We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Effective Product Management is an essential process in every business organization. Product Management Metrics help Product Managers to track the performance of the products’ growth and customer satisfaction. It is also important to know which metrics one should be using to track performance. Understanding and executing these metrics are integral components of fulfilling product manager roles and responsibilities, ensuring the successful development and management of a product throughout its lifecycle. This blog will give you a detailed look into 12 Product Management Metrics.
If you are confused about which Product Management Metrics are best, then this blog is for you. We will give you an insight into the different KPIs in detail.
Table of Contents
1) What is Product Management Metrics?
2) What is Key Performance Indicator (KPI)?
3) Importance of tracking Product Management Metrics
4) Top 12 Product Management Metrics and KPIs
5) Conclusion
What is Product Management Metrics?
Product Management Metrics refer to the key performance indicators (KPIs) and measurable data points used to assess and evaluate the success of a product or a product portfolio. These metrics help Product Managers collect useful information about how their products and their performance overall.
Product management metrics cover various aspects of the product lifecycle, from its development and launch to its ongoing usage and customer satisfaction. Using these metrics, Product Managers make data-driven decisions, prioritise their efforts, and identify areas that need improvement to enhance the product's performance.
Some common Product Management Metrics include Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC), Customer Lifetime Value (CLV), Churn Rate, Monthly Active Users (MAU), Net Promoter Score (NPS), Feature Adoption Rate, Conversion Rate, and many others.

Top 12 Product Management Metrics and KPIs
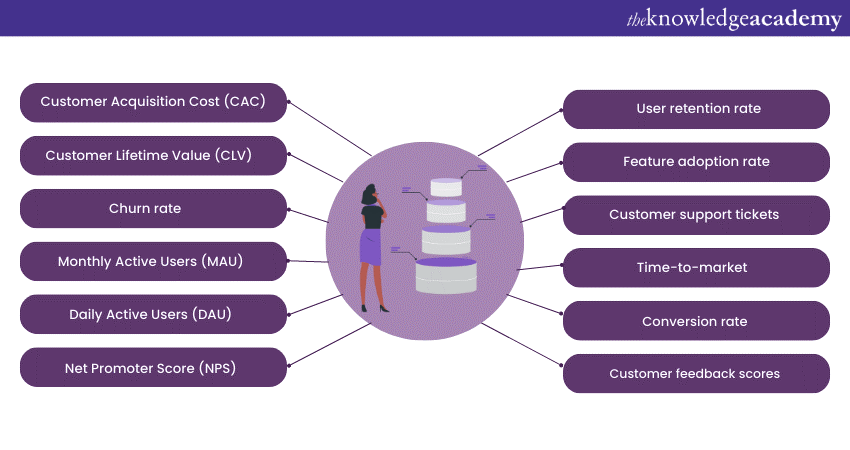
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) is a key Product Management Metric. It enables Product Managers to evaluate the efficiency of their marketing and sales strategies by looking into the expenses incurred to acquire new customers. By understanding the CAC, Product Managers can make informed decisions to optimise their acquisition efforts and ensure a healthy ROI.
Lowering the CAC can lead to increased profitability and sustainability, making it a key focus for Product Managers aiming to achieve long-term success in their market. Comparing the CAC with other relevant metrics like CLV, Product Managers can understand their customer acquisition impact on growth and profitability. Therefore, monitoring and analysing the CAC helps them plan their strategies and allocate resources more effectively.
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) is one of the best Product Management Metrics to know a customer's worth to the company over the entire duration of their relationship. By calculating CLV, Product Managers get valuable insights into the total revenue that a customer is expected to generate throughout their interactions with the company. This information proves invaluable for making strategic decisions and prioritising resources effectively.
Understanding the CLV allows Product Managers to focus on customer retention. By identifying high CLV customers, the company can nurture and engage them, leading to increased loyalty and long-term profitability. CLV metric helps Product Managers to make informed decisions regarding customer acquisition costs. By comparing the expected lifetime value of customers to the cost of acquiring them, businesses can assess the overall return on investment (ROI) for their marketing and sales efforts.
To calculate CLV, Product Managers need to consider various factors, including customer spending patterns, purchase frequency, and average customer lifespan. By employing this metric, businesses can use their marketing strategies to meet the needs of high CLV customers.
Churn Rate
Churn Rate metric is used for measuring customer satisfaction. It quantifies the percentage of customers who stop using a product or service over a specific period. It sheds light on the effectiveness of a company's offerings and customer experience.
High churn rates can signal potential problems with the product or service, customer support, or overall satisfaction levels. By monitoring the churn rate, Product Managers can quickly identify and address areas that require improvement. It leads to improved customer retention and loyalty.
Lowering the churn rate has far-reaching benefits for businesses. Not only does it directly impact revenue by retaining existing customers, but it also contributes to improved brand reputation and customer satisfaction. Satisfied customers are more likely to recommend the product or service to others, thus creating a positive cycle of growth.
Monthly Active Users (MAU)
Monthly Active Users (MAU) provides valuable insights into a product's popularity and relevance among its user bases. It tracks the number of unique users who actively engage with the product during a specific month. It offers Product Managers a clear picture of user activity and interest.
MAU is useful in assessing user retention and measuring the product's likeability. A growing MAU count indicates that the product is retaining users and maintaining their interest over time. On the other hand, a declining MAU may signal potential issues that require attention. such as a need for product updates or improvements.
MAU serves as a benchmark for calculating the impact of marketing and promotional activities. By comparing MAU trends before and after marketing campaigns, Product Managers can assess the effectiveness of their strategies in attracting and retaining users.
Understanding MAU is particularly crucial in today's digital landscape, where user engagement and continuous usage are key indicators of a product's success. By maintaining a strong MAU count, Product Managers make sure that the product remains relevant, competitive, and meets user needs.
Daily Active Users (DAU)
Daily Active Users (DAU) metric provides Product Managers with valuable insights into user engagement on a daily basis. Similar to Monthly Active Users (MAU), DAU helps assess the frequency and intensity of user interactions with the product.
A high DAU count indicates that users find the product valuable and relevant enough to use it regularly. High user engagement is a positive sign of the product's overall success and popularity. It also means that the product effectively meets user needs, leading to continuous usage and satisfaction.
Enhance your logistics expertise and boost your career with our Logistics Management Training course. Sign up now!
Monitoring DAU trends comes handy in competitive markets where user attention is minimum. Consistently tracking DAU helps Product Managers to identify any drop in user engagement quickly. After analysing the reasons behind a decline in DAU, Product Managers can take measures to address issues and keep users engaged.
For products that heavily rely on daily usage, DAU is very important. Daily usage means social media platforms, productivity tools, and communication apps. For such products', increasing DAU is often a key business objective, and Product Managers must use tactical strategies to keep it in check.
Net Promoter Score (NPS)
Net Promoter Score (NPS) is a KPI that measures customer loyalty and satisfaction. It is based on a simple question: "How likely are you to recommend our product to others?" Customers are then categorised into promoters (score 9-10), passives (score 7-8), and detractors (score 0-6).
NPS gives a clear indication of how customers perceive their products. A high NPS, with a strong presence of promoters, demonstrates that customers are highly satisfied with the product. These promoters are more likely to recommend products, contributing to organic growth and positive word-of-mouth marketing.
Similarly, a low NPS indicates a greater number of detractors, who may have had negative experiences with the product. Addressing the concerns of detractors is critical, as their negative feedback can influence potential customers. It leads to decreased sales and reputation damage.
Regularly measuring this KPI allows Product Managers to track customer sentiment over time and identify trends in customer satisfaction. It also helps in comparing the product's performance against industry benchmarks and competitors, providing a broader context for improvement.
Acting upon NPS feedback is essential for Product Managers. Understanding customer pain points and improving the overall user experience can elevate customer satisfaction, retain existing customers, and attract new ones.
User retention rate
User retention rate helps in understanding the effectiveness of the product in retaining customers over time. This KPI tracks the percentage of users who continue to use the product over a specified period. It indicates the product's value and its overall user experience.
A high User retention rate is a positive sign that users find the product relevant and satisfying enough to keep using it regularly. This metric indicates the level of product stickiness and customer loyalty, both of which are critical for long-term success and growth.
It is essential for identifying any potential issues or weaknesses in the product. If the retention rate is low, Product Managers can investigate the reasons behind it. It can be poor user experience, missing features, or lack of ongoing support. Addressing these issues helps in improving user satisfaction and retention.
This KPI is also closely linked to customer lifetime value (CLV). By retaining customers over an extended period, businesses can increase CLV and maximise the revenue potential of each customer.
User retention rate over time allows Product Managers to assess the impact of product updates, new features, and marketing efforts on user engagement and retention. This data-driven approach helps Product Managers make informed decisions to improve the product and strengthen its competitive position in the market.
Take the leap towards a successful supply chain career. Join our Supply Chain Management Training course today!
Feature adoption rate
Product Managers use this key KPI feature adoption rate to see the success of new product features and their acceptance among users. Tracking the adoption rate of newly introduced features provides valuable feedback on their relevance and impact on user experience.
A high feature adoption rate indicates that users find the new features valuable and beneficial. It also suggests that the product team has successfully identified and addressed user needs through these new additions. On the other hand, a low adoption rate may signal that the features lack appeal or fail to meet user expectations.
Looking into feature adoption rates, Product Managers can allocate resources more efficiently. They can focus on developing and promoting features that connect well with users. It leads to increased customer satisfaction, loyalty, and retention.
Additionally, feature adoption rate insights can help Product Managers prioritise their action plan. By identifying popular features and those that require improvement, product teams can use resources and efforts, accordingly.
Customer support tickets
Customer support tickets are a source of information for knowing the pain points and issues that users encounter while using the product. Tracking the number and types of customer support tickets is a vital part of understanding customer feedback and satisfaction levels.
A high volume of customer support tickets may indicate areas of the product that require improvement or features that need to be clarified. Categorising and analysing the types of tickets received helps Product Managers to identify common themes and trends.
Responding quickly to customer support tickets improves the brand reputation and customer loyalty. It is essential for Product Managers to build trust and confidence in the product and encourage users to remain loyal and recommend it to others.
Customer support ticket KPI data can also guide the product team in identifying potential areas for additional features or improvements. By integrating user feedback into the product development process, Product Managers can create a more user-centric and customer-focused product.
Time-to-market
Time to market measures the time taken from the inception of a new product to its successful launch in the market. A shorter time to market is good for businesses as it allows them to quickly meet market demands and gain a competitive edge. Products that are brought to market faster have a higher likelihood of capturing market share than competitors.
Efficient time-to-market is also essential for meeting customer needs. By reducing development time, Product Managers can ensure that the product remains relevant to changing customer preferences. It results in higher customer satisfaction.
Tracking time-to-market helps Product Managers identify loopholes and inefficiencies in the product development process. By identifying areas that cause delays, product teams can implement process improvements and stabilise workflow. It is more of a responsive process to increase business profitability.
Conversion Rate
The conversion rate is an important KPI which holds significant relevance for Product Managers and marketers equally. It tracks the percentage of users who complete a desired action, such as signing up for a service or making a purchase. This metric is essential in assessing the effectiveness of product marketing efforts and the overall user experience.
A high conversion rate indicates that users are successfully engaging with the product and responding positively to the calls to action. It reflects the relationship between the product's value proposition and user expectations. It also tracks the effectiveness of marketing strategies in conversions.
A low conversion rate may indicate potential issues with the product or marketing approach. It signals that users are not adequately motivated or convinced to take the desired action. It prompts Product Managers to investigate possible pain points or areas for improvement.
Monitoring conversion rates at different stages of the user journey is essential. Analysing conversion rates for each step, from initial interest to completing the action, helps Product Managers identify the areas and friction points that hinder user progress. By addressing these barriers, Product Managers can optimise the user experience and streamline the conversion process and boost business.
Customer feedback scores
Customer feedback scores are a valuable source of information that gives deeper insights into the strengths and weaknesses of their product. By systematically collecting and analysing feedback from customers, this KPI helps to understand user perceptions, preferences, and pain points.
The process of collecting customer feedback scores involves various methods such as surveys, reviews, and feedback forms. These scores are based on a rating scale, with customers providing scores for different aspects of the product, such as usability, features, and customer support.
The feedback collected provides Product Managers with direct and unfiltered insights into how users perceive the product's performance. Positive feedback scores highlight the product's strengths, indicating that it connected well with customers and contributed to their satisfaction.
On the other hand, negative feedback scores reveal areas where improvements are required. Product Managers can identify specific pain points and address them through various product updates. It can lead to a more user-friendly and satisfying experience.
It also plays a crucial role in understanding user sentiments and preferences. By analysing patterns in feedback data, Product Managers can identify emerging trends and demands to make a future roadmap.
Conclusion
With the advancement in technology and the ever-evolving business sphere, it is vital to stay updated with the latest tools. We hope the blog gave you an understanding of the 12 Product Management Metrics and the purposes of each tool. These KPIs, when used effectively, can bring exponential growth to your business.
Unlock your potential with industry-leading training. Explore our Industry Training courses now!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Facilitation Skills Training
Facilitation Skills Training
Fri 21st Jun 2024
Fri 2nd Aug 2024
Fri 18th Oct 2024
Fri 20th Dec 2024







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


