We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Financial Management stands as a critical pillar in the world of business, and it’s just as important in the IT field. Think of ITIL Financial Management as the financial playbook for delivering IT services. It’s all about making sure money matters are clear and above board, planning the budget wisely, keeping the accounts in check, and getting the most bang for your buck from IT spending.
In the evolving landscape of IT Service Management, understanding the nuances of ITIL Financial Management becomes crucial. In this blog, we will learn about ITIL Financial Management in detail, including its main processes, benefits, and roles and functions. Read ahead to learn more!
Table of Contents
1) What is the ITIL Financial Management?
2) Objectives of ITIL Financial Management in ITIL
3) Three main processes of Financial Management in ITIL?
4) Benefits of Financial Management in ITIL
5) Important Financial Management decision
6) Financial Management in ITIL: Roles and functions
7) Conclusion
What is ITIL Financial Management?
ITIL Financial Management fits into the ITIL framework like a glove, focusing on smart money moves in IT services. It’s all about putting financial resources where they’ll do the most good. From setting up the budget to keeping the books straight, managing costs, and even handling the nitty-gritty of charging and billing – it’s got it all covered.
This practice is like a financial compass for companies, guiding them to use their IT stash wisely and in line with their big-picture goals. By doing so, it plays a huge part in driving a company’s success and lining its pockets with profits.
Objectives of Financial Management in ITIL
The objectives of Financial Management in ITIL are varied but focused on effective management and optimisation of financial resources in providing IT services. Some key objectives include:
a) Cost optimisation: One of the primary objectives is to cost-optimise the services rendered in IT and investigate how waste can be reduced and the activities of the process streamlined.
b) Budget control: Financial Management in ITIL focuses on establishing and maintaining control of the amount budgeted to be spent on IT services. This usually involves monitoring expenditures, variance management, and ensuring expenditures are within the authorised budgets.
c) Financial planning: Financial Management involves planning future IT spending and investments. This requires forecasting and identifying costs, evaluating opportunities for cost savings or optimisation, and ensuring that monies are strategically allocated to support business goals.
d) Risk management: Financial management aims to manage the financial risks of investments and IT expenditures. This includes identifying the financial risks and responding by putting controls in place to minimise these risks. Additionally, it ensures that financial regulations and policies support them.
Enhance your skills in service desk operations with our ITIL® 4 Practitioner: Service Desk Training. Join today to excel in IT service management!
Three main processes of Financial Management in ITIL
Proper management of finances is essential for IT services. The three main processes of Financial Management in ITIL are:
Budgeting
Budgeting refers to calculating the potential income and expenditure of funds for an organisation. It is essential as it helps companies track and monitor their spending habits. Any signs of overspending can be fixed in its early stages.
Determining the budget in advance allows organisations to compare their monthly income and costs with the pre-set values. They can change their spending or saving methods based on the data collected from that comparison.
Budgeting is done once a year, and it comes with multiple benefits. It can help your businesses in various ways:
a) Budgeting helps organisations to plan their operations in advance
b) It provides an incentive for employees to achieve their business goals
c) Comparing the monthly expenditure to the budget can reveal data that can be used to control certain financial activities
d) It can be used as a factor for managers' performance reviews.
Accounting
Accounting keeps track of an organisation's spending habits and anything that constitutes financial information. The credibility of a company's financial statements relies on the quality of accounting practices, and it helps IT companies identify the areas where cost saving is possible. Some of the cost elements used by accounting are:
a) Operational costs
b) Capital costs
c) Direct costs
d) Indirect costs
e) Fixed costs
f) Variable costs
Identifying ITIL Advantages and Disadvantages, meticulous financial documentation aids future performance assessment, enhancing transparency, accountability, and compliance. The method of accounting is beneficial to companies in other ways as well:
a) Improved decision-making
b) Company results can be communicated effectively to various groups like stakeholders, investors, creditors, etc.
c) Data on financial assets and liabilities are recorded properly
Charging
Charging refers to the practice of being paid by customers after companies offer the required services. The conditions to pay differ with the type of organisation. IT companies can be internal service providers or serve external customers. The former kind of organisation is not required to bill their services and only needs to allocate their costs, while the latter needs to prepare bills for all their services. Discover best practices in ITIL Change Management to optimise financial processes and service delivery.
Learn all about the concept of customer journey and user communities by signing up for our ITIL® 4 Specialist: Drive Stakeholder Value DSV course now!
Benefits of Financial Management in ITIL
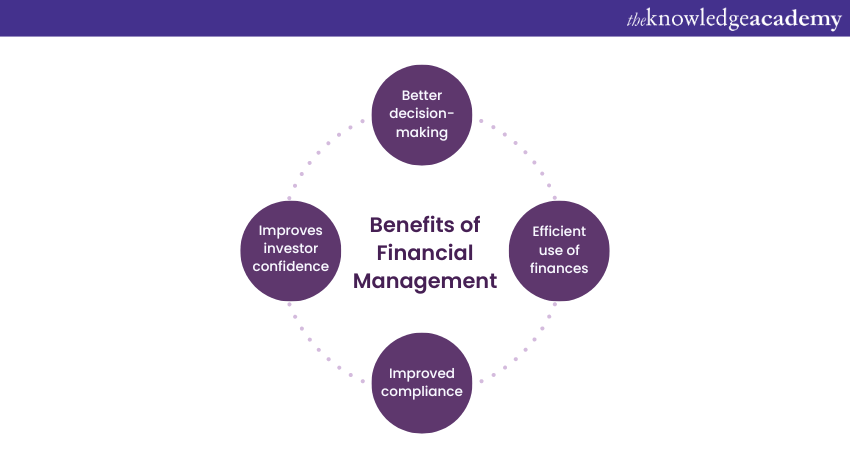
Implementing proper Financial Management practices saves costs and improves ITIL projects' overall efficiency and effectiveness. Let's explore the benefits:
a) Better decision-making: Processes like accounting ensures the documentation of every financial transaction of the company. The ability to access all this data allows Financial Managers to make faster and better decisions. It also helps increase clarity on the financial situation of companies.
b) Efficient use of finances: Managing and maintaining finances properly helps sustain a company by preventing it from facing financial difficulties. Processes like budgeting and accounting provide clear information, which can be used to identify areas where certain activities may have gone over budget or where allotted funds need to be utilised properly.
c) Improved compliance: Proper Financial Management protects companies from illegal activities like fraud, tax evasion, and money laundering. Since financial policies and laws, such as tax laws, can change at any time, it is essential to maintain a systematic record of finances. This can help protect the company against the adverse consequences of such changes.
d) Improves investor confidence: Managing finances properly makes it easier for stakeholders and investors to understand an organisation's financial situation at any time. The quality of Financial Management in IT organisations can reflect their integrity and attract more investors.
Financial Management in ITIL: Roles and Functions
Numerous roles or sub-processes are included in ITIL Financial Management, such as Financial Management Process Owner, Financial Manager, Financial Auditor, etc. Let's look at some of the Financial Management specific roles and their functions in detail:
Financial Manager
A Financial Manager is in charge of handling all the financial activities of an IT organisation, and their responsibilities include conducting data analyses and providing financial advice to Senior Managers. Some of the primary duties of a Financial Manager include the following:
a) Budget, accounting, and charging planning: Financial Managers are responsible for budgeting, accounting, and charging in IT companies. They take care of an organisation's financial aspects, including raising and allocating funds.
One of their biggest challenges is balancing equity and debt while trying to raise funds. This is followed by allocating funds based on organisation size and the medium used to raise funds.
b) Aiming for profit: Businesses thrive on profits, proving the need for proper planning and control over financial activities to achieve it. But profits depend on factors like business competition and the country's economic state. Financial Managers are responsible for ensuring that the company aims to attain profits.
c) Reviewing Key Performance Indicators (KPI): KPIs refer to quantifiable measures of performance in a given timeframe. Financial KPIs help determine the economic standpoint of the company. Financial Managers shoulder the responsibility of identifying the KPIs and analysing their results. Here are some of the vital financial KPIs:
1) Gross profit margin
2) Liquidity metrics
3) Burn rate
4) Debt-to-equity ratio
5) Accounts payable
6) Accounts receivable
Financial Auditor
Undergoing audits is a necessity for any company that produces an income.Financial Auditors are responsible for ensuring that the organisation's monetary records are kept in order and that they follow the latest taxation laws and financial policies. Let's look at a Financial Auditor's responsibilities in detail:
a) Reviewing financial statements: Financial Auditors help organisations create their financial statements by reviewing them. If the Auditor detects any errors, they are suggest improvements to the financial records and advise the top executives to follow specific strategies.
b) Conduct concentrated audits: Although Financial Auditors are responsible for evaluating organisations as a whole, sometimes they're required to perform audits for specific departments alone.
When organisations need information regarding a certain department's contribution to the company's financial well-being, department-specific audits are conducted. It helps in identifying payroll fraud activities as well.
c) Fraud detection: Financial Auditors can trace back fraudulent activities to their origin once detected. Various auditing techniques and software can be used to simplify the process. Fraud, like data duplication, can be easily detected using advanced auditing tactics and software.
There are certain skills that Financial Auditors must possess. This includes persistence, good decision-making skills, curiosity, accuracy, and more. These skills are not only crucial for financial auditors but also align with qualities that can enhance efficiency and effectiveness in various roles within ITIL careers.
Build your career in the sector of IT Service Management (ITSM) with an ITIL certification. Sign up for our ITIL® 4 Foundation Certification Training course now!
Important Financial Management decisions
Effective Financial Management is a crucial aspect of ITIL implementation. It ensures that IT services align with business goals while maintaining cost efficiency. Several critical decisions in ITIL Financial Management play a pivotal role in achieving these objectives. Let's delve into some crucial considerations:
Chargeback − to charge or not to charge
One fundamental decision is whether to implement chargeback mechanisms. Chargeback involves allocating IT costs to specific business units based on their service usage.
This decision requires a thorough evaluation of the organisation's structure, culture, and business objectives. Chargeback can promote cost accountability among business units, encourage responsible resource usage, and drive more transparent Financial Management.
Notional charges
Notional charges consist of assigning hypothetical costs to internal departments within an organisation without actual fund transfers taking place. This approach facilitates a better and more holistic understanding of resource consumption patterns and encourages responsible usage without the complexities of financial transactions.
Notional charges serve as a stepping stone towards more comprehensive financial management strategies, offering insights into cost distribution while maintaining flexibility in resource allocation.
Tiered subscription
Tiered subscription models provide customers with a range of service levels at varying costs. This approach tailors services to individual needs, granting flexibility and value within the ITIL 4 Service Value System. Customers can choose a tier that aligns with their requirements and budget.
It optimises resource allocation, ensuring resources are efficiently utilised while providing options for scalability. This model enhances customer satisfaction, as services are customisable and adaptable, ultimately driving better cost-effectiveness and service delivery.
Metered usage
Metered usage, a pivotal component of effective IT Financial Management, involves real-time tracking and billing based on actual resource consumption. This approach improves cost transparency, allowing precise allocation of expenses according to usage.
By measuring data, processing, or network consumption, organisations gain insights into service demand patterns, enabling informed decisions on resource provisioning. Metered usage optimises budget utilisation, prevents wastage through over-provisioning, and aligns IT expenditures with business needs, promoting economic efficiency and resource accountability.
Fixed or user cost
When considering cost models in ITIL Financial Management, the choice between fixed and user-based costs is pivotal. Fixed costs offer predictability by charging a consistent amount for services, simplifying budgeting.
User-based costs, conversely, reflect actual usage, providing accuracy but potentially causing fluctuations in expenses. Deciding hinges on the organisation's preference: stability with fixed costs or precision with user-based charges. Striking the right balance ensures efficient resource allocation and aligns financial strategies with business needs.
Financial analysis and reporting
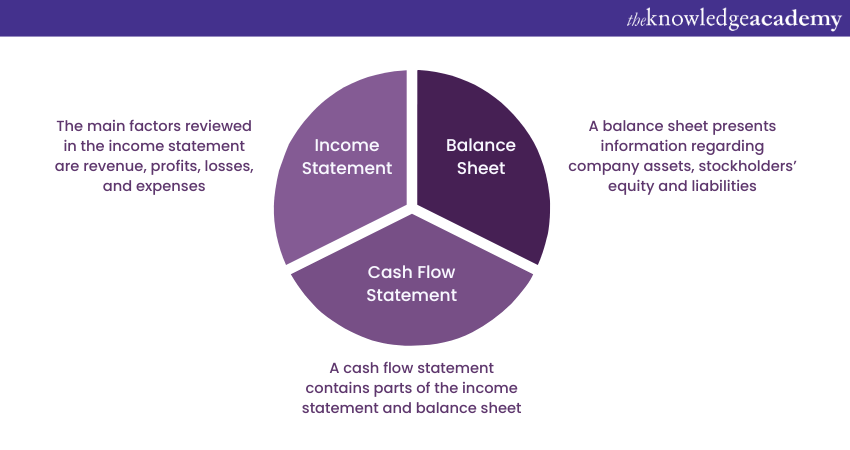
Financial analysis and reporting refer to companies' financial data collection and analysis. The data includes company expenditure, profit, cash flow, etc., and it helps organisations keep their finances in check. Financial analysis and reporting are also important for tax reasons. Different types of financial reporting can also prove helpful for IT companies:
a) Income statement: As the name suggests, an income statement documents the company income and expenses collected over a specific period of time. The main factors reviewed in this process include revenue, profits, losses, and expenses.
b) Balance sheet: A balance sheet presents information regarding company assets, stockholders' equity, and liabilities. It reflects the company's financial situation in a monthly or quarterly period. Potential investors who wish to know more about the company can also use the balance sheet.
c) Cash flow statement: A cash flow statement is an essential financial report. It provides data on the total revenue generated by the company and the areas where the cash is being used. It can prove extremely useful for businesses as it contains components from the income statement and balance sheet.
Service invoicing
Service-oriented industries, such as IT, hospitality, media, etc., are required to send invoices to their customers. Service invoices help organisations track their services provided to customers. Once a service order is placed and confirmed, a service sheet is prepared.
The service sheet is an integral part of service invoicing as it contains all the information regarding the service order. This includes phone numbers of field contractors, field engineers, and approving authorities.
Organisations then design the service invoice, which includes several elements added to the service invoice template:
a) Organisation logo
b) Date of invoice
c) Date of payment which is due
d) Invoice amount
e) Terms of payment
Conclusion
By now, you’ve probably got a good grip on ITIL Financial Management. It’s like the financial whiz of IT services, juggling tasks like budgeting, accounting, and cost-cutting, all while making sure every penny counts.
In today’s fast-paced world, this practice is super important for companies to get the most out of their investments, slash unnecessary expenses, and boost their overall game. So, think of ITIL Financial Management as the savvy business coach that helps organisations score big in the profit league!
Gain an understanding of how to implement digital and IT strategies with our ITIL® 4 Leader: Digital and IT Strategy Certification - sign up now!
Frequently Asked Questions

The key metrics and KPIs for measuring financial performance in ITIL include cost per service, cost per user, ROI of IT investments and budget variance. These provide insights into cost efficiency, resource allocation and the overall financial health of IT services.

ITIL Financial Management contributes to overall IT service improvement by optimising cost-effectiveness and ensuring alignment of IT expenditures with business objectives. It enables informed decision-making to enhance service quality and delivery.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various ITIL® Certification Training, including ITIL 4 Foundation Certification Course, ITIL 4 Specialist: Create Deliver and Support CDS, and ITIL 4 Specialist: Drive, Plan and Improve DPI. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into ITIL 4 Guiding Principles.
Our IT Service Management Blogs cover a range of topics related to ITIL 4, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Business Improvement skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming IT Service Management Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 ITIL® 4 Foundation Certification Course
ITIL® 4 Foundation Certification Course
Mon 29th Jul 2024
Wed 31st Jul 2024
Mon 5th Aug 2024
Wed 7th Aug 2024
Sat 10th Aug 2024
Mon 12th Aug 2024
Wed 14th Aug 2024
Mon 19th Aug 2024
Wed 21st Aug 2024
Sat 24th Aug 2024
Tue 27th Aug 2024
Thu 29th Aug 2024
Mon 2nd Sep 2024
Wed 4th Sep 2024
Sat 7th Sep 2024
Mon 9th Sep 2024
Wed 11th Sep 2024
Mon 16th Sep 2024
Wed 18th Sep 2024
Sat 21st Sep 2024
Mon 23rd Sep 2024
Wed 25th Sep 2024
Mon 30th Sep 2024
Wed 2nd Oct 2024
Sat 5th Oct 2024
Mon 7th Oct 2024
Wed 9th Oct 2024
Mon 14th Oct 2024
Wed 16th Oct 2024
Sat 19th Oct 2024
Mon 21st Oct 2024
Wed 23rd Oct 2024
Mon 28th Oct 2024
Wed 30th Oct 2024
Sat 2nd Nov 2024
Mon 4th Nov 2024
Wed 6th Nov 2024
Mon 11th Nov 2024
Wed 13th Nov 2024
Sat 16th Nov 2024
Mon 18th Nov 2024
Wed 20th Nov 2024
Mon 25th Nov 2024
Wed 27th Nov 2024
Sat 30th Nov 2024
Mon 2nd Dec 2024
Wed 4th Dec 2024
Mon 9th Dec 2024
Wed 11th Dec 2024
Sat 14th Dec 2024
Mon 16th Dec 2024
Wed 18th Dec 2024
Mon 6th Jan 2025
Wed 8th Jan 2025
Mon 13th Jan 2025
Wed 15th Jan 2025
Mon 20th Jan 2025
Wed 22nd Jan 2025
Mon 27th Jan 2025
Wed 29th Jan 2025
Mon 3rd Feb 2025
Wed 5th Feb 2025
Mon 10th Feb 2025
Wed 12th Feb 2025
Mon 17th Feb 2025
Wed 19th Feb 2025
Mon 24th Feb 2025
Wed 26th Feb 2025
Mon 3rd Mar 2025
Wed 5th Mar 2025
Mon 10th Mar 2025
Wed 12th Mar 2025
Mon 17th Mar 2025
Wed 19th Mar 2025
Mon 24th Mar 2025
Wed 26th Mar 2025
Mon 31st Mar 2025
Wed 2nd Apr 2025
Mon 7th Apr 2025
Wed 9th Apr 2025
Mon 14th Apr 2025
Wed 16th Apr 2025
Tue 22nd Apr 2025
Mon 28th Apr 2025
Wed 30th Apr 2025
Tue 6th May 2025
Mon 12th May 2025
Wed 14th May 2025
Mon 19th May 2025
Wed 21st May 2025
Tue 27th May 2025
Mon 2nd Jun 2025
Wed 4th Jun 2025
Mon 9th Jun 2025
Wed 11th Jun 2025
Mon 16th Jun 2025
Wed 18th Jun 2025
Mon 23rd Jun 2025
Wed 25th Jun 2025
Mon 30th Jun 2025
Wed 2nd Jul 2025
Mon 7th Jul 2025
Wed 9th Jul 2025
Mon 14th Jul 2025
Wed 16th Jul 2025
Mon 21st Jul 2025
Wed 23rd Jul 2025
Mon 28th Jul 2025
Wed 30th Jul 2025
Mon 4th Aug 2025
Wed 6th Aug 2025
Mon 11th Aug 2025
Wed 13th Aug 2025
Mon 18th Aug 2025
Wed 20th Aug 2025
Mon 25th Aug 2025
Mon 1st Sep 2025
Wed 3rd Sep 2025
Mon 8th Sep 2025
Wed 10th Sep 2025
Mon 15th Sep 2025
Wed 17th Sep 2025
Mon 22nd Sep 2025
Wed 24th Sep 2025
Mon 29th Sep 2025
Wed 1st Oct 2025
Mon 6th Oct 2025
Wed 8th Oct 2025
Mon 13th Oct 2025
Wed 15th Oct 2025
Mon 20th Oct 2025
Wed 22nd Oct 2025
Mon 27th Oct 2025
Wed 29th Oct 2025
Mon 3rd Nov 2025
Wed 5th Nov 2025
Mon 10th Nov 2025
Wed 12th Nov 2025
Mon 17th Nov 2025
Wed 19th Nov 2025
Mon 24th Nov 2025
Wed 26th Nov 2025
Mon 1st Dec 2025
Wed 3rd Dec 2025
Mon 8th Dec 2025
Wed 10th Dec 2025
Mon 15th Dec 2025
Wed 17th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


