service providers must adhere to data protection regulations and ensure customer data is treated with confidentiality and privacy. This includes implementing measures to prevent unauthorised access, data leakage, or data misuse. Providers should also have clear data handling and data policies, and procedures for data breach notification.
Customers, On the other hand, customers should be aware of the cloud service providers’ privacy practices. They must carefully review privacy agreements, terms of service, and data handling policies to ensure that their data is handled in compliance with applicable regulations. Understanding where the data is stored, who has access to it, and how long it is retained is crucial in maintaining data privacy.
Compliance
Compliance with industry regulations and standards is a joint responsibility between cloud service providers and customers. Providers should ensure that their infrastructure and services comply with relevant regulatory requirements, such as HIPAA for healthcare data or PCI DSS for payment card data. They should also offer Cloud Computing Tools and features that enable customers to meet their compliance obligations.
Customers, particularly those operating in regulated industries, should perform due diligence to ensure that the cloud service provider meets their specific compliance requirements. This may include requesting documentation, and Certifications, or conducting audits to verify compliance.
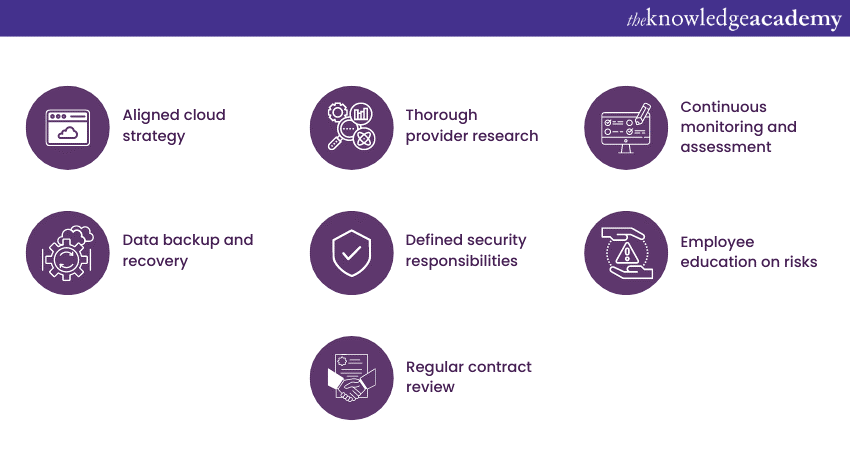
Best practices
To protect data in the cloud, organisations should follow best practices. This includes using strong encryption for sensitive data, implementing data backups and disaster recovery plans, regularly monitoring suspicious activities, and conducting employee training on security awareness and data handling.
Additionally, organisations should adopt a defence-in-depth approach, implementing various levels of security controls such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and regular vulnerability assessments. Regular security assessments and penetration testing can help identify and address vulnerabilities in cloud deployments.

Challenges and risks of cloud computing
Cloud computing offers numerous benefits, but it also presents challenges and risks that organisations need to address to ensure a successful cloud implementation.
Vendor lock-in
Vendor lock-in refers to the dependency on a particular cloud service provider, making it challenging to switch providers or migrate data and applications to a different platform. This can limit flexibility and hinder future business decisions. To mitigate this risk, organisations should carefully evaluate cloud service providers, consider multi-cloud or hybrid cloud strategies, and design applications to be compatible with multiple platforms to facilitate easy migration if necessary.
Downtime and service disruptions
Cloud service disruptions or outages can lead to business disruptions, loss of productivity, and financial loss. While cloud service providers strive to ensure high availability and uptime, occasional disruptions can occur. Organisations should consider service level agreements (SLAs) that guarantee a certain level of uptime and have backup and disaster contingency plans in place to mitigate the impact of downtime. Regular monitoring, redundancy, and failover mechanisms can also help minimise disruptions.
Dependency on Internet connectivity
Cloud computing heavily relies on internet connectivity. In situations where internet access is restricted or unreliable, accessing cloud services and data can become challenging. Organisations should consider backup connectivity options, such as redundant internet connections or local caching mechanisms, to ensure continued access to critical resources and applications.
Data security and privacy
Storing data in the cloud raises concerns about data security and privacy. Organisations must assess the security measures implemented by cloud service providers, including data encryption, access controls, and compliance with data protection regulations. It is essential to understand the provider's data handling policies, performs due diligence, and implement additional preventive measures, such as encryption at rest and in transit, to protect sensitive data.
Compliance and legal issues
Organisations operating in regulated industries must ensure that their cloud deployments comply with industry-specific regulations and legal requirements. Cloud service providers should provide transparency regarding compliance certifications and regulations they adhere. Organisations should conduct thorough due diligence, review contracts and agreements, and consider data residency requirements to ensure compliance with applicable laws and regulations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this overview provided insights into What Is Cloud Computing and its significance in today's technology landscape. We discussed key points such as its characteristics, benefits, challenges, and risk management strategies. As cloud technology continues to revolutionise industries, exploring its potential can unlock new opportunities for businesses and individuals alike.
Try our Microservices Architecture Training and learn concepts of load balancing and security!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming Cloud Computing Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Cloud Computing Training
Cloud Computing Training
Thu 15th Aug 2024
Thu 5th Dec 2024







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


