We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

The Financial landscape requires robust Financial Analyst Skills for professional success. The intricate world of Finance demands individuals who can navigate complex data, decipher trends, and confidently make strategic decisions. As businesses strive to stay competitive and investors seek reliable insights, Financial Analyst Skills have become more critical than ever.
This blog will explore the ten key Financial Analyst Skills essential for achieving excellence in this dynamic field. From data interpretation to statistical analysis, each skill contributes to the multifaceted toolkit that empowers Financial Analysts to navigate challenges and provide opportunities in the ever-changing Financial landscape.
Table of Contents
1) Who is a Financial Analyst?
2) Different Financial Analyst Skills
a) Analytical skills
b) Data interpretation
c) Financial modelling
d) Programming and automation
e) Risk management techniques
f) Statistical analysis
g) Forecasting and trend analysis
3) Conclusion
Who is a Financial Analyst?
A Financial Analyst is a professional who performs Financial Analysis for clients, which can be external or internal to a company. Their role involves analysing economic trends, market conditions, and financial data to provide informed guidance on business investment decisions. They may work in various sectors, including banks, investment firms, or within businesses, and typically have academic backgrounds in finance, economics, accounting, or statistics.
Financial Analysts are often categorised into two types:
a) Buy-side Analysts are those who develop investment strategies for institutions that manage large funds.
b) Sell-side Analysts are those who provide research and recommendations to facilitate the sale of stocks, bonds, and other investments.
To become a Financial Analyst, one usually needs a bachelor’s degree in a related field and may benefit from internships and further certifications or advanced degrees for career advancement. The role requires strong analytical skills, proficiency in financial software, and the ability to communicate complex information effectively.

Different Financial Analyst Skills
Financial Analysts require a diverse skill set to analyse financial data effectively, evaluate investment opportunities, and provide recommendations to clients or management. Here are the skills required for a Financial Analyst:
Analytical skills
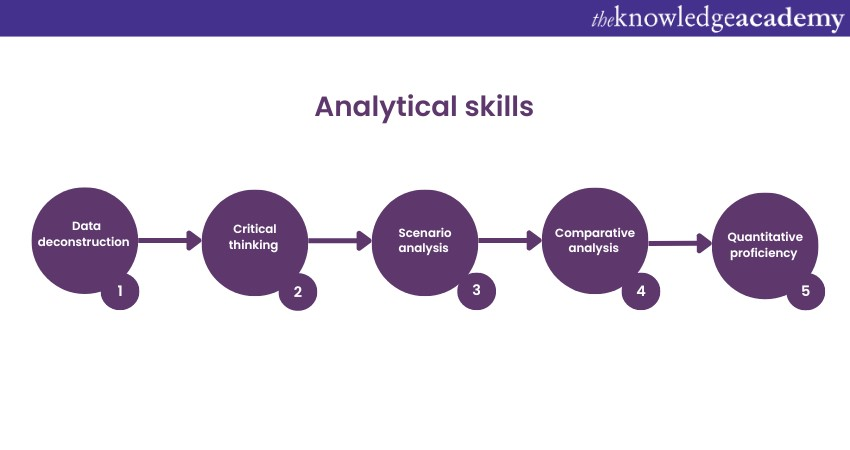
Analytical skills form the foundation of a Financial Analyst's expertise. In a field driven by data, these skills are the compass that guides professionals through the intricate maze of Financial information. Let's understand the various sub-topics that constitute this crucial skill set.
Analytical skills form the foundation of a Financial Analyst's expertise. In a field driven by data, these skills are the compass that guides professionals through the intricate maze of Financial information. Let's understand the various sub-topics that constitute this crucial skill set.
Data deconstruction
At the core of analytical prowess lies the ability to deconstruct complex datasets into understandable components. Financial Analysts possess a keen eye for detail, allowing them to sift through mountains of information to uncover hidden patterns, outliers, and connections that might elude the untrained eye.
Critical thinking
Critical thinking is the engine that drives effective decision-making. Financial Analysts are adept at scrutinising data from multiple angles, questioning assumptions, and considering their findings' micro and macro implications. This skill enables them to provide insightful recommendations that align with overarching business objectives.
Scenario analysis
Analytical skills empower Financial Analysts to conduct scenario analysis, a technique crucial for risk assessment and strategy formulation. Analysts can anticipate potential outcomes, identify vulnerabilities, and devise contingency plans by modelling various scenarios based on different assumptions and variables.
Comparative analysis
Financial Analysts excel in comparative analysis, which involves benchmarking a company's performance against industry peers or historical data. This practice provides valuable insights into a company's strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement, guiding decision-makers toward informed actions.
Quantitative proficiency
Numerical aptitude is a cornerstone of analytical skills. Financial Analysts can manipulate and interpret quantitative data, applying statistical techniques to derive meaningful conclusions. This enables them to quantify risks, evaluate investment opportunities, and project future Financial performance.
Gain knowledge of how to analyse Financial statement and various techniques. Sign up for our Financial Management Training now!
Data interpretation
In Financial Analysis, skilfully interpreting data is a linchpin that separates adept Financial Analysts from the rest. Navigating through copious amounts of data requires finesse and precision, and the practice of data interpretation serves as a beacon in this endeavour. Let's explore the various facets that encompass this vital skill.
Data contextualisation
Effective data interpretation begins with contextualisation. Financial Analysts understand that data is not just a series of numbers; it's a narrative that tells the story of a company's Financial health, market trends, and economic influences. Analysts thoroughly understand the forces shaping financial landscapes by placing data within their broader context.
Key metric identification
Not all data points are created equal. Skilled Financial Analysts possess the ability to identify the key metrics that truly matter in a given analysis. Analysts can extract valuable insights that drive decision-making by focusing on these critical indicators.
Trend recognition
One of the pivotal roles of data interpretation is recognising trends. Financial Analysts meticulously sift through historical data to identify patterns. These patterns include revenue fluctuations, expense trends, or market cycles. These trends offer a roadmap to predicting future outcomes and spotting potential opportunities and threats.
Outlier detection
An adept Financial Analyst is vigilant for outliers—data points that deviate significantly from the norm. These anomalies can provide essential insights into exceptional circumstances, anomalies, or irregularities that might have gone unnoticed. Detecting outliers helps in understanding the full scope of a Financial scenario.
Correlation and causation
Data interpretation delves into the relationships between various data points. Financial Analysts assess correlations to identify how changes in one variable affect another. This understanding helps grasp the causal links within Financial ecosystems and make informed predictions.
Visual representation
Data visualisation is an integral part of interpretation. Skilled Financial Analysts leverage charts, graphs, and infographics to translate complex data sets into easily digestible visuals. Visual representation not only aids in understanding but also in conveying insights to non-technical stakeholders effectively.
Predictive insights
Data interpretation isn't limited to the past—it extends into the future. Financial Analysts can make informed predictions about future Financial trends by scrutinising historical data. These predictions guide strategic decision-making and risk assessment.
Interested in working with numbers and data? Sign up for our Accounting & Finance Training now!
Financial modelling
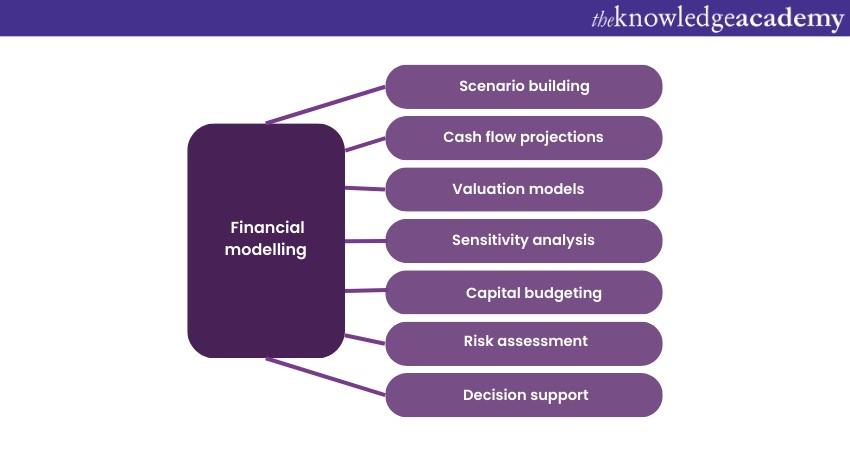
Financial modelling is the cornerstone of strategic decision-making for Financial Analysts. It involves creating mathematical representations of a company's Financial performance, often projecting future scenarios based on various assumptions. This technique empowers analysts to explore potential outcomes, analyse risks, and make well-informed choices. Let's dive into the key components that comprise this indispensable skill.
a) Scenario building: Constructing simulations that explore multiple potential outcomes based on different assumptions.
b) Cash Flow projections: Anticipating and analysing cash inflows and outflows over time for accurate Financial planning.
c) Valuation models: Determining a company's or asset's intrinsic value using various valuation methods like DCF and comparable analysis.
d) Sensitivity analysis: Assessing the impact of changing variables on outcomes to understand potential risks.
e) Capital budgeting: Evaluating investment decisions by analysing their long-term Financial implications.
f) Risk assessment: Integrating risk factors into models to quantify potential vulnerabilities.
g) Decision support: Providing data-backed insights for informed strategic decisions.
Programming and automation
In Financial Analysis, programming and automation have emerged as indispensable skills. Financial Analysts who can harness the power of code and automation tools gain a competitive edge in processing vast amounts of data, optimising workflows, and extracting actionable insights. Let's explore the key elements that make up this crucial skill set.
Coding proficiency
Financial Analysts skilled in programming languages like Python, R, or SQL can expedite Data Analysis and manipulation. By utilising these programming languages, analysts can create scripts that automate repetitive tasks, resulting in less time spent manually handling data.
Data extraction and cleaning
Automated scripts can scrape data from various sources, such as Financial databases or websites, streamlining the data collection. Furthermore, programming allows for data cleaning and transformation, ensuring that the information used for analysis is accurate and consistent.
Algorithmic trading
For Financial Analysts in quantitative fields, programming skills open the door to algorithmic trading. These analysts develop algorithms that make autonomous trading decisions based on predefined criteria. This technique enables swift execution of trades and risk management.
Data visualisation
Programming skills complement data visualisation tools. Analysts can create interactive dashboards and visualisations using libraries like Matplotlib and D3.js. This enhances the communication of insights to stakeholders and facilitates a deeper understanding of complex data sets.
Model development
Programming supports the creation of sophisticated Financial models. Analysts can develop intricate models for risk assessment, portfolio optimisation, and forecasting, allowing for more accurate and sophisticated analyses.
Automation of reports
Automation not only speeds up analysis but also report generation. Financial Analysts can create templates that auto-populate with the latest data, ensuring stakeholders receive timely and accurate reports.
Machine Learning integration
Proficiency in programming facilitates the integration of Machine Learning techniques into Financial Analysis. This empowers analysts to build predictive models that adapt to changing market conditions, enhancing forecasting accuracy.
Gain knowledge of formulas, shortcuts, and advanced formulas in Excel, Sign up for our Financial Modelling Training now!
Risk management techniques
Risk management techniques stand at the core of a Financial Analyst's skill set, allowing them to navigate uncertainties and safeguard assets in a volatile Financial world. These techniques enable analysts to identify potential pitfalls, assess their impact, and formulate risk mitigation strategies. Let's understand the key components that constitute this critical skill.
a) Risk identification: Identifying potential risks in Financial decisions, market fluctuations, and economic changes.
b) Quantitative analysis: Using statistical methods to quantify risks' likelihood and potential impact.
c) Scenario analysis: Projecting how different scenarios might affect Financial outcomes to strategise proactively.
d) Diversification strategies: Creating diversified portfolios spreads risk across various assets and reduces potential losses.
e) Hedging techniques: Using Financial instruments to offset potential losses from adverse market movements.
f) Stress testing: Subjecting portfolios or models to extreme scenarios to gauge their resilience.
g) Contingency planning: Developing plans outlining responses to potential risk scenarios.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis is a crucial skill for Financial Analysts, enabling them to uncover hidden trends, correlations, and patterns within Financial data. This skill involves applying statistical techniques to quantitative data, facilitating more informed decision-making. Key sub-topics within statistical analysis include:
a) Descriptive statistics: Financial Analysts use mean, median, and standard deviation measures to summarise and describe data distributions.
b) Correlation analysis: This technique helps analysts understand the relationships between variables, identifying dependencies that impact Financial outcomes.
c) Regression analysis: Regression models allow analysts to predict one variable's behaviour based on the relationships with other variables, aiding in forecasting Financial trends.
d) Hypothesis testing: Analysts use hypothesis tests to validate assumptions and make inferences about larger populations based on sample data.
e) Time series analysis: Time series techniques help analysts analyse data points collected over time, making them invaluable for Financial forecasting and trend analysis.
f) Monte Carlo simulation: This method models different scenarios by simulating a range of possible outcomes, providing insights into potential risks and rewards.
Forecasting and trend analysis
Forecasting and trend analysis are crucial elements of a Financial Analyst's toolkit, allowing them to predict future financial outcomes and capitalise on emerging opportunities. This skill involves utilising historical data to identify patterns and extrapolate trends, providing insights for strategic decision-making. Key sub-topics within forecasting and trend analysis include:
a) Time series forecasting: Financial Analysts use time series techniques, such as moving averages and exponential smoothing, to forecast future values based on historical data points.
b) Regression analysis for trends: Analysts use regression models to uncover underlying trends within data and predict how variables interact over time.
c) Seasonal adjustments: Adjusting for seasonal variations helps analysts understand recurring patterns and make accurate predictions that account for cyclical fluctuations.
d) Qualitative factors: Incorporating qualitative data, like market trends and industry developments, enhances the accuracy of forecasts by considering external influences.
e) Data visualisation: Visualisation tools assist in presenting historical data and projected trends, making it easier for stakeholders to understand and act upon the insights.
Conclusion
Mastering the Financial Analyst Skills discussed here empowers Financial Analysts to navigate complex data, mitigate risks, and predict trends. With these abilities, analysts become invaluable assets, driving informed decisions, ensuring optimal strategies, and embracing the ever-changing landscape of Financial Analysis.
Navigating the Financial landscape of your business with our Finance For Non-Financial Managers course - Sign up now!
Frequently Asked Questions

Financial Analysts should prioritise learning skills like accounting, interpersonal communication, and problem-solving. Industry expertise, including regulatory environment awareness and analytical/math skills, are also crucial.

Financial Analysts should be adept at using Microsoft Excel, data visualisation tools like Tableau, and financial modelling software. Knowledge of statistical software like R is beneficial.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Accounting & Finance Courses, including Payroll Course, Finance for Non-Financial Managers, Financial Management Course and more. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Credit Risk.
Our Business Skills Blogs cover a range of topics related to Fintech, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Accounting & Finance skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Financial Modelling Course
Financial Modelling Course
Fri 7th Jun 2024
Fri 2nd Aug 2024
Fri 4th Oct 2024
Fri 6th Dec 2024







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


