We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
As part of Google’s rich ecosystem, Google Cloud Storage presents a variety of solutions tailored to diverse data needs. Ranging from Machine Learning (ML) to data analytics, each service relies fundamentally on storage options, a vital component of Cloud Computing. Storage is key in facilitating effective data management and accessibility both for individual applications and enterprise-scale operations.
According to Statista, Google Cloud generated revenue of 20.67 billion GBP in 2022. This was a testament to its popularity, because of the wide suite of tools it provides. If you wish to understand the capabilities of different options provided by Google, keep reading this further. This blog offers a thorough exploration of Google Cloud Storage, focusing on its primary characteristics while also exploring different classes and Cloud Storage options.
Table of Contents
1) What is Google Cloud Storage?
2) Key features of Google Cloud Storage
3) Google Cloud Storage classes
4) What are the different Google Cloud Storage options?
5) Cloud Storage tools
6) Google Cloud Storage use cases
7) Conclusion
What is Google Cloud Storage?
Google Cloud Storage (GCS) is a fundamental component of Google's extensive range of cloud computing services, bundled under the umbrella term Google Cloud Platform (GCP). This product, which was officially launched in 2010, offers an integrated, flexible, and secure option for data storage and retrieval via the internet.
The genesis of Google Cloud Storage lies in Google's necessity to develop robust and scalable infrastructure solutions that could manage the extensive datasets required for their diverse and complex array of services. As one of the world's largest and most influential technology companies, Google naturally amassed considerable expertise in handling large datasets. They soon realised their wealth of experience in this area could be leveraged to offer an object storage service that could be utilised by developers and businesses across the globe.
In our modern, digitised world, GCS has become an increasingly essential tool. With data generation expanding at an unprecedented rate, GCS provides an invaluable service that is affordable and reliable, thus enabling businesses to store and analyse their data. One of the standout features of GCS is its automated backup and lifecycle management capabilities. These features are critical for businesses, as they streamline the data management process, making it an indispensable tool in our increasingly digital world.
Key Features of Google Cloud Storage
Google Cloud Storage offers a broad range of features to efficiently and reliably store, share, and manage data:
1) High capacity and scalability: It supports storing objects of terabyte size and allows numerous buckets per account.
2) Strong data consistency: Google Cloud Storage ensures strong read-after-write consistency for uploads and deletes. Once an object is uploaded, you can immediately download, delete, or access its metadata. Any attempt to access a deleted object promptly returns a 404 Not Found status. List operations are eventually consistent from anywhere on the Internet.
3) Availability: Upload operations are atomic, meaning an object becomes available only after it's fully uploaded. Objects are always consistent; there are no partial or corrupted objects.
4) Google Developers Console projects: It's accessible through the Google Developers Console, allowing you to manage project members, billing, authentication, and work with various APIs. You can have multiple projects, each with its Google Cloud Storage instance.
5) Bucket locations: You can specify geographic storage locations for your buckets, choosing between Europe and the US.
6) REST APIs: Google Cloud Storage provides two RESTful programming interfaces (XML and JSON APIs) for creating applications using standard HTTP methods.
7) OAuth 2.0 authentication: It utilises OAuth 2.0 authentication and authorisation, allowing token-based authentication for applications to act on your behalf.
8) Authenticated browser downloads: You can offer browser-based authenticated downloads to individual Google account holders by setting up Google account-based ACLs and sharing a scoped URL for authenticated downloads.
9) Google account support for sharing: Access Control Lists (ACLs) control access to objects and buckets, enabling sharing with the world, Google groups, Google-hosted domains, or specific Google account holders.
Google Cloud Storage classes
In Google Cloud Storage, classes define the different tiers of data storage, each tailored to varying use cases concerning data access frequency, data retention periods, and budget requirements. Choosing the right storage class allows you to determine the trade-off between the cost of storing your data and how often you expect to access it. Here's an explanation of each:
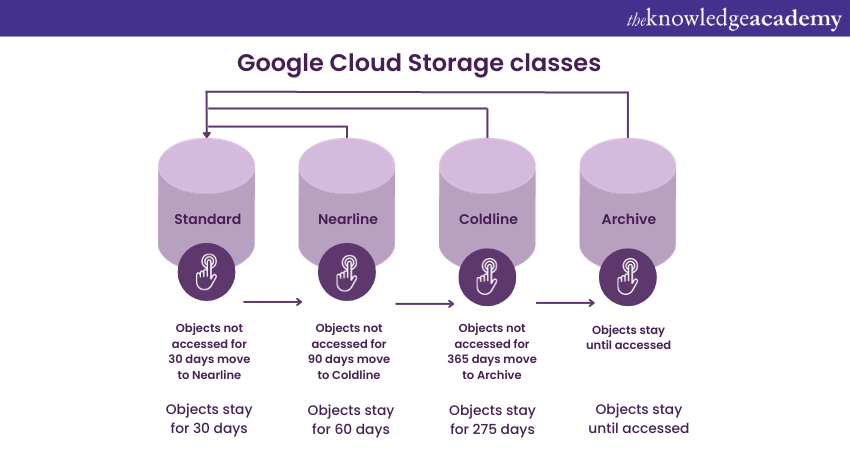
1) Standard: The Standard Storage Class in Google Cloud Storage is the default choice and offers the highest level of availability and performance. It's best suited for data that is accessed frequently or requires low-latency access. For instance, a media company could use the Standard Storage Class to store and deliver high-definition video content to their users, ensuring seamless streaming with minimal buffering.
2) Nearline: The Nearline Storage Class is a more economical choice for data that is accessed less frequently, typically less than once a month. While storage costs are lower, access costs are slightly higher compared to the Standard Class. An example might be a company storing monthly financial reports. These reports aren't required on a daily basis but might need to be accessed at the end of each financial quarter.
3) Coldline: The Coldline Storage Class is designed for data that users access even less frequently, typically less than once a quarter. It offers lower storage costs than Standard and Nearline but higher costs to retrieve data. An example use case could be a business storing yearly tax records. Such data doesn't need to be accessed regularly but is important to retain for compliance purposes.
4) Archive: The Archive storage class provides the lowest cost solution for long-term data storage with very infrequent access, possibly less than once a year. This class has the lowest storage cost but the highest retrieval cost. Archive storage could be used, for instance, by research institutions that need to retain large volumes of raw research data for years, even if they rarely need to access it.
Interested in GCP? Get started with our Google Cloud Platform Fundamentals Course!
What are the different Google Cloud Storage options?
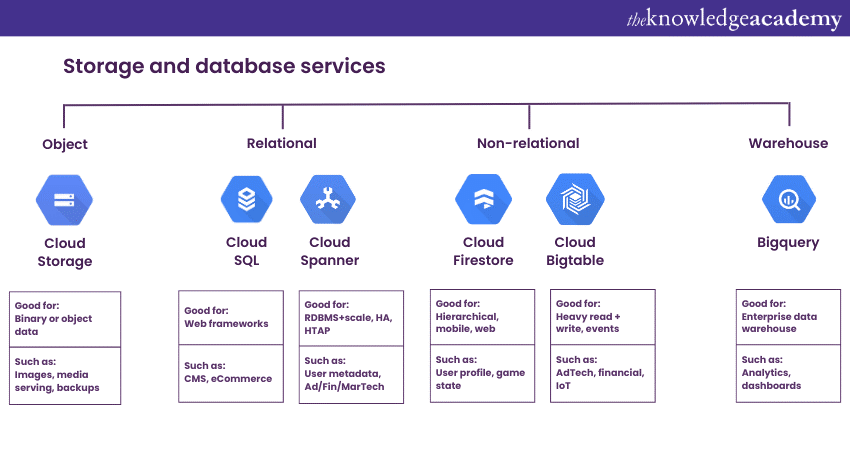
Google Cloud Platform offers a multitude of storage options based upon varying use cases, making it extremely popular among developers and enterprises. These range from data warehousing for in-depth analytics, Machine Learning and real-time application data for app developers. Some other options are specialised for archival storage for long-term data retention and solutions for website hosting and content management. The core options in Google Cloud can be categorised as follows:
Persistent Disk
Google Cloud's Persistent Disk is a robust block storage service that operates somewhat differently to Google Cloud Storage. While GCS, an object storage service, stores data as individual units or 'objects', Persistent Disk employs a block storage approach. This method arranges data into blocks within a sector, each identifiable by a unique identifier, which purely marks its location without the incorporation of metadata.
The block-based approach delivers a unique blend of speed and flexibility, making it an ideal fit for systems requiring high-speed operations. In terms of performance, Persistent Disk offers a consistently low-latency experience coupled with high Input/Output Operations Per Second (IOPS). These traits make it a crucial component for certain applications, such as databases or file systems, that require swift, low-latency access to disk volumes.
An integral feature of Persistent Disk is its seamless integration with Google Cloud services such as Google Compute Engine (GCE) and Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE). This compatibility ensures a unified experience, as Persistent Disk manages the data storage when using GCE or GKE, guaranteeing consistency and reliability. With automatic encryption, in-zone replication, and auto-resizing, Persistent Disk proves to be a secure and adaptable solution for diverse data storage needs.
Cloud Filestore
Google’s Cloud Filestore service is an ideal solution for applications requiring shared file storage. It is a fully managed Network Attached Storage (NAS) service that provides a simple and integrated file system interface. This facilitates shared file system capabilities, offering the ability to share data across multiple compute instances. Cloud Filestore offers reliable and high-speed file storage for deploying a Content Management System (CMS), hosting a dynamic website and processing data-heavy workloads.
Cloud Filestore is available in two performance tiers: Standard and Premium. The Standard tier is suitable for general file storage in Google Cloud, while the Premium tier caters to high-performance needs, such as video processing or machine learning. This tiered system offers flexibility, allowing you to select the tier that matches your performance requirements and budget, making Cloud Filestore a cost-effective and adaptable solution for various file storage needs.
Try our Architecting Infrastructure With Google Cloud Platform Training today!
Firestore and Bigtable
Google Cloud offers Firestore and Bigtable. Firestore is a versatile, scalable NoSQL cloud database ideal for mobile, web, and server development projects. Its key features include synchronising data across client applications via real-time listeners and providing offline support for mobile and web apps, enabling a seamless user experience (UX) regardless of connectivity.
In contrast, Bigtable is Google's NoSQL Big Data database service. It's specifically crafted for large-scale operational and analytical applications. Bigtable caters to businesses dealing with vast amounts of data, offering a reliable platform for handling such volumes. It's a great option for a variety of applications, ranging from user analytics to financial data analysis.
Cloud SQL and Cloud Spanner
Google Cloud presents comprehensive solutions for relational database requirements through services like Cloud SQL and Cloud Spanner. Cloud SQL is a popular relational database service, fully managed in nature, it provides support for different database systems such as MySQL, SQL Server and PostgreSQL. This service takes the burden of database management off the user's shoulders, effectively handling tasks like replication, patch management, and failure detection.
In contrast, Cloud Spanner is a globally distributed relational database service providing a blend of traditional and modern database functionalities. It delivers the benefits of a conventional relational database, including ACID transactions, relational schemas, and SQL querying. However, Cloud Spanner goes a step further by offering the scalability that's characteristic of non-relational databases. This makes it a hybrid solution that combines the consistency of relational databases with the robust scalability of non-relational ones.
Cloud Storage tools
Mostly, there are four crucial tools that help to interact with the Google Cloud Storage Services. Let’s talk about them in the following points:
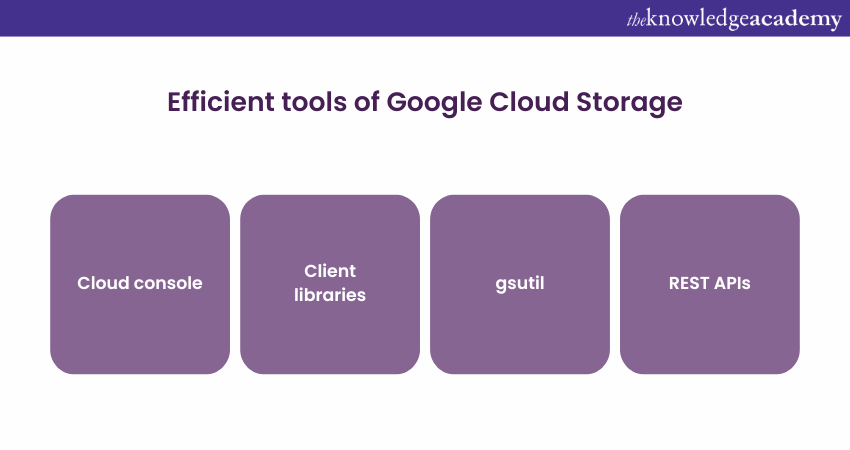
a) Cloud console: It renders a browser-based web informational interface to handle the records.
b) Client libraries: The client libraries permit users to effectively manage data with the help of their preferred popular programming languages. Some of those languages include C++, C#, Go, Java, Node.js, PHP, Python and Ruby.
c) gsutil: It is a standard command line tool /terminal that permits users to interact with the contents of the cloud storage in real-time.
d) REST APIs: It runs on top of the JSON or XML API that handles the data.
Google Cloud Storage use cases
Here are some primary use cases for Google Cloud Storage:
a) Backups and archives: Google Cloud Storage offers cost-effective, high-durability storage for data that isn't frequently accessed. This makes it an excellent choice for reducing the expenses associated with backups and archives while maintaining quick access. The stored backup data is versatile and can be utilised for more than just recovery, thanks to low-latency access across all storage classes through a unified API.
b) Integrated repository for analytics and Machine Learning: Google Cloud Storage provides high availability and performance within a single region, making it well-suited for computing, analytics, and Machine Learning (ML) workloads within specific geographic areas. Its strong consistency ensures the accuracy and reliability required for analytics tasks.
c) Media content storage and delivery: For low-latency, high-query-per-second content delivery to users dispersed across various geographic regions, Google Cloud Storage's geo-redundant storage with top-notch availability and performance is an optimal choice. This service caters to the availability and throughput demands for streaming audio or video directly to applications or websites.
Unleash the capabilities of cloud computing with our Google Cloud Training today!
Conclusion
Google Cloud Storage offers an array of solutions, each tailored to cater to unique needs. Considering factors such as real-time access and performance requirements, you can select a storage service that fits your application. The optimal choice can profoundly influence application performance and overall business success. Therefore, it's vital to comprehend each Google Cloud Storage option and stay updated with their continuous innovations, ensuring you make decisions that best support your evolving requirements.
Interested in how networks work? Try our Networking With Google Cloud Platform Course!
Frequently Asked Questions

Google Drive and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) serve different purposes. Google Drive is primarily for file storage and collaboration. In contrast, GCP offers a range of cloud computing services for businesses, including storage, computing, and data analytics.

Utilise Google Cloud Storage for scalable, durable, and secure object storage. It's ideal for storing large volumes of data, backups, and multimedia content. Use it when you need reliable and cost-effective storage solutions for your business applications and projects.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Google Cloud Certifications, including the Google Cloud Platform Fundamentals Training, Google BigQuery Training, and Google Search Appliance Fundamentals. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Cloudformation vs Terraform.
Our Cloud Computing Blogs cover a range of topics related to Google Cloud Stroage, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Cloud Computing skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Cloud Computing Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Google Cloud Platform Fundamentals
Google Cloud Platform Fundamentals
Fri 12th Jul 2024
Fri 11th Oct 2024







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


