We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Modern consumers demand faster deliveries, real-time tracking, and high-quality services, which brings the need for advanced Logistics solutions. This is where Logistics Management comes in. But do you know What is Logistics Management?
It's a strategic approach that ensures timely product movement and storage through efficient resource allocation, technology integration, and strategic planning. Meeting the immediacy and precision that today's consumers seek, Logistics Management goes beyond just fulfilling current needs.
As businesses expand globally, the need to manage complex Supply Chains spanning multiple countries and regions is becoming very important. Thus, it’s crucial to learn about this approach. Read this blog to understand everything about What is Logistics Management and how it can optimise the transportation, distribution, and storage of goods.
Table of Contents
1) Logistics Management definition
2) Evolution of Logistics Management
3) Key components of Logistics Management
4) The importance of effective Logistics Management
5) Challenges in modern Logistics Management
6) Technological advancements in Logistics Management
7) Conclusion
Logistics Management definition
Logistics Management is, at its core, a discipline that organises, implements, and controls the flow and storage of goods, services, and information. This process is not just limited to transportation. Instead, it represents an integrated effort that combines aspects of procurement, conversion, and distribution from the point of origin to the point of consumption.
The primary aim of Logistics Management is efficiency. It ensures that the right product reaches the right destination at the right time. This is achieved through a holistic approach that looks at every step, from sourcing raw components to the delivery of the final product to the end consumer.
Control is also a significant theme in Logistics Management. By controlling the movement and storage of products in a cost-effective manner, businesses can improve their system and meet the needs of their customers. Thus, it acts as a bridge, ensuring a seamless connection between production processes and the consumers who rely on their products.
Transform your Logistics Management expertise: Join our Logistics Management Training today!
Evolution of Logistics Management
After getting the answer to the question: What is Logistics Management? The primary concern is how this approach has evolved. Often, when one hears the term Logistics Management, images of large warehouses, trucks, and shipment processes come to mind. However, this is merely scratching the surface of a multifaceted discipline. It encompasses a comprehensive string of procedures, each aiming for smooth resource transmission.
Historically rooted in military operations, the term Logistics once referred to the strategic movement and allocation of troops and supplies. However, in the realm of modern business, its significance has expanded exponentially. Now, it doesn't just ensure that products reach consumers in a timely fashion. It also emphasises the necessity of optimising these routes for cost, efficiency, and sustainability.
One cannot discuss Logistics without mentioning the pivotal role of information. As tangible products traverse from producer to consumer, a parallel flow of data begins. This includes crucial details like stock quantities, transport timelines, and client information. This digital trail provides invaluable insights, enabling businesses to anticipate demand, streamline resources, and offer timely communication to clientele.
Additionally, the realm of Logistics Management is not static. In our rapidly digitalising world, e-commerce platforms and globalised trade paradigms have redefined traditional Logistics frameworks. Advanced software, real-time tracking tools, and predictive analytics have become indispensable allies. These tools not only ensure physical items move efficiently but also facilitate the strategic leveraging of data to adapt to market fluctuations and evolving consumer expectations.
This digitalisation has made the meaning of Logistics Management multifaceted. It’s now an intricate blend of strategy, technology, and foresight. Together, these components collaborate to form the intricate dance that ensures products and services reach their destinations seamlessly in today's interconnected global marketplace. The figure given is an example of understanding Transport Logistic System in modern businesses:
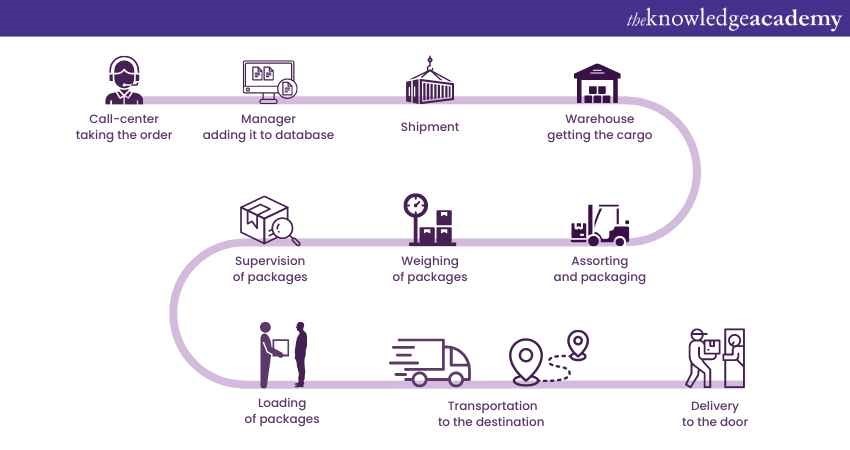
Key components of Logistics Management
Behind the simple act of moving goods lies Logistics Management. Beyond just transportation, it encompasses numerous components, each integral to the smooth functioning of the Supply Chain. From managing inventory levels to forging strong relationships with vendors, it is the silent force that keeps the wheels of commerce turning.
a) Inventory Management: Tracks and forecasts product levels. Balances demand with available stock without overstocking.
b) Warehousing: Stores products before distribution. Prioritises space optimisation and minimises storage duration.
c) Transportation: Selects optimal transport modes, like road or air. Also, aims for timely, cost-effective product delivery.
d) Material handling: Manages in-house product movement. It includes tasks like loading and arranging items efficiently.
e) Packaging: Goes beyond simple wrapping. Packaging of goods ensures safe transport and aids in branding. Considerations often include material choice and environmental impact.
f) Information flow: Uses digital tools for improved Logistics. Information flow helps track shipments, optimise routes, and predict demands.
g) Vendor and customer relations: It involves building and maintaining partnerships. Further, streamlined collaborations can lead to enhanced efficiencies and cost savings.
h) Demand forecasting: Uses past data to predict future demand. Thus, demand forecasting helps businesses prepare and adjust strategies accordingly.
i) Distribution network design: Determines warehouse locations and product delivery paths. It is a crucial element in reaching global customers efficiently.
j) Reverse Logistics: Reverse Logistics involves managing returns and product recalls. It is a vital aspect in ensuring customer satisfaction and sustainable practices.
k) Risk management: Identifies potential Supply Chain disruptions. It involves developing strategies to mitigate or overcome these challenges.
l) Sustainability: Modern Logistics now emphasises eco-friendly practices. They focus on reducing environmental impact through various means.
The importance of effective Logistics Management
After you have learnt about What is Logistics Management, it’s time to understand its importance. From building a brand reputation to shaping strategic decisions, Logistics plays an indispensable role. Let's dive into its multifaceted significance and learn its pivotal elements:
a) Building trust through timely deliveries: A company's reliability is judged by its promptness, affecting its reputation and trustworthiness. By ensuring timely deliveries, businesses can win the trust and loyalty of their customers and partners. However, delays can lead to wider disruptions.
b) Achieving cost efficiency: Logistics Management is about utilising resources optimally. A structured system minimises wastages and redundancies, leading to significant operational savings.
c) Inventory optimisation: Overstocking increases capital and incurs costs, while stock-outs can halt production and result in lost sales. However, including Inventory Management is the key.
d) Meeting customer satisfaction: Consumers today expect quick deliveries. Thus, meeting their expectations enhances brand loyalty and overall customer satisfaction.
e) Staying Agile in dynamic markets: Markets change rapidly. Thus, an Agile Logistics system ensures businesses remain competitive and responsive to these shifts.
f) Global expansion and Logistics: For businesses eyeing international markets, proper management of Logistics helps navigate cross-border regulations and manage transportation effectively.
g) Risk management in Logistics: Disruptions can strain Logistics, but a robust strategy identifies potential risks and creates effective mitigation plans.
h) The push for sustainable Logistics: Sustainability in Logistics is crucial. Eco-conscious consumers favour green Logistics, which can also lead to cost benefits.
i) Laying the foundation for business growth: Logistics supports growth. A streamlined operation ensures a business can handle increased demands during expansion.
j) Achieving a competitive edge: Efficiency in Logistics provides a business advantage, positioning it ahead of competitors in the market.
k) Informed decision making through data: Real-time Logistics data is invaluable. It aids strategic decisions, optimising resource allocation, and proactive problem-solving.
l) Navigating the compliance labyrinth: Logistics ensures adherence to industry regulations, safeguarding businesses from legal complications and potential fines.
Learn how to craft market-winning strategies by joining our Product Management Training now!
Challenges in modern Logistics Management

As businesses expand, consumer expectations also rise. In such a scenario, navigating obstacles becomes vital. From grappling with geopolitical complexities to meeting ever-evolving customer demands, today's Logistics Managers find their roles increasingly challenging. Let's see what these challenges are that Logistics Managers face during Logistics Management:
Supply Chain disruptions
Disruption in the Supply Chain can be caused due to the following:
a) Natural disasters can halt transport routes, causing unforeseen delays.
b) Political upheavals can undermine stable supply sources.
c) Global events, like pandemics, unpredictably strain Logistics.
Increasing customer expectations
Increased customer expectations can be due to the following:
a) Today's customers often demand rapid deliveries, stressing Logistics speed.
b) Real-time tracking isn't just a perk; it's expected.
c) Quick, efficient customer service is now a standard.
Sustainability demands
Environmental demands can have the following impact on Logistics Management:
a) Many businesses face pressure to lower their carbon emissions.
b) Environmentally friendly packaging is becoming a norm.
c) Consumers lean towards businesses practising sustainable sourcing.
Learn how to lead your industry with our Industry Training - sign up today!
Geopolitical issues
Geopolitical issues can give rise to the following problems:
a) Trade disputes can inflate import/export expenses.
b) Sanctions can lead to abrupt Supply Chain modifications.
c) Cross-border taxation varies, complicating cost calculations.
Labour shortages
Shortage of skilled labour can be due to the following reasons:
a) Skilled drivers and operators are often in short supply.
b) Warehousing sees high turnover rates, affecting consistency.
c) Retaining skilled workers remains a persistent challenge.
Complex global Supply Chains
The vast network of global Supply Chain can hinder the following:
a) Effective communication across cultures is paramount. However, a lack of proper communication medium can disrupt the flow of information
b) Navigating diverse regulations is time-consuming.
c) Different countries mean varied payment methods.
Rising costs
With rising inflation comes the following challenges:
a) Fuel prices can be volatile, affecting transport costs.
b) Adhering to regulations can prove costly.
c) As economies grow, wages rise, pushing operational costs.
Data management challenges
With a vast network of Supply Chains, data can be prone to the following disruptions:
a) Merging different IT systems is a complex task.
b) Accurate, timely data is crucial for decision-making.
c) With rising cyber threats, data security is paramount.
Security concerns
Logistics Management can face security issues like the following:
a) Logistics is susceptible to cyber vulnerabilities.
b) Safeguarding goods from theft is crucial.
c) Each transportation mode has its security challenges.
Infrastructure limitations
Infrastructure challenges can also pose the following disruptions:
a) Some regions suffer from outdated transportation networks.
b) Ports or airports may face congestion issues.
c) Modern warehousing is a need, not a luxury.
Technological advancements in Logistics Management
Advancements like Artificial Intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), and automation are enhancing operational efficiency and reshaping the very core of Logistics practices. So, let’s have a look at how groundbreaking technologies are setting the course for the future of Logistics Management:
a) Adoption of AI and Machine Learning: AI improves demand forecasting, optimising inventory and reducing costs.
b) IoT in Supply Chain monitoring: IoT devices provide real-time tracking, enhancing transparency and efficiency.
c) Blockchain for secure transactions: Blockchain ensures tamper-proof transactions, bolstering trust in Supply Chain processes.
d) Automated warehousing solutions: Robotics and automation streamline warehousing, speeding up processing and reducing errors.
e) Drones for faster deliveries: Drones are revolutionising delivery processes, especially in hard-to-reach areas.
f) Augmented Reality (AR) in training and maintenance: AR tools assist with equipment maintenance and training, enhancing efficiency.
g) Predictive analytics for decision making: Analytics provide insights for proactive decisions, foreseeing potential Supply Chain disruptions.
h) Robotics Process Automation (RPA): RPA automates repetitive tasks, enhancing accuracy and reducing manual intervention.
i) 3D printing in Logistics: On-demand manufacturing becomes possible, reducing the need for vast inventories.
j) Smart containers and IoT: Using containers with sensors to monitor cargo conditions, ensuring product quality during transit.
k) Digital platforms and integration: Unified platforms streamline operations, improving collaboration between Logistics partners.
l) Self-driving vehicles: Autonomous trucks and ships can revolutionise long-haul deliveries, reducing human errors.
Conclusion
Understanding What is Logistics Management is crucial for modern businesses. It's the strategic coordination ensuring goods are efficiently moved and stored. This discipline emphasises streamlined processes and astute resource management. It showcases the necessity of foresight and proactive planning to address current and imminent demands.
Gain an in-depth understanding of optimising Supply Chain links with our Supply Chain Management Training - join today!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Logistics Management Training
Logistics Management Training
Fri 3rd May 2024
Fri 19th Jul 2024
Fri 27th Sep 2024
Fri 8th Nov 2024







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


