We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Are you overwhelmed by the vast ocean of data and unsure where to start your journey as a Data Analyst? You’re not alone. The path to becoming a Data Analyst can seem labyrinthine, with an ever-expanding array of skills to master and tools to learn. Navigating this requires a clear and concise Data Analyst Roadmap. Without it, you risk getting lost in the data wilderness, wasting time and energy on outdated or irrelevant techniques.
Fear not! Our blog, “Data Analyst Roadmap: A Quick Guide,” is the compass you need. This blog provides a step-by-step Data Analyst Roadmap to master essential skills, tools, and techniques. It equips you with the knowledge needed to excel in the field of Data Analysis, transforming data chaos into a structured career path.
Table of Contents
1) Who is a Data Analyst?
2) Importance of a Data Analyst?
3) Exploring the Data Analyst Roadmap
4) Looking at the industry-specific roles for Data Analysts
5) Salaries of Data Analyst profiles
6) Conclusion
Who is a Data Analyst?
A Data Analyst is a person who investigates, makes sense from, and renders as useful assets, big clumps of data to discern confidential data trends and perceptions. By converting raw data into valuable information, it assists businesses in making essential decisions. Excel is used by Data Analysts to clean, organise and model their data to ensure its accuracy and relevance. They are tasked with finding trends, patterns, and anomalies in data, producing common visualisations like charts and graphs, and creating detailed reports.
In finance, healthcare, marketing, technology, etc., Data Analysts make use of data-driven evidence to solve specific business problems. They frequently work with other departments — IT, marketing, management, etc. — to discuss and identify business goals to steer their analyses toward those goals (i.e., the value of a customer, impact of an order cancellation, potential fraud, etc.)
The ability to work with programming languages like SQL, Python, and R and understand Data Visualisation tools like Tableau and Power BI are some of the core skills of a Data Analyst. Moreover, they need excellent analytical skills, attention to detail, and the ability to communicate their results to non-technical employees in an easy way.
What is the importance of a Data Analyst?
Data Analysts are indispensable in the modern landscape where data is pivotal. They decipher complex data to provide insights that guide organisations in making well-informed choices. Their expertise helps businesses grasp the nuances within their data, paving the way for improved strategic decisions and operational efficiencies.
By scrutinising data, these Analysts pinpoint potential enhancements, streamline operations, and curtail expenses. For example, in the realm of marketing, they evaluate campaign success, monitor consumer actions, and propose tweaks to boost investment returns. In the financial sector, they spot promising investment avenues, gauge risks, and bolster fiscal outcomes.
Data Analysts also play a vital role in improving Customer Experiences. By analysing customer feedback and behaviour, they can help companies personalise their services, predict future needs, and enhance customer satisfaction. This is particularly crucial in competitive industries where customer loyalty is key.
Furthermore, Data Analysts contribute to innovation by uncovering new business opportunities and driving data-driven product development. Their insights can lead to the creation of new products or services that better meet market demands.
Exploring the Data Analyst Roadmap
The Data Analyst Career Roadmap comprises many checkpoints from which aspirants can get guidance. These checkpoints are highlighted below, as shown:
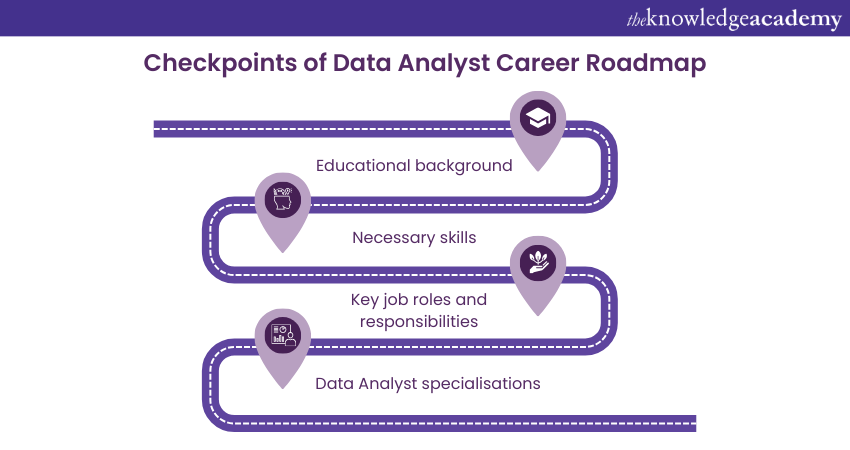
Educational background
The educational qualification required for a Data Analyst generally starts from a minimum of a Bachelor’s degree in a course that focuses on statistics and analytical abilities. They can range from Mathematics, Economics, Computer Science, Information Management, and/or Statistics to any other field. These disciplines also equip the learner with a concrete statistical dsbackground relevant to Data Analysis skills.
Also, although a Bachelor’s degree is usually expected to be attained to get into the company, senior positions may call for a master’s degree or some other postgraduate qualification. Master’s degrees in Data Science or Data Analysis are popular and in high demand by employers at the present time. Such programs may include topics such as machine learning, advanced statistics, and Data Visualisation.
Additionally, besides the academic background, there are some other certifications that can contribute to the professional competence of a Data Analyst. For instance, specialist certifications associated with programming languages such as Python or R or, Data Analysis tools such as SQL or Tableau can be highly beneficial for enhancing a candidate’s marketability.
Learn to process data for analysis and modelling, by signing up for the Microsoft Power BI Data Analyst PL300 Course now!
Necessary skills
To excel in the field of Data Analysis, several key skills are necessary:
a) Statistical and mathematical skills: Data Analysts deal extensively with numbers, making strong mathematical and statistical skills vital. These abilities allow analysts to identify trends, create models, and interpret data effectively.
b) Analytical thinking: The ability to think analytically is crucial. Data Analysts must be able to identify patterns, make sense of complex datasets, and extract insights that can guide business decisions.
c) Proficiency in Data Analysis tools: Data Analysts often use specialised software and programming languages to handle and analyse data. Familiarity with SQL, Excel, Python, R, and Data Visualisation tools like Tableau or Power BI is highly advantageous.
d) Attention to detail: Small discrepancies in data can have significant implications, making attention to detail an essential quality. Data Analysts need to be meticulous in their work to ensure the accuracy of their analyses.
e) Communication skills: The ability to convey intricate data findings in a straightforward and comprehensible way is essential. Data Analysts are required to present their analyses to stakeholders effectively, frequently employing Data Visualisation methods to simplify the comprehension of the information
f) Problem-solving: Finally, problem-solving skills are crucial. The role often involves identifying issues and finding effective solutions, using data as the guiding resource.
Enhance your knowledge to provide excellent customer experience, by signing up for the Customer Experience Training now!
Key job roles and responsibilities
The role of a Data Analyst is multifaceted, with responsibilities that span a broad range of functions. Here are the key job roles and responsibilities of a Data Analyst:
a) Data collection: Data collection is usually the first task in a Data Analyst's job. That is, they may input information from several sources including but not limited to, databases, online sources, surveys, and sales figures. This process is like this, and it must be done with accuracy and consistency so as to guarantee data correctness and reliability.
b) Data cleaning and processing: Data cleaning and processing, followed by data collection, is a task performed by Data Analysts to prepare the data for analysis. This may include eliminating duplicates, dealing with discarded or inconsistent data, and converting data into an analytics-ready format.
c) Data Analysis: After the data is in good shape and prepped, the key journey commences with Data Analysis. By employing statistical techniques, Data Analysts dig deeply into the data and extract patterns, correlations, trends, or outliers. They might make models of apps, test hypotheses or apply machine learning approaches.
d) Data interpretation: The information obtained from these analyses must be further interpreted and grasped within the specific context. Extraction of the statistical findings translates Data Analysts into actionable business insights, which are further explained as they relate to the organisation's objectives or strategies.
e) Data visualisation and reporting: Frequently analysts have to make the data understandable to non-technical people. Doing this, they use infographics, charts, graphs, and dashboards that present the outcomes in a meaningful and eye-opening manner. In addition, they publish reports that explain their methods, conclusions, and suggestions.
f) Collaboration with other teams: Data Analysts usually share their reports and results with different teams within an organisation, including marketing, sales, operations, and finance departments. They help these squads with the analytics needed for informed decision-making and, in return, guide the strategy while improving performance.
g) Problem-solving: Data Analysts appear to be on the front line in solving company issues. They focus on the use of data to establish problems or difficulties, describe their causes and propose possible actions. As an example, they may observe a decrease in sales in a specific region. By examining data they find the reason, and devise a plan to overcome it.
h) Staying up-to-date: The ever-evolving world of Data Analysis incorporates new methodologies, tools and practices at the same time. Consequently, Data Analysts should be mindful of the latest trends, keep up with new developments in this field, and always strive to improve their skills.
Acquire the basic knowledge of visualisation in Business Intelligence, by signing up for the Data Analysis and Visualisation with Python Course now!
Data Analyst specialisations
The field of Data Analysis is broad, and within it, various specialisations have emerged, each with its unique focus. Here are some common specialisations of a Data Analyst:
a) Business Data Analyst: One of the main roles of a business Data Analyst is to determine the company's internal operations and improve these processes. They take a broad look at things like sales, marketing and operations and derive insights into how to improve performance, streamline practices, or make executive decisions.
b) Healthcare Data Analyst: Healthcare Data Analysts are the professionals who analyse data produced within the healthcare sector. For instance, they could be reviewing patient data to spot high rates of a disease or, assess the performance of the drugs or aid healthcare professionals in planning.
c) Financial Data Analyst: In financial sector, Data Analysts work with their skills and explore financial data as well as forecast market trend. They can consider price quotes of securities, economic indices or corporate financials to make investment decisions, evaluate financial risks, or formulate the fiscal policy.
d) Marketing Data Analyst: This Analysts are Marketing Data specialists in their field. They may be involved in the evaluation of marketing campaigns or consumer behavior while segmenting customers. Their inputs can be made to direct marketing, which enables targeting customers more efficiently and improves financial result greatly.
e) Social Media Data Analyst: As social media widely spread, there appeared another direction of the profession. Social media Analysts devote their attention to data from social media platforms to get a grasp of online behaviours, sentiments, or social media campaigns' influence.
Looking at the industry-specific roles for Data Analysts
Data Analysts play a vital role across a range of industries, using their analytical abilities to support decision-making, strategy, and performance. Let's look at some industry-specific roles for Data Analysts:
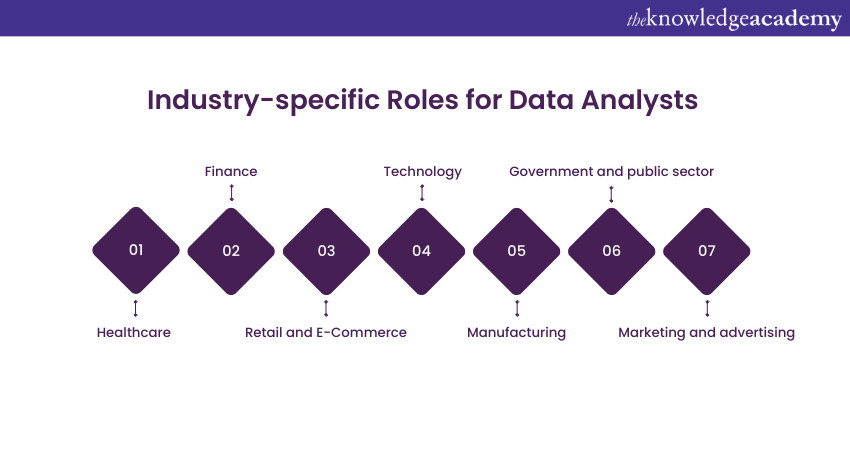
a) Healthcare: Data Analysts provide important input in the healthcare sector by facilitating practical medical care, medical cost management, and medical research. They scan patient files, trial information, and operation data of patients. Their experts’ knowledge may help to identify factors that predispose diseases, improve the protocols of treatment and simplify the healthcare delivery service.
b) Finance: Financial Data Analysts or it is referred to as quantitative analysts or 'quants,' are one of the most essential individuals in this industry. They process financial market information including risks and strategy decisions. They could devise elaborate mathematical models to forecast market movements or assess the effects of economic hackneyed phrases.
c) Retail and E-Commerce: Data Scientists in the industry perform a function of assessing customer behaviour, sales patterns and market data. Their ideas contribute to the tuning of marketing campaigns, product lines assortment and increased quality of customer experience. For example, they will divide customers into groups with similar behaviour and predict future sales procedures with the help of historical data.
d) Technology: Tech firms utilise large amouts of data, therefore, Data Analysts are essential. They explore users' behaviours for the purpose of determining product development, evaluate website traffic for enhancing user experience or scrutinise operational data for the sake of operations’ optimisation.
e) Manufacturing: In manufacturing, Data Analysts provide tools to reduce expenses and improve effectiveness. They may, for example, go into production and supply chain data to search for bottlenecks, logistics optimisation or predictive maintenance.
f) Government and public sector: Public sector Data Analysts are an important part in the policymaking, delivery of services and allocation of resources. For example it may do an analysis of the demographic data to formulate social policies, evaluate service usage data to make public services better or investigate financial data to aid with budgeting decisions.
g) Marketing and advertising: The marketing and advertising approaches of the industries which are based on data, are improved through the efforts of Data Analysts. They look at campaign performance, customer build up, track market trends, and website metrics. Their findings are meant to develop customised messages, precise outlay of marketing funds and engaging the brand.
Salaries of Data Analyst profiles
Here are the various salaries of Data Analyst profiles, displayed according to the different levels of experience and industry domains, listed in the table below:
|
Profile |
Entry-Level (0-2 Years |
Mid-Level (2-5 Years) |
Senior Level (5+ Years) |
|
General Data Analyst |
£25,000 - £35,000 |
£35,000 - £50,000 |
£50,000 - £70,000 |
|
Business Data Analyst |
£30,000 - £40,000 |
£40,000 - £55,000 |
£55,000 - £75,000 |
|
Financial Data Analyst |
£35,000 - £45,000 |
£45,000 - £60,000 |
£60,000 - £80,000 |
|
Healthcare Data Analyst |
£25,000 - £35,000 |
£35,000 - £50,000 |
£50,000 - £70,000 |
|
Marketing Data Analyst |
£28,000 - £38,000 |
£38,000 - £53,000 |
£53,000 - £73,000 |
Source: Glassdoor
Conclusion
You are now more familiar with the Data Analyst Career Roadmap, which comprises various elements such as the job role, educational requirements, necessary skills, job specialisations and the earning potential of various designations. This diverse field offers many exciting opportunities for those with an analytical mindset and a passion for uncovering insights from data.
Frequently Asked Questions

A bachelor's degree in statistics, mathematics, computer science, or related fields is typically required. Mastery of programming languages such as Python or R, combined with expertise in statistical analysis and the use of data visualisation tools, is crucial.

These include programming languages like Python and R, database querying languages such as SQL, and visualisation software like Tableau and Power BI. They also utilise database management systems including MySQL and PostgreSQL, as well as Machine Learning libraries such as scikit-learn.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Big Data and Analytics Training, including Data Science Analytics Course, Big Data Analysis Course and Big Data Architecture Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into What is Data?
Our Data, Analytics & AI Blogs covers a range of topics offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Data Analysis skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Data, Analytics & AI Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Advanced Data Analytics Course
Advanced Data Analytics Course
Mon 12th Aug 2024
Mon 9th Dec 2024







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


