We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
If not interpreted correctly, Data –the most important resource of modern organisations can turn out to be quite irrelevant during Business Analysis. This is where Tableau steps in. Tableau Data Visualisation makes it a piece of cake to format data in numerous ways and make the most out of it. Want to know how? This blog will help you with all you need to know about Tableau Data Visualisation, including its advantages and disadvantages, its importance and the different visualisations it provides.
Table of Contents
1) What is Tableau Data Visualisation?
2) Advantages of Data Visualisation in Tableau
3) Why is Tableau Data Visualisation important?
4) Installation of Tableau Data Visualisation
5) What are the different types of Data Visualisations?
6) Conclusion
What is Tableau Data Visualisation?
Data Visualisation can be defined as the graphical representation of information and data. Using visual elements such as charts, graphs and maps, Data Visualisation provides an accessible method to see and understand trends, patterns and outliers in data.
In addition, Data Visualisation provides an excellent way for employees or business owners to present their data to non-technical audiences without any confusion. In the modern world driven by Big Data, Data Visualisation tools and technologies are essential for analysing huge amounts of information and making data-driven decisions.
Now, pertaining to the Tableau software, it is designed to provide users with powerful Data Visualisation tools, turning unprocessed data into meaningful visual stories. Its user-friendly drag-and-drop interface simplifies intricate data, generating dynamic charts, graphs, and dashboards.
Further, real-time updates and interactive features help users facilitate in-depth exploration, allowing them to effortlessly identify patterns and trends. With a wide range of Data Visualisation choices, such as Heat Maps and Scatter Plots, Tableau ensures that data analysis is not just functional but also presented in a compelling way. This supports informed decision-making across various sectors.
Advantages of Data Visualisation in Tableau
Some of the many advantages that Data Visualisation with Tableau provides include the following:
1) It is intuitive: Many people find visuals much easier to comprehend than numbers or words. This means that people find Tableau Data Visualisations much more intuitive than any other method of representing data.
2) It facilitates simple data sharing: As data in it is visual form is easier to understand, it naturally leads to better analysis. This is because people can readily comprehend and draw conclusions from visualisations. Tableau makes it Visualisation is easy to use if you want to identify patterns, trends and outliers, which can help you analyse the data to make meaningful conclusions.
3) It facilitates better analysis: As Data Visualisation is easier to understand, it naturally leads to better analysis. This is because people are readily able to comprehend and draw conclusions from visualisations. It is easy to use a visualisation if you want to identify patterns, trends and outliers, which can help when you are analysing the data to make meaningful conclusions.
4) It offers interactive Data Visualisation: Tableau serves visual storytelling's purpose, making it easier for organisations to make better-informed decisions. Iit easily shares information, interactively explores opportunities and visualises patterns and relationships. This helps an organisation gain better insight into their data resources, which in turn helps them operate more efficiently and generate better revenue.
Unleash the potential of your business’ intelligence by signing up for our Business Intelligence Reporting Course – register now and elevate your business insights!
Why is Tableau Data Visualisation important?
Technological developments in the modern world have enhanced the importance of Data Visualisation. Data Visualisation helps people analyse, interact with and understand data better. Whether simple or complex, the right Data Visualisation can help streamline working processes by bringing everyone on the same page – regardless of how experienced they are.
There are a lot of reasons why businesses adopt Data Visualisation, a few of which are listed as follows:
1) Visualisation helps individuals and organisations gain a clearer understanding and better insights into a topic.
2) Visualisation helps individuals, and organisations predict the future quickly and make better-informed decisions.
3) Visualisation of data facilitates the convenient and efficient interpretation of data in large volumes.
4) Data Visualisation is known to convey information universally.
5) Data Visualisation makes it simpler to share one’s ideas with other individuals during the working process in an organisation.
6) Data Visualisation lets the concerned individuals know where they can adjust or make changes to their business working process for better results.
7) Data Visualisation provides scalability or the ability of a computing process to be used or produced in a range of capacities. Scalability refers to a computer application's ability to continue functioning at an optimum level even when the contextual data is altered in size or volume.
8) Data Visualisation makes interpretation easy for individuals in an organisation to track and identify trends and patterns and work on them accordingly.
It is difficult to think of any professional industry that is not positively impacted by data being made more understandable with the help of Data Visualisation. Almost every field benefits from a proper understanding of its data resources, including – government, finance, marketing and the history of consumer goods, service industries, education and sports. The practical, real-life application of Data Visualisation is undeniable, and visualising data in the proper context is one of the most useful professional skills one could develop.
The better one can convey their points visually – whether on a dashboard or a slide deck – the better their career in Data Analysis. As people rapidly update their skill sets to excel in an evolving data-driven world, it is increasingly valuable for professionals to know how to use data to make well-informed decisions. They can use visuals to explain the who, what, when, where, and how's. Data visualisation bridges the gap between traditional and visual learning.
Master Power BI for powerful business intelligence reporting. Register for our Microsoft Power BI Certification Training course and transform your data into actionable insights!
Installation of Tableau Data Visualisation
Depending on your chosen product, install the software on your computer. Once you agree to the license terms displayed, you can then confirm the installation by clicking on the Tableau Icon. Once the specified screen appears, you are ready to proceed. Here are the further steps involved:
a) You can then initiate the installation of Tableau Data Visualisation, by selecting the appropriate product based on your requirements and preferences.
b) Download the software onto your computer and proceed to install it. During installation, carefully review and accept the license agreement.
c) After completing the installation, verify its success by clicking on the Tableau Icon. A confirmation screen should appear, indicating that the installation was successful, allowing you to proceed with utilising Tableau for powerful and insightful data visualisation.
This streamlined process ensures a seamless setup, enabling users to harness the full capabilities of Tableau for effective data analysis.
What are the different types of Data Visualisations?
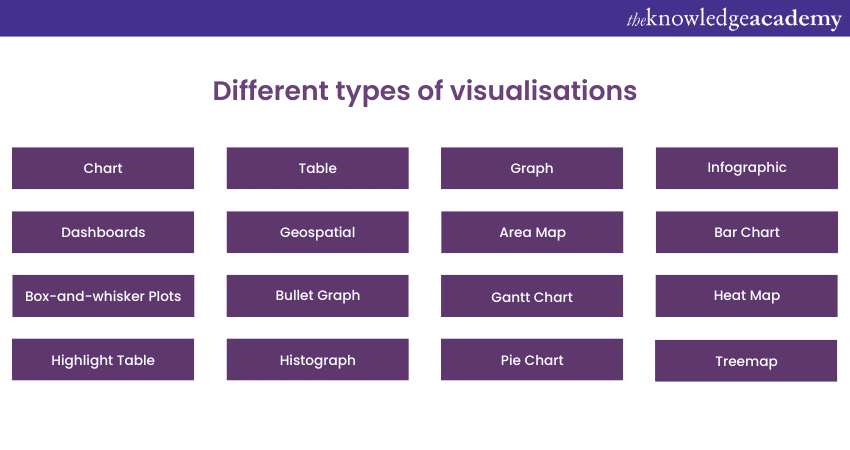
Whenever one thinks of Data Visualisation, their first thought is likely to be a simple bar graph or a pie chart. While these may be an important part of Data Visualisation and a common ground for many data graphics, the right visualisation should always be paired with the appropriate information set. A whole set of visualisation methods can be used to present data effectively and interestingly. You can use the following types of infographics to present your data:
1) Chart: A chart refers to information presented in a tabular and graphical form with data displayed along two axes. A chart can be in the form of a graph, diagram or map.
2) Table: A table can be defined as a set of figures that are displayed in rows and columns.
3) Graph: A graph is a diagram of points, segments, lines, curves or areas that are used to represent certain variables in comparison to each other. The information is visually represented – usually along two axes at a right angle.
4) Dashboards: A dashboard can be defined as a collection of visualisations and data displayed in one place, which usually helps with analysing and presenting data.
5) Geospatial: Geospatial is a visualisation that shows data in a mapped form using various shapes and colours to show the relationship or correlation between different pieces of data and specific locations.
6) Area Map: An area map is a form of geospatial visualisation. Area maps usually represent specific values set over a map of a country, state or other geographic location. Two of the most common types of area maps are choropleths and isopleths.
7) Bar Chart: A bar chart represents numerical values compared to each other. The length of the bar in the bar chart represents the value of each variable.
8) Box-and-whisker Plots: A box-and-whisker plot represents a selection of ranges (referred to as the box) across a set measure (referred to as the bar).
9) Bullet Graph: A bullet graph can be defined as a graph that features a bar marked against a background. The bullet graph represents progress or performance when compared against objectives, usually denoted by a line on the graph.
10) Gantt Chart: A Gantt chart is typically used in Project Management. Gantt charts can be defined as bar chart depictions of timelines and tasks.
11) Heat Map: A heat map can be defined as a type of geospatial visualisation mapped in a form that displays specific data values in different colours.
12) Highlight Table: A highlight table is a form of table that uses colours to categorise similar data. This allows the viewer to read it with better ease and intuition.
13) Histogram: A histogram is a type of bar chart that splits a continuous measure into different bins. Splitting the continuous measure helps analyse the distribution.
14) Pie Chart: A pie chart is a circular chart with triangular segments representing data as a percentage of a whole.
15) Tree Map: A tree map represents different and related values in rectangles nested together.
Harness the full potential of Microsoft BI with our Microsoft BI Training course. Join now and gain the skills to drive data-driven decision-making in your organization!
Conclusion
As the age of Big Data progresses, visualisation is an increasingly used key tool to interpret trillions of data produced each day correctly. Tableau Data Visualisation helps tell stories by curating the data into a simpler form, making it easier to understand and identify trends and outliers. A well-made visualisation helps tell a story, as it removes the additional, unnecessary noise from raw data and highlights the information that can be used for profit.
Unlock the power of Data Visualisation with our comprehensive Tableau Desktop Training course and revolutionise your business intelligence reporting.
Frequently Asked Questions

Tableau revolutionises data visualisation by providing a user-friendly platform that transforms raw data into interactive and insightful visualizations. Through its intuitive interface, users can seamlessly connect to diverse data sources, create dynamic dashboards, and explore trends or patterns effortlessly. With robust features like drag-and-drop functionality, powerful analytics, and real-time collaboration, Tableau empowers individuals and organizations to make data-driven decisions, gaining valuable insights and uncovering actionable intelligence from complex datasets with ease.

Tableau's most utilised visualisation is arguably the "Bar Chart". This fundamental and versatile chart type effectively displays the magnitude of data points, making it ideal for comparing values across categories. With its simplicity, clarity, and ease of interpretation, the Bar Chart is a staple in data visualisation. Tableau enhances its effectiveness by allowing users to customise and interact with the chart dynamically, enabling a comprehensive understanding of data relationships and trends within the context of their specific analyses.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Business Intelligence Reporting courses, including Microsoft Power BI Course, Microsoft BI Training etc. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Data Visualisation with Tableau.
Our Office Application blogs covers a range of topics related to Power BI, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Office Application skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Programming & DevOps Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Tableau Desktop Training
Tableau Desktop Training
Mon 17th Jun 2024
Mon 9th Sep 2024
Mon 2nd Dec 2024







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


