We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Six Sigma is a problem-solving methodology that provides organisations with a structured approach to improve processes, reduce defects, and enhance overall performance. Implementing it helps achieve higher quality outputs, increased customer satisfaction, and improved operational efficiency. You first need to learn How Does Six Sigma Work to implement it.
According to Reliable Plant, 53% of Fortune 500 companies use Six Sigma. At its core, it focuses on finding and eliminating the root causes of problems and variations within a process. In this blog, you will learn How Does Six Sigma Work, how to implement it, and its advantages.
Table of Contents
1) What is Six Sigma?
2) How does Six Sigma work?
3) How to implement Six Sigma?
4) Advantages of Six Sigma
5) Conclusion
What is Six Sigma?
Six Sigma is a disciplined problem-solving approach that aims to achieve process excellence by minimising variations and defects. It was first introduced by Motorola in the 1980s and has since been adopted by numerous organisations across various industries. By implementing its principles and tools, organisations can achieve higher levels of efficiency, customer satisfaction, and profitability.

How does Six Sigma work?
The Six Sigma works on the methodology of a systematic and structured approach to improve a process, reduce defects, and enhance overall performance. It provides a roadmap for problem-solving and process optimisation, aiming to achieve excellence in quality and customer satisfaction.
This methodology consists of five phases, commonly called DMAIC: Define, Measure, Analyse, Improve, and Control. Let's explore each phase in detail:
a) Define phase: The project goals and objectives are established in this phase. The focus is on identifying the problem or opportunity for improvement and clearly defining the project scope. Key activities include defining customer requirements, setting measurable goals, and creating a project charter.
b) Measure phase: This phase involves gathering data and measuring the current state of the process. It aims to quantify the performance of the process and identify the key metrics that need improvement. Various data collection methods and statistical tools are used to collect and analyse relevant data.
c) Analyse phase: In the Analyse phase, the collected data is analysed to identify the root causes of defects, errors, or variations in the process. This phase involves applying statistical analysis, cause-and-effect diagrams, hypothesis testing, and other problem-solving techniques to uncover the underlying factors contributing to the problem.
d) Improve phase: This phase focuses on developing and applying solutions to address the root causes identified in the previous phase. It involves brainstorming, experimenting, and piloting potential solutions. The goal is to optimise the process and significantly improve quality, efficiency, and productivity.
e) Control phase: This phase ensures that the improvements made in the previous phase are sustained over time. It involves establishing control mechanisms, standardising processes, and implementing ongoing monitoring and measurement systems. Statistical process control tools are often used to track the performance of the process and ensure it stays within the desired parameters.
A data-driven and fact-based approach drives the Six Sigma methodology. It emphasises using statistical tools, such as control charts, regression analysis, and hypothesis testing, to make informed decisions and validate improvement initiatives.
By following the Six Sigma methodology, organisations can systematically identify and eliminate sources of variation, reduce defects, and enhance customer satisfaction. It provides a structured framework for regular improvement, empowers teams to solve complex problems, and fosters a culture of excellence. Understanding the DMAIC helps in understanding How Does Six Sigma Work.
Take the first step towards operational excellence with our Six Sigma Yellow Belt course!
How to implement Six Sigma?
Implementing Six Sigma in an organisation requires careful planning and execution. Understanding its implementation can help you better understand how Six Sigma works. Follow these steps to implement it and drive process improvement successfully:
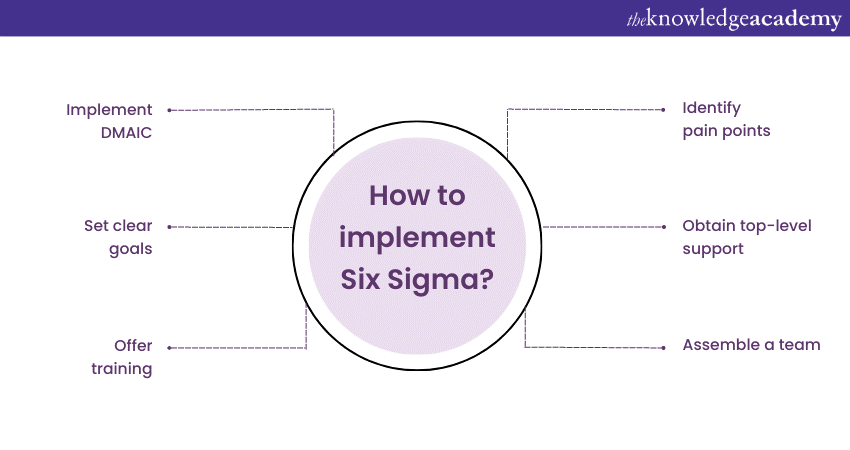
a) Identify the need: Assess your organisation's current processes and determine areas that can benefit from Six Sigma. Identify pain points and areas with high potential for improvement.
b) Gain leadership support: Obtain buy-in from top-level management to ensure commitment and allocation of necessary resources for Six Sigma implementation.
c) Dedicated team: Assemble a team of individuals with a strong understanding of the organisation's processes and a passion for improvement. This team will be responsible for driving Six Sigma projects.
d) Provide training: Offer comprehensive training programs on Six Sigma methodologies, tools, and techniques to equip employees with the necessary skills to contribute effectively.
e) Select projects: Choose projects with clear goals and measurable objectives that align with organisational priorities. Select projects that have the potential for significant impact and improvement.
f) Apply DMAIC methodology: Follow the Define, Measure, Analyse, Improve, Control (DMAIC) framework for each selected project. This step-by-step approach ensures a systematic and structured improvement process.
g) Utilise statistical tools: Use statistical tools and techniques such as process mapping, root cause analysis, hypothesis testing, and control charts to analyse data and identify improvement opportunities.
h) Monitor and sustain: Establish control measures to monitor the performance of implemented improvements. Regularly review and update processes to ensure sustained improvement over time.
By following these steps and incorporating the principles of Six Sigma, organisations can effectively implement the methodology and drive positive change within their processes, leading to improved efficiency, reduced defects, and increased customer satisfaction.
Take the next step in your professional journey and become a Six Sigma expert with our Six Sigma Green Belt Training – Signup now!
Advantages of Six Sigma
Implementing Six Sigma in an organisation yields numerous advantages across various aspects of the business. Here are the key benefits of Six Sigma:
a) Improved quality: By reducing defects and process variations, it enhances product and service quality, increasing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
b) Enhanced efficiency: Streamlining processes, eliminating waste, and optimising resource utilisation improves operational efficiency and productivity.
c) Cost reduction: Six Sigma projects optimise processes, reduce waste, and improve resource allocation, resulting in cost savings and improved financial performance.
d) Data-driven decision-making: Six Sigma emphasises data analysis and statistical tools to make informed decisions based on evidence, improving the accuracy of decision-making processes.
e) Employee engagement: It promotes employee involvement, empowerment, and skill development through participation in improvement projects, fostering a culture of continuous learning.
f) Customer focus: By aligning processes with customer requirements, it enhances customer satisfaction, builds stronger relationships, and provides a competitive edge.
g) Continuous improvement: It establishes a culture of continuous improvement, encouraging innovation, collaboration, and excellence for long-term success.
h) Strategic alignment: Six Sigma aligns improvement efforts with strategic objectives, ensuring targeted improvements in areas critical to overall performance.
Conclusion
We hope you enjoyed reading this blog on How Does Six Sigma Work. This methodology offers a systematic and data-driven approach to process improvement. By applying the DMAIC framework, organisations can drive measurable and sustainable quality, efficiency, and customer satisfaction improvements.
Unlock your potential for process improvement with Six Sigma Certification Training Courses and propel your organisation to new heights of success.
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming Business Improvement Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Six Sigma Green Belt
Six Sigma Green Belt
Mon 20th May 2024
Tue 28th May 2024
Mon 3rd Jun 2024
Mon 10th Jun 2024
Mon 17th Jun 2024
Sat 22nd Jun 2024, Sun 23rd Jun 2024
Mon 24th Jun 2024
Mon 1st Jul 2024
Mon 8th Jul 2024
Mon 15th Jul 2024
Sat 20th Jul 2024, Sun 21st Jul 2024
Mon 22nd Jul 2024
Mon 29th Jul 2024
Mon 5th Aug 2024
Mon 12th Aug 2024
Sat 17th Aug 2024, Sun 18th Aug 2024
Mon 19th Aug 2024
Tue 27th Aug 2024
Mon 2nd Sep 2024
Mon 9th Sep 2024
Sat 14th Sep 2024, Sun 15th Sep 2024
Mon 16th Sep 2024
Mon 23rd Sep 2024
Mon 30th Sep 2024
Mon 7th Oct 2024
Sat 12th Oct 2024, Sun 13th Oct 2024
Mon 14th Oct 2024
Mon 21st Oct 2024
Mon 28th Oct 2024
Mon 4th Nov 2024
Sat 9th Nov 2024, Sun 10th Nov 2024
Mon 11th Nov 2024
Mon 18th Nov 2024
Mon 25th Nov 2024
Mon 2nd Dec 2024
Sat 7th Dec 2024, Sun 8th Dec 2024
Mon 9th Dec 2024
Mon 16th Dec 2024
Mon 6th Jan 2025
Mon 13th Jan 2025
Mon 20th Jan 2025
Mon 27th Jan 2025
Mon 3rd Feb 2025
Mon 10th Feb 2025
Mon 17th Feb 2025
Mon 24th Feb 2025
Mon 3rd Mar 2025
Mon 10th Mar 2025
Mon 17th Mar 2025
Mon 24th Mar 2025
Mon 31st Mar 2025
Mon 7th Apr 2025
Mon 14th Apr 2025
Tue 22nd Apr 2025
Mon 28th Apr 2025
Tue 6th May 2025
Mon 12th May 2025
Mon 19th May 2025
Tue 27th May 2025
Mon 2nd Jun 2025
Mon 9th Jun 2025
Mon 16th Jun 2025
Mon 23rd Jun 2025
Mon 30th Jun 2025
Mon 7th Jul 2025
Mon 14th Jul 2025
Mon 21st Jul 2025
Mon 28th Jul 2025
Mon 4th Aug 2025
Mon 11th Aug 2025
Mon 18th Aug 2025
Tue 26th Aug 2025
Mon 1st Sep 2025
Mon 8th Sep 2025
Mon 15th Sep 2025
Mon 22nd Sep 2025
Mon 29th Sep 2025
Mon 6th Oct 2025
Mon 13th Oct 2025
Mon 20th Oct 2025
Mon 27th Oct 2025
Mon 3rd Nov 2025
Mon 10th Nov 2025
Mon 17th Nov 2025
Mon 24th Nov 2025
Mon 1st Dec 2025
Mon 8th Dec 2025
Mon 15th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


