We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
 |
|
Today, Tableau has become a powerful Data Visualisation and Business Intelligence tool for professionals engaged in Data Analysis. Therefore, if you are new to the world of Data Analysis, it is crucial to understand What is Tableau.
According to an Enlyft survey, over 125,000 companies use Tableau, mostly in the IT and Services industry. The same survey reveals that Tableau accounts for over 17 per cent of Business Intelligence tools used in any organisation.
So, Tableau is the most powerful and easy-to-use Data Visualisation tool used in the Business Intelligence sector. Wish to learn more about this software? Read this blog to gain a deep understanding of What is Tableau. Also, explore its features and benefits in the field of Data Analysis.
Table of Contents
1) What is Tableau: A brief definition
2) A look at the various features of Tableau
3) Exploring the benefits of Tableau
4) Introduction to Tableau Product Suite
5) Data Types available in Tableau
6) File Types used in Tableau
7) Connecting to data sources in Tableau
8) Tableau Desktop interface
9) Dimensions and Measures in Tableau
10) Building Dashboards using Tableau
11) Excel vs Tableau
12) Conclusion
What is Tableau: A brief definition
Tableau is a powerful Data Visualisation and Business Intelligence tool that allows users to analyse data. It also provides capabilities to present data visually, appealing and interactively. Tableau’s user-friendly interface and extensive capabilities make it a popular choice for organisations and individuals across various industries.
The key strengths of Tableau lie in its ability to connect to many data sources, including spreadsheets, databases, and Cloud services. This connectivity enables users to easily import and integrate data from multiple sources, allowing for comprehensive analysis and reporting.
Tableau’s visual analytics features are particularly noteworthy. The software provides numerous charts, graphs, maps, and other visualisation types. Thisenables users to create compelling and informative visual representations of their data. Users can easily customise and interact with the data. This feature allows them to explore and drill down into the data to gain insights.
Moreover, two features which are particularly emphasised in Tableau are collaboration and sharing. The software allows its users to publish and share interactive dashboards and reports, making it easy to disseminate information across teams and organisations. More importantly, users can also create and participate in data-driven discussions, fostering collaboration and knowledge sharing.
A look at the various features of Tableau
A crucial reason for users to learn about What is Tableau is that it offers a wide range of features that make it a versatile and powerful Data Visualisation and Business Intelligence tool. Here are some key Tableau Features:
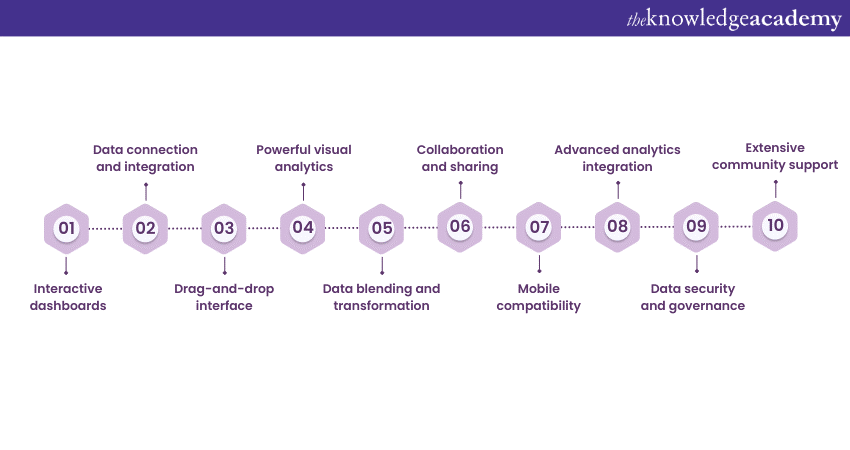
1) Interactive dashboards: Tableau allows users to create interactive dashboards that provide comprehensive Data Visualisations. Users can filter, drill down, and dynamically explore data, gaining real-time insights.
2) Data connection and integration: Tableau connects to various data sources, including spreadsheets, databases, and Cloud services. It enables users to import and integrate data from multiple sources, facilitating comprehensive analysis.
3) Drag-and-drop interface: Tableau's intuitive drag-and-drop interface makes it easy to build visualisations and create reports without the need for complex coding or scripting. Users can simply drag and drop data fields to create charts, graphs, and maps.
4) Powerful visual analytics: Tableau offers many visualisations, such as Bar Charts, Scatter Plots, Heat Maps, Donut Chart and more. Users can customise and combine different visual elements to create compelling and informative data representations.
5) Data blending and transformation: Tableau allows users to blend and transform data from different sources, enabling seamless integration and analysis. It provides data cleaning, reshaping, and aggregation tools, ensuring data accuracy and consistency.
6) Collaboration and sharing: Tableau supports collaboration by allowing users to share interactive dashboards and reports with others. Users can publish their visualisations to Tableau Server or Tableau Public, making sharing insights across teams and organisations easy.
7) Mobile compatibility: Tableau is compatible with mobile devices, ensuring that users can access and interact with their visualisations on the go. Mobile responsiveness allows for seamless viewing and exploration of data on smartphones and tablets.
8) Advanced analytics integration: Tableau integrates advanced analytics tools like R and Python. This enables users to incorporate statistical models and predictive analytics into their visualisations.
9) Data security and governance: Tableau offers robust security features, including user authentication, data encryption, and access controls. It ensures that sensitive data remains protected and complies with privacy regulations.
10) Extensive community support: Tableau has a large and active community of users who share knowledge, best practices, and resources. Users can access forums, user groups, and online resources to enhance their Tableau skills and get assistance when needed.
Enhance your Business Intelligence skills today – Join our Business Intelligence Reporting Course!
Exploring the benefits of Tableau
Tableau offers its users numerous benefits, making it a valuable tool for Data Visualisation and Analysis. Users can understand What is Tableau in further detail by exploring some key benefits of the tool as follows:
1) Easy and intuitive: Tableau's user-friendly interface and drag-and-drop functionality make it accessible to users with varying levels of technical expertise. Users can quickly learn how to create visualisations, eliminating the need for extensive training or coding knowledge.
2) Interactive visualisations: Tableau allows users to create interactive dashboards and reports that enable real-time exploration and analysis of data. Users can interact with visualisations, apply filters, drill down into details, and gain valuable insights through a hands-on approach.
3) Fast and efficient data analysis: Tableau’s powerful processing engine enables users to quickly handle large datasets and perform complex calculations. Users can conduct ad-hoc analyses, visualise trends, and identify patterns with minimal lag time, facilitating faster decision-making.
4) Comprehensive data connectivity: Tableau supports connectivity to many data sources, including databases, spreadsheets, and cloud services. This enables users to seamlessly integrate and blend data from multiple sources, providing a holistic view of their data.
5) Powerful visual analytics: Tableau offers a rich set of visualisations, charts, graphs, and maps that allow users to present data in a visually compelling and informative manner. Users can choose from various visualisation options and customise them to communicate insights to stakeholders effectively.
6) Collaboration and sharing: Tableau facilitates team collaboration by providing a platform for sharing dashboards and reports. Users can publish their visualisations to Tableau Server or Tableau Public, enabling others to access and interact with the data, fostering data-driven discussions and decision-making.
7) Mobile accessibility: Tableau’s mobile compatibility ensures that users can access visualisations on the go using smartphones and tablets. This allows for real-time data exploration and decision-making, even when users are away from their desktops.
8) Data-driven insights: Tableau empowers users to uncover meaningful insights from their data through visual exploration. By presenting data in a visually engaging way, Tableau helps users identify trends, correlations, and outliers, enabling data-driven decision-making and informed business strategies.
9) Scalability and flexibility: Tableau's architecture allows for scalability, accommodating growing data volumes and expanding user bases. The architecture can be deployed either on-premises or in the Cloud, providing flexibility to suit various organisational needs and infrastructures.
10) Active community support: Tableau’s architecture allows for scalability, accommodating growing data volumes and expanding user bases. The architecture can be deployed on-premises or in the Cloud, providing flexibility to suit various organisational needs and infrastructures.
Learn to visualise relevant data and combine databases by signing up for the Tableau Desktop Training now!
Introduction to Tableau Product Suite
The Tableau Product Suite has several offerings catering to different Data Visualisation and Analysis needs. Here’s an overview of the Tableau Product Suite:
1) Tableau Desktop: Tableau Desktop is the core product in the suite and is primarily used for Data Visualisation and Analysis. It provides users with an interface to conveniently connect to data sources, create interactive dashboards, and design compelling visualisations. Tableau Desktop is available for both Windows and macOS.
2) Tableau Prep: Tableau Prep is a data preparation tool that helps users clean, shape, and transform their data before visualising it in Tableau Desktop. It offers a visual and intuitive interface where users can perform data cleaning tasks, such as data deduplication, merging, and splitting, to ensure data accuracy and consistency.
3) Tableau Server: Tableau Server is a collaborative platform that allows users to publish and share interactive dashboards and reports with others in their organisation. It provides a safe environment for storing and accessing Tableau workbooks. Users can also schedule data refreshes, manage permissions, and create data-driven discussions within Tableau Server.
4) Tableau Online: Tableau Online is a Cloud-based version of Tableau Server. It offers the same functionality as Tableau Server but eliminates the need for on-premises infrastructure and maintenance. Users can access Tableau Online from any web browser and collaborate with colleagues in real time.
5) Tableau Public: Tableau Public is a free version of Tableau that allows users to publish their visualisations on the web and share them with the public. While providing limited data security and privacy options, Tableau Public is a great platform for showcasing data stories. It also makes visualisations accessible to a broader audience.
6) Tableau Mobile: Tableau Mobile is a companion app that lets users access and interact with their Tableau visualisations on smartphones and tablets. It provides a responsive and optimised experience. This allows users to explore data on the go and make data-driven decisions anytime, anywhere.
Data Types available in Tableau
In Tableau, several Data Types are available to handle different types of data. Here are some commonly used Data Types in Tableau:
|
Data Type |
Description |
|
String |
Alphanumeric text data |
|
Integer |
Whole numbers without decimal places |
|
Float |
Numeric data with decimal places |
|
Date |
Date values, including day, month, and year |
|
Datetime |
Date and time values combined |
|
Boolean |
Binary values representing true or false |
|
Geographical |
Spatial data, including latitude and longitude coordinates |
|
Currency |
Monetary values with currency symbols |
|
Percentage |
Numeric values representing a percentage |
|
Dimension |
Categorical or qualitative data |
|
Measure |
Quantitative data for aggregation and calculation |
File Types used in Tableau
Tableau allows users to save and share their work using various File formats specific to Tableau. These File formats have different purposes and features, depending on users’ needs. The table below summarises the different Types of Files that Tableau supports:
|
File Type |
File Extension |
Description |
|
Tableau Workbook |
.twb |
This is the most common File Type in Tableau that contains information about worksheets, dashboards, and stories. It does not include the actual data, but only the connection information and the analysis performed on the data. |
|
Tableau Packaged Workbook |
.twbx |
This is a Zip File that combines a workbook file (.twb) and any local data sources, such as extracts, text files, Excel files, etc. It enables users to share their work with others who do not have access to the original data source. |
|
Tableau Data Source |
.tds |
This is a Shortcut File that helps in quickly connecting to the data source that you use frequently. It does not contain the data itself, but only the connection information and any changes users have made to the data, such as calculations, groups, joins, etc. |
|
Tableau Packaged Data Source |
.tdsx |
This is a Zip File that combines a data source file (.tds) and any local data files, such as extracts, text files, Excel files, etc. It enables users to share the data source and the data with others. |
|
Tableau Data Extract |
.tde or .hyper |
This is a File that stores a local copy of some or all of the data from a data source. It can be used to improve performance, work offline, and share data with others. |
|
Tableau Bookmark |
.tbm |
This is a File that saves a single worksheet and its formatting. It can be used to reuse a worksheet in another workbook or share it with others. |
Connecting to data sources in Tableau
Tableau is a powerful Data Visualisation tool that can connect to various data sources and help users create interactive dashboards and reports. There are two types of connections in Tableau: live and extract. A live connection means that Tableau queries the data directly from the source, while an extract connection means that Tableau creates a local copy of the data and stores it in a file.
Extracts can improve performance and enable offline access, but they need to be refreshed periodically to reflect the changes in the original data.
a) To connect to a data source in Tableau, you can follow these steps:
b) Open Tableau Desktop and click on Connect to Data on the start page.
c) Select the type of data source from the list of options. Tableau supports many data sources, such as databases, files, servers, web data connectors, etc.
d) Enter the required information to connect to the data source, such as server name, username, password, etc. Depending on the type of data source, the information may vary.
e) Drag and drop the tables or files you want to use in your analysis to the data source pane. If needed, you can join, union, or blend multiple tables or files.
f) Click on Sheet to start creating your visualisation. You can also switch between live and extract connections by clicking on the data source name at the top left corner of the screen.
Tableau Desktop interface
Tableau Desktop is the main application that allows users to create and share Data Visualisations, dashboards, and stories. Tableau Desktop has a user-friendly interface that consists of various components and menus. Let’s explore the main elements of the Tableau Desktop interface and their functions. The Tableau Desktop interface can be divided into four main areas:
a) The Data pane: This is where users can see the data sources they have connected to and the fields available foranalysis. The fields are classified into Dimensions and Measures, colour coded as blue and green.
b) The Canvas: Users can create visualisation by dragging and dropping fields from the data pane to the rows, columns, marks, or filter shelves. The canvas will automatically generate a chart based on the selected fields. Users can also change the chart type, format, and style using the marks card and the toolbar.
c) The Sheets: This is where users can see the worksheets, dashboards, and stories that they have created in a workbook. A worksheet is a single view of the data, a dashboard is a collection of multiple views, and a story is a sequence of views that tell a narrative. Users can switch between different sheets by clicking on their tabs at the bottom of the screen. They can also rename, duplicate, delete, or rearrange the sheets.
d) The Show Me: This feature helps users to choose the best chart type for their data based on the selected fields. The Show Me menu lists possible chart types and highlights the ones compatible with users’data. They can also hover over each chart type to see a description and an example of how it looks.
Brush up on Interview skills with Tableau Interview Questions and Answers.
Dimensions and Measures in Tableau
Dimensions and Measures are two types of data fields that Tableau uses to create visualisations. Dimensions are categorical or qualitative values, such as names, dates, or locations. Measures are numerical or quantitative values, such as sales, profit, or quantity. Dimensions and measures have different roles and properties in Tableau and are colour-coded as blue and green, respectively. Dimensions help to categorise, segment, and reveal the details in the data. They affect the level of detail in the view and produce headers when added to the rows or columns shelves.
In contrast, Measures contain the data that can be measured and aggregated. They typically produce axes when added to the rows or columns shelves and can be used to create calculations, filters, or reference lines.
Dimensions and Measures can be converted to each other by changing their data type or aggregation. For example, a Measure can be converted to a Dimension by changing its data type to string or using a discrete aggregation, such as count or count distinct. Similarly, a Dimension can be converted to a Measure by changing its data type to numeric or using a continuous aggregation, such as sum or average. Dimensions and Measures can also be created from existing fields using calculated fields, groups, sets, bins, and parameters. These features allow users to manipulate and customise the data according to their analytical needs.
Building Dashboards using Tableau
Dashboards are collections of multiple views that display related data on a single screen. Dashboards can help users monitor, compare, and analyse data from different perspectives and gain insights for decision-making. Tableau offers a variety of tools and features to help users build effective and interactive Dashboards. To build Dashboards using Tableau, users need to follow these steps:
a) Create the worksheets that will be used in the Dashboard. Users can create charts and graphs using Tableau's data fields and visualisation options. Users can also apply filters, calculations, parameters, and other features to enhance the analysis and interactivity of the worksheets.
b) Open a new Dashboard and drag and drop the worksheets from the sheets pane to the dashboard canvas. Users can arrange and resize the worksheets and use the layout containers to organise the dashboard layout. Users can also use the tiled or floating options to control how the worksheets are displayed on the dashboard.
c) Add objects to the Dashboard using the objects pane. Users can add objects like titles, text, images, web pages, or filters to the Dashboard for additional information or functionality. Users can also use the tiled or floating options to control how the objects are displayed on the Dashboard.
d) Configure the Dashboard settings using the Dashboard Menu and the Toolbar. The Dashboard Menu lets users set size, device layout, background, and borders. Users can also use the Toolbar to add actions, such as filter, highlight, or URL actions to the Dashboard to enable interactivity between the worksheets and the objects.
e) Save and share the Dashboard with others. Users can save the Dashboard as a Tableau workbook (.twb) or a Tableau packaged workbook (.twbx) file. Moreover, they can publish the Dashboard to Tableau Server or Tableau Online or export the Dashboard as an image, PDF, or PowerPoint file.
Excel vs Tableau
Excel and Tableau are popular Data Analysis tools with different strengths and weaknesses.Some of the differences and advantages of Excel and Tableau are as follows:
|
Feature |
Excel |
Tableau |
|
Primary purpose |
Spreadsheet for basic calculations. |
Data Visualisation for interactive dashboards and advanced analytics. |
|
User-friendliness |
Easier for beginners. |
Steeper learning curve, better for advanced users. |
|
Data handling |
Handles up to 1 million rows, with performance issues for large datasets. |
Handles billions of rows, connects to various sources with better performance. |
|
Chart and graph types |
Creates basic charts with limited customisation. |
Offers a wide range of chart types with extensive customisation options. |
|
Statistical functions |
Performs basic statistical functions, requires formulas. |
Performs advanced statistical functions, allows drag-and-drop analysis. |
|
Real-time processing |
Limited real-time processing capabilities. |
Can process and visualise data in real-time. |
Conclusion
We hope that after reading this blog you got the answer to the question – What is Tableau? It offers users a powerful and user-friendly platform for Data Visualisation and analysis. Tableau empowers users with an intuitive interface, extensive connectivity options, and powerful visual analytics capabilities to explore, understand, and communicate their data effectively.
Learn how to use the reporting functions of Business Intelligence solutions with our Business Intelligence Reporting Courses!
Frequently Asked Questions

Tableau is a software that is used for Data Visualisation and Analysis. It allows users to connect to various data sources, such as databases, spreadsheets, web applications, and more, and create interactive dashboards and reports that can be shared and explored. Tableau is used for many purposes, such as Business Intelligence, Data Science, Education, Journalism, and Research.

Tableau can be installed on mobile devices using the Tableau Mobile app, which is available for iOS and Android devices. The app lets users access and interact with their Tableau dashboards and reports on the go and receive alerts and notifications. Users can also use the app to capture data from their device’s camera, microphone, or location and use it in Tableau.

Tableau is not completely free, but it offers different pricing plans and options for different types of users and needs. For example, Tableau Public is a free version of Tableau that allows anyone to create and publish visualisations on the web, but with limited features and data privacy. Tableau Desktop is the main product that enables users to create and edit dashboards and reports, and it has a free trial period and a discounted price for students and teachers.

Tableau can benefit any department that works with data and needs to make data-driven decisions. Some examples of departments that use Tableau include the following:
a) Marketing: Tableau can help Marketers analyse customer behaviour, segment customers, measure campaign performance, optimise marketing mix, and more.
b) Sales: Tableau can help Salespeople track sales performance, forecast sales, identify opportunities, manage accounts, and more.
c) Finance: Tableau can help Finance professionals monitor financial performance, analyse profitability, manage budgets, forecast cash flow, and more.
d) Operations: Tableau can help operations Managers optimise processes, improve efficiency, reduce costs, manage inventory, and more.
e) Human Resources (HR): Tableau can help HR professionals measure employee engagement, retention, turnover, productivity, and more.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
Upcoming Office Applications Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Tableau Desktop Training
Tableau Desktop Training
Mon 17th Jun 2024
Mon 9th Sep 2024
Mon 2nd Dec 2024







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


