We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
A city planner designs a city to ensure seamless connections between roads and services, much like an Integration Architect manages an enterprise's computer systems, software applications, and data systems. In today's world, "What is an Integration Architect?" is a crucial question because these professionals design technical frameworks and strategies that enable transparent interconnection across various technologies, ensuring smooth and secure data flows to keep an organisation running efficiently.
Table of Contents
1) Understanding What is Integration Architecture
2) Types of Integration Architecture
3) Importance of Integration Architecture
4) Components Integration Architecture
5) Benefits of Integration Architecture
6) Roles and responsibilities of an Integration Architect
7) Conclusion
Understanding What is Integration Architecture
Integration Architecture represents a systematic approach and a detailed plan that outlines how an organisation’s array of software applications, systems, and technological assets can function together compatibly. This encompasses the strategies for design and execution, as well as the instruments and middleware solutions that facilitate efficient links and data exchange among different IT landscapes.
It is comparable to constructing a universal connector. Such an architectural framework ensures the effortless transfer and amalgamation of information throughout the various systems within an organisation.
Types of Integration Architecture
There are different Types of Integration Architecture. Each has its distinctive and beneficial design, meant to fulfil specific needs and objectives. Here are the main types:
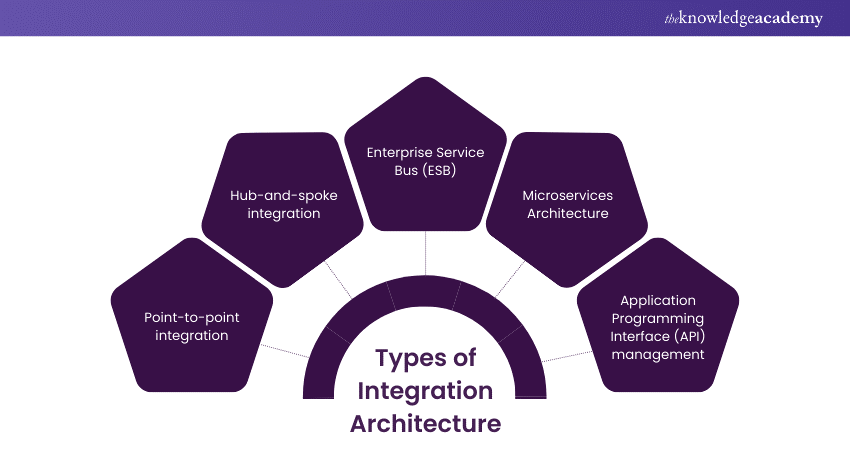
1) Point-to-point integration: It is the basic and the simplest form of integration. In simple words, there are direct ways between the two places. It may be defined as the connection of two systems that share data with one another. Therefore, connecting more systems brings complexity and managing them becomes confusing.
2) Hub-and-spoke integration: Think of a central hub, much like a main train station, from which all the spokes emanate in different directions. Here, the systems will be interfaced with the individual system through a hub, which relays the messages to the said system (the spokes). This simplifies connections but can create a bottleneck if the hub becomes overburdened.
3) Enterprise(us (ESB): This is much like providing an intelligent transit system across the city that could accommodate traffic routing through the most efficient paths. The ESB offers a flexible approach for systems to interoperate on one common platform. It is designed to support a very high level of integration for various applications. Also, it is equipped with high-end features like message transformation and routing.
4) Microservices Architecture: Think of a bicycle trail system that connects several city neighbourhoods so that each isolated trail connects with others as necessitated. Microservices architecture represents the architecture of applications broken down into more minor, related services communicating over a network. This approach offers high scalability and the flexibility to use different technologies for different services.
5) Application Programming Interface (API) management: Think of APIs as public transport manual that everyone can read, to know how to get from point A to B. API management includes the development and administration of interfaces. Through these applications can communicate to assure not only secure but also controlled data exchange between organisational systems and systems from the outside environment.
Importance of Integration Architecture
Integration Architecture acts as the backbone for various technological systems within an organisation, facilitating effective communication and leading to several benefits:
1) Improved effectiveness: Integration Architecture enables the sharing of data and processes across various systems, eliminating redundancy of efforts and streamlining operations. This can significantly reduce the resources and time needed to carry out tasks.
2) Better data quality and accessibility: Efficient system integration allows organisational data to be shared and updated in real-time. Minimises errors and ensures decision-makers can access valid and current information.
3) Enhanced agility: The ever-changing business world demands readiness for change. Integration Architecture offers flexibility, allowing the IT environment to integrate new technologies or processes without interrupting operations.
4) Scalability: As the company grows, so does its IT system. The proper Integration Architecture grows with the business, supporting new integrations and data volumes without a decrease in performance.
5) Improved customer satisfaction: Integrating backend systems, like inventory management, with frontend systems, like e-commerce platforms, leads to seamless service delivery. This results in better response times, personalisation, and service efficiency.
6) Cost saving: Although setting up an Integration Architecture requires an initial investment, significant long-term cost savings are realised through reduced manual labour, fewer errors, and lower maintenance costs.
7) Compliance and security: Data is an important asset, so consistency and security measures are paramount. Integration Architecture enforces data governance policies and security measures across all systems, aiding compliance with regulatory requirements.
Components of Integration Architecture
Here is the list of components that makes Integration Architecture:
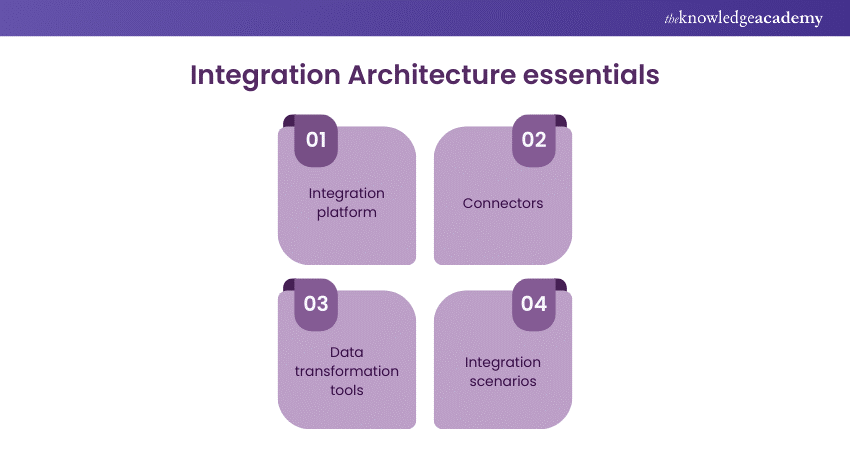
Integration platform
An Integration platform serves as the foundation of any robust Integration Architecture. It acts as a workhorse. This way, it lets an organisation's software, systems, and services communicate. They can also work together. Think of it as the nerve centre of Enterprise IT. It manages the flow of data across different systems. They can be on-premises or in the cloud. An effective Integration platform makes it easy to connect various IT assets.
It offers tools and features like messaging, application interfaces, and process orchestration. It supports integration patterns, including point-to-point, hub-and-spoke, and microservices architectures. It provides a unified environment for integration efforts. This plays a critical role in improving efficiency, agility, and scalability.
Connectors
Connectors are the bridges between systems, applications, or services. They allow them to communicate and share data. These adapters translate and route messages between systems. They bridge format, protocol, and standard differences. Connectors are vital for minimising custom coding and simplifying the integration process. They can range from simple, off-the-shelf connectors for popular applications and databases.
They can also be more complex, custom-built connectors for specific enterprise needs. A good Integration Architecture will have a rich library of connectors. They enable fast and flexible integration across many IT assets.
Data transformation tools
Data transformation tools are crucial in Integration Architecture. They convert data from one format or structure to another. This ensures that different systems can understand and use it. This step is vital when combining systems with varying models of data. It's also key for gathering data from many sources for analytics and reporting.
The tools can do simple tasks, like changing field names. They can also do complex tasks. These include data cleansing, validation, and aggregation. Data transformation is crucial for data integrity and quality. It enables accurate, timely insights.
Integration scenarios
Integration scenarios describe the use cases and patterns for integration within an organisation. These scenarios are blueprints. They guide how systems support business processes and goals. For example, tasks include syncing customer data across CRM and ERP systems. Automating supply chain operations accomplishes this.
Connecting inventory management systems with vendor platforms does it. Another task is enabling real-time data analytics. Integrating transaction systems with data warehouses does this. Understanding and defining these scenarios is critical. They are key for choosing the right integration strategies, technologies, and tools. It also helps focus on integration efforts by business impact. This ensures that resources support the most critical operations.
Benefits of Integration Architecture
Integration Architecture is crucial in modern businesses. It helps them work well and adapt. This lets them give great customer experiences. Here are the benefits of Integration Architecture:
1) Cost reduction
Integration Architecture offers several avenues for cost reduction within an organisation:
a) Elimination of redundant systems: Get rid of redundant systems. They can do this by combining systems and apps. This merge cuts maintenance costs, licensing fees, and the need for more hardware.
b) Streamlined processes: Integration Architecture enables automation and streamlining of business processes. This automation reduces manual intervention. It also cuts errors and boosts efficiency. This leads to cost savings.
c) Efficient resource utilisation: Integration Architecture enables better resource use. It does this by optimising data flow and sharing resources across different systems. This optimisation minimises idle resources. It ensures that we use infrastructure investments well.
d) Scalability and flexibility: Scalability and flexibility are key. Well-designed Integration Architecture can handle changes and expansions without added costs. Scalable integration solutions let businesses grow. They do so without high costs for restructuring or re-implementing systems.
e) Reduced IT support costs: IT costs will be reduced. Organisations can centralise IT management and support with integration. This central approach reduces the need for many IT teams. They support different systems. This cuts support costs.
Do you want to learn how to design a support strategy? Register now for our Enterprise Architect Training!
2) Enhanced customer Satisfaction
Integration Architecture contributes to improved customer satisfaction in the following ways:
a) Seamless customer experience: Integration Architecture connects customer-facing systems. These include websites, mobile apps, and CRM platforms. This integration enables a collective view of customer interactions and data. It leads to personalised and consistent channel experiences.
b) Faster response times: Integration Architecture enables real-time data synchronisation and system communication. As a result, businesses can answer customer inquiries. They can process orders and solve problems more quickly. This improves overall satisfaction.
c) Tailored offerings: Integrated systems show a customer's preferences, behaviours, and history. This insight helps organisations customise products, services, and marketing for each customer. It boosts relevance and satisfaction.
d) Improved service quality: Integration Architecture boosts service quality. It helps departments like sales, marketing, and support work together. This collaboration ensures that we handle customer inquiries well. It also ensures that customers get consistent and accurate information.
3) Improved application management and analysis
Integration Architecture enhances application management and analysis capabilities in the following ways:
a) Centralised data management: Integration Architecture centralises data from different sources. It puts it into a single repository, making it easier to manage and analyse. This central data hub lets organisations do advanced analytics. It helps them find insights and make data-driven decisions.
b) Real-time reporting and monitoring: Integration Architecture enables real-time data sync and reporting. It gives organisations up-to-date insights into business performance. Monitoring key metrics in real-time allows for proactive decisions. It also allows for faster responses to market changes.
c) Enhanced Business Intelligence: Integrated systems let organisations get valuable insights from data. They do this by combining information from many sources. This complete view of data makes deeper analysis easy. It helps find trends and do predictive modelling. It lets organisations improve processes and drive innovation.
d) Simplified Application Lifecycle Management (ALM): Simplified Application Lifecycle Management (ALM) features an Integration Architecture. It streamlines application deployment, maintenance, and retirement by providing a unified framework for managing connected systems. This simplification cuts complexity, downtime, and application alignment with business goals.
4) Increased company productivity
Integration Architecture boosts productivity across the organisation through:
a) Automated workflows: Integration Architecture boosts service quality. It helps departments like sales, marketing, and support work together. Automation cuts manual work. It speeds time-to-market and frees employees to focus on higher-value tasks.
b) Collaborative tools and communication: Integration Architecture makes it easy for tools to collaborate. These tools include email and document sharing. Integrated communication systems facilitate teamwork, knowledge sharing, and decision-making, increasing productivity and innovation.
c) Unified access to information: Employees get a unified view of information and resources. It's across systems. This comes from Integration Architecture. This single access point removes the need to switch between apps. It also boosts efficiency and cuts down on search time for information.
d) Mobile and remote access: The architecture supports mobile and remote access. It lets people access critical business systems and data. Employees can access information. They can also collaborate with colleagues and perform tasks from anywhere. This enhances productivity and allows flexible work.
Learn how you can gather Integration requirements with our Integration Architect Training!
Roles and responsibilities of an Integration Architect
The role of an Integration Architect is critical. They design, implement, and maintain integration solutions within an organisation. Here are the key responsibilities and roles associated with an Integration Architect:
1) Solution design: The Integration Architect designs integration solutions. The solutions must meet the organisation's business requirements. To create strong systems, understand a company's processes, data flows, and system layouts.
2) Technology evaluation: Integration Architects evaluate many integration technologies, platforms, and tools. They select the most suitable ones for the organisation's needs. They stay updated on new trends and advancements in integration tech. They do this to ensure that the chosen solutions follow industry best practices.
3) Standards and governance: Integration Architects set standards and guidelines for projects. They aim to ensure consistency, reliability, and security. They define governance frameworks for managing integration assets, setups, and lifecycle processes.
4) Collaboration and communication: Collaboration and Communication are key. Integration Architects work with stakeholders. The stakeholders come from different business units, IT teams, and external partners. They gather requirements. They explain design decisions. They align solutions with business objectives. Good communication is vital. They help translate technical concepts into understandable terms for non-technical stakeholders.
5) Architecture documentation: Integration Architects document architectures, designs, and patterns. They use industry-standard notations and tools. Clear documentation is comprehensive. It ensures stakeholders share a understanding of the integration solution and its parts.
6) Implementation oversight: Integration Architects supervise the integration solution implementation. They offer guidance and technical leadership to development teams. They ensure that they build integration designs to specs, standards, and best practices.
7) Performance optimisation: Integration Architects optimise integration solutions for performance, scalability, and reliability. They find and fix performance bottlenecks. They make data processes faster. They design fault-tolerant architectures to ensure high availability.
8) Security and compliance: Integration Architects address security and compliance requirements. They do this by adding strong authentication and authorisation. They also add encryption and data protection to integration solutions. They ensure that Integration Architectures follow industry regulations and organisational security policies.
9) Troubleshooting and support: Integration Architects troubleshoot and fix complex integration issues. They work with development teams, system administrators, and support personnel. They offer technical expertise and guidance. They help during system outages, slow performance, and other incidents.
10) Continuous improvement: Integration Architects enhance integration solutions. They do this to meet evolving business needs, tech advances, and performance goals. They conduct post-implementation reviews, gather feedback, and identify opportunities for optimisation and innovation.
Are you interested in analysing and translating business requirements into Integration Requirements? Sign up for our Enterprise Integration Advanced Training now!
Conclusion
Integration Architects play a pivotal role in crafting, deploying, and enhancing integration frameworks. They are responsible for ensuring fluid interoperability among heterogeneous systems, facilitating the smooth flow of data and the simplification of operations. As experts, they contribute to improved productivity and customer satisfaction. By understanding "What is Integration Architect," organisations can adapt to changing business needs through effective Integration Architecture, fostering collaboration across different systems.
Enhance your auditing and logging techniques with our Identity and Access Management Architect Training!
Frequently Asked Questions

The best system Integration Architecture depends on the needs of an organisation. It also depends on its technical requirements and project goals. You must evaluate each option. The options are point-to-point integration, hub-and-spoke integration, ESB, microservices, and API management. You must find the best one for a given situation.

For system integration, many tools are available. They include Enterprise Service Bus (ESB) platforms like MuleSoft and Apache Camel. Also, there are Integration platform as a Service (iPaaS) solutions. Examples are Dell Boomi and Jitterbit. It includes messaging brokers like Apache Kafka. It also includes API management tools such as Apigee and Kong.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Enterprise Architect Training, including the Certified Enterprise Architect Professional (CEAP) Course, BCS Foundation and Practitioner Certificate in Enterprise and Solution Architecture Course, and Enterprise Integration Fundamentals Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Big Data Integration.
Our Business Improvement Blogs cover a range of topics related to Enterprise Architect Training, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Enterprise Architect skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Business Improvement Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Certified Enterprise Architect Professional (CEAP)
Certified Enterprise Architect Professional (CEAP)
Wed 31st Jul 2024
Wed 27th Nov 2024
Thu 20th Feb 2025
Thu 15th May 2025
Thu 31st Jul 2025
Thu 30th Oct 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


