We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Navigating the complexities of Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) is a critical decision for businesses seeking optimal web performance. In this comparison of ‘Cloudflare vs CloudFront’, two giants in the CDN domain, we explore the nuances that differentiate these services.
As organisations strive for faster load times, enhanced security, and global reach, understanding the strengths and weaknesses of Cloudflare and CloudFront becomes paramount. Check out this blog on Cloudflare vs Cloudfront, discussing the CDN infrastructure and customisation options to help users make informed decisions about content delivery.
Table of Contents
1) What is CloudFlare?
2) What is Amazon CloudFront?
3) Difference Between Cloudflare and CloudFront
a) Data transmission
b) Availability through URLs
c) CDN infrastructure
d) Delivering content
e) CDN locations
f) Core function
g) Subscription plans
h) Outbound data costs
i) HTTP/HTTPS requests
j) SSL/TSL certification
4) Conclusion
What is CloudFlare?
Cloudflare, founded in 2009, stands as a global leader in web performance optimisation, security, and content delivery. Operating at the intersection of CDN (Content Delivery Network) and cybersecurity, Cloudflare offers a suite of services designed to enhance the speed, reliability, and security of websites and applications.
At its core, Cloudflare functions as a distributed network of servers strategically positioned around the world. These servers act as intermediaries between a website's origin server and end-users, optimising the delivery of content by caching static resources and intelligently routing dynamic content. This results in reduced latency, faster page load times, and an overall improved user experience.
Beyond its CDN capabilities, Cloudflare is renowned for its robust security features. The platform provides protection against a spectrum of online threats, including DDoS attacks, SQL injection, and other malicious activities. Its Web Application Firewall (WAF) and SSL/TLS encryption ensure a secure communication channel between users and the web server, safeguarding sensitive data.
Cloudflare's user-friendly interface, extensive network infrastructure, and commitment to innovation have made it a go-to solution for businesses seeking to optimise their online presence while fortifying their digital defences. Whether enhancing website performance or fortifying against cyber threats, Cloudflare continues to play a pivotal role in shaping the digital landscape.
What is Amazon CloudFront?
Launched by Amazon Web Services (AWS) in 2008, Amazon CloudFront is a powerful and scalable content delivery network (CDN) service designed to accelerate the delivery of web content to users across the globe.
Positioned within the comprehensive AWS ecosystem, CloudFront seamlessly integrates with other AWS services, making it a preferred choice for businesses leveraging Amazon's cloud infrastructure.
At its core, CloudFront enhances the performance of websites and applications by caching static assets like images, scripts, and videos at multiple edge locations worldwide. This geographically distributed network of servers ensures low-latency access for end-users, reducing load times and improving overall responsiveness.
One notable strength of Amazon CloudFront lies in its flexibility. Businesses can easily configure and customise the CDN settings to suit their specific requirements, adjusting cache behaviours, distribution settings, and security measures.
Moreover, CloudFront supports a wide array of content types, including dynamic content generated by application servers, making it suitable for diverse use cases. Security is a paramount feature of Amazon CloudFront.
With the integration of AWS Shield, CloudFront provides robust protection against Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks, ensuring the availability and reliability of web applications even during periods of high traffic or malicious intent.
Difference Between Cloudflare and CloudFront
Here are the many key differences described between Cloudflare and CloudFront in a tabular format:
|
Parameter |
Cloudflare |
Amazon CloudFront |
|
Data transmission |
Efficient transmission with a global Anycast network |
Global content delivery leveraging Amazon's backbone network |
|
Availability through URLs |
Ensures high availability with its robust network infrastructure |
Reliable availability with multiple edge locations |
|
CDN infrastructure |
Large and distributed network with data centres worldwide |
Integrated within the extensive AWS global network |
|
Delivering content |
Accelerates content delivery through caching, optimisation, and security features |
Optimises content delivery with caching, low latency, and scalability |
|
CDN locations |
250+ cities worldwide with a vast number of edge locations |
Over 200 edge locations globally for optimal content distribution |
|
Core function |
Web optimisation, security, and content delivery network |
Accelerated content delivery with a focus on scalability and integration with AWS services |
|
Subscription plans |
Various plans catering to different user needs, including a free plan |
Pay-as-you-go pricing with tiered plans, additional costs for specific features |
|
Outbound data costs |
Offers a variety of plans with different pricing structures |
Pay-as-you-go pricing model based on data transfer and requests |
|
HTTP/HTTPS requests |
Supports both HTTP and HTTPS requests with SSL/TLS encryption |
Allows HTTP and HTTPS requests with SSL/TLS support |
|
SSL/TLS certification |
Provides SSL/TLS certificates with various validation levels |
Supports SSL/TLS certificates for secure data transmission |
|
APIs |
Offers a comprehensive set of APIs for customisation and automation |
Integrates with AWS APIs for seamless interaction with other services |
|
Global networking |
Leverages a massive global network for optimal content delivery |
Utilises Amazon's extensive global network infrastructure |
|
Safeguarding against DDoS attacks |
Robust DDoS protection with advanced mitigation capabilities |
Enhanced DDoS protection through integration with AWS Shield |
|
System integration |
Integrates with various systems and platforms for seamless functionality |
Seamlessly integrates with other AWS services and tools |
|
Operational performance |
Provides a range of performance optimisation features |
Delivers high operational performance through AWS infrastructure |
|
Data analysis |
Offers analytics tools for insights into website performance |
Integrates with AWS analytics tools for comprehensive data analysis |
|
DNS administration |
Provides advanced DNS management features |
Allows DNS administration with integration into AWS Route 53 |
Below are the detailed descriptions of each of the above parameters:
a) Data transmission
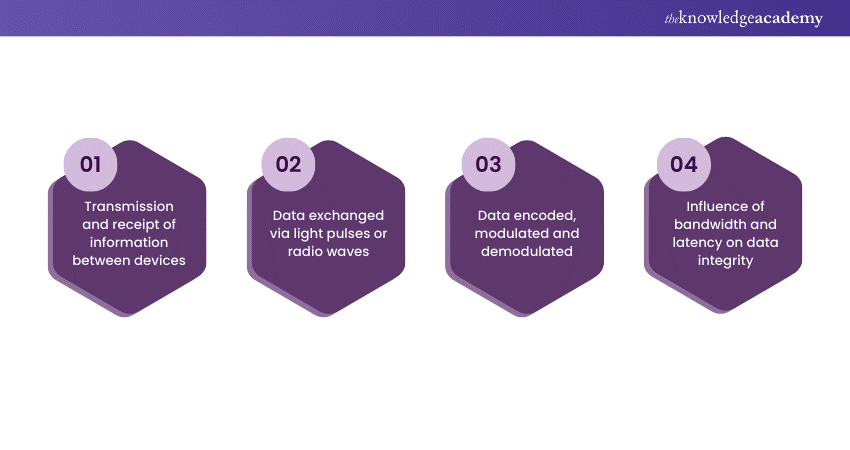
Data transmission refers to the process of sending and receiving information between two or more devices through a communication channel. This exchange of data can occur over various mediums, such as wired or wireless connections. In a digital context, data is typically transmitted in the form of electrical signals, light pulses, or radio waves.
The efficiency and reliability of data transmission are critical in telecommunications, networking, and various technologies. The process involves encoding data into a suitable format, modulating it for transmission, and then demodulating it upon reception. Factors like bandwidth, latency, and error rates influence the speed and integrity of data transmission. Whether through physical cables, optical fibres, or radio frequencies, data transmission is fundamental to the functioning of modern communication systems, enabling the seamless flow of information across diverse platforms and devices.
b) Availability through URLs
Availability through URLs refers to the accessibility of resources or content via Uniform Resource Locators (URLs) on the internet. A URL serves as a unique address that specifies the location of a particular resource, such as a webpage, document, or multimedia file. The concept of availability emphasises the ability of users to access these resources consistently and reliably.
For websites and online services, high availability through URLs is crucial for a positive user experience. It implies that the linked content is consistently accessible and responsive, with minimal downtime or disruptions. Achieving robust availability often involves deploying redundant servers, load balancing, and employing content delivery networks (CDNs) to distribute and deliver resources efficiently.
Organisations prioritise availability to ensure that their online presence remains accessible to users worldwide, contributing to user satisfaction, trust, and overall success in the digital landscape. Reliable URLs and optimal availability are foundational elements for a seamless and effective online presence.
Attain in-depth knowledge of Cloudflare by signing up for our CloudFlare Training now!
c) CDN infrastructure
Content Delivery Network (CDN) infrastructure is a distributed network of strategically located servers designed to optimise the delivery of web content to end-users. Comprising multiple data centres across various geographical locations, a CDN reduces latency and accelerates the loading of web pages by caching and delivering content from servers closest to the user.
The infrastructure typically includes edge servers situated at the network periphery, serving as intermediaries between the origin server (where the content is hosted) and the end-user. These servers store cached copies of static content like images, scripts, and videos, ensuring rapid access to frequently requested resources.
CDN infrastructure enhances scalability, reliability, and performance, which is crucial for websites and applications with global user bases. Through load balancing, efficient data routing, and optimisation techniques, CDNs contribute to a seamless user experience, decreased bandwidth usage, and improved overall web performance.
The strategic placement of CDN servers minimises latency, making it an essential component for content providers and businesses seeking to enhance their online presence.
d) Delivering content
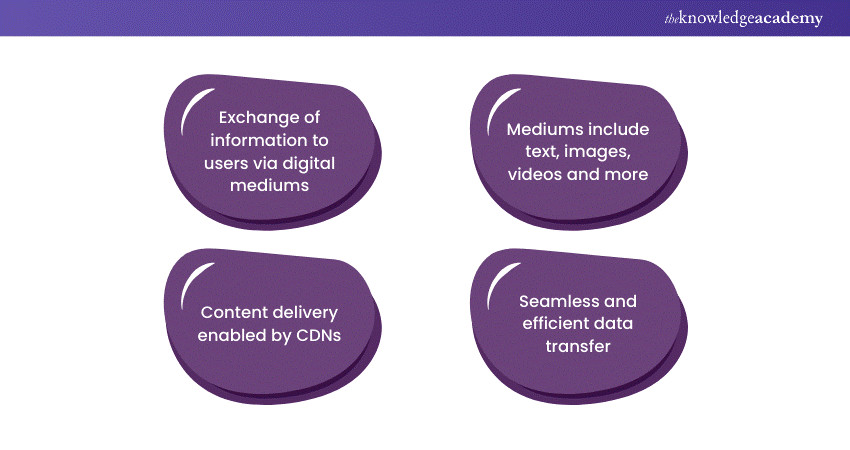
Delivering content involves the process of transmitting and presenting information to end-users through various digital mediums. In the context of the internet, this typically revolves around web content, such as text, images, videos, and interactive elements. The goal is to ensure a seamless and efficient transfer of data from the content source (origin server) to the user's device.
Content delivery is often facilitated by technologies like Content Delivery Networks (CDNs), which optimise the distribution of content by strategically placing servers worldwide. These servers cache and deliver static assets, reducing latency and enhancing the speed of access. The delivery process also involves protocols like HTTP/HTTPS, ensuring secure and standardised communication between servers and clients.
Efficient content delivery is paramount for a positive user experience, as it influences website performance, load times, and overall accessibility. Businesses and content providers continually refine their content delivery strategies to meet user expectations and navigate the challenges of diverse digital landscapes.
e) CDN locations
CDN locations refer to the strategically positioned servers within a Content Delivery Network (CDN) across various geographical points. These locations, also known as edge servers or Points of Presence (PoPs), play a pivotal role in optimising content delivery to end-users. By dispersing these servers globally, CDNs aim to reduce latency and enhance the performance of websites and applications.
The distribution of CDN locations ensures that content is cached closer to users, minimising the physical distance data needs to travel. This results in faster load times and improved responsiveness, especially for static resources like images, scripts, and videos. CDN providers strategically select these locations based on network traffic patterns, user demographics, and the geographical distribution of their audience.
In essence, the effectiveness of a CDN is closely tied to the number and strategic placement of its locations, enabling businesses to offer a seamless and accelerated user experience on a global scale.
f) Core function
The core function of a system or technology represents its fundamental purpose or primary activity. It encapsulates the central task or capability that the system is designed to perform, serving as the cornerstone of its functionality. The core function is the essential feature that differentiates and defines the system's overall utility.
In technology, for instance, the core function of a software application might be data processing, communication, or content creation. For a device, it could be a specific hardware capability like image capture, data storage, or computational processing.
Understanding and optimising the core function is crucial for designing effective and efficient systems. It guides the development process, shapes user experience, and influences the overall success and usability of the technology or system in fulfilling its intended purpose.
g) Subscription plans
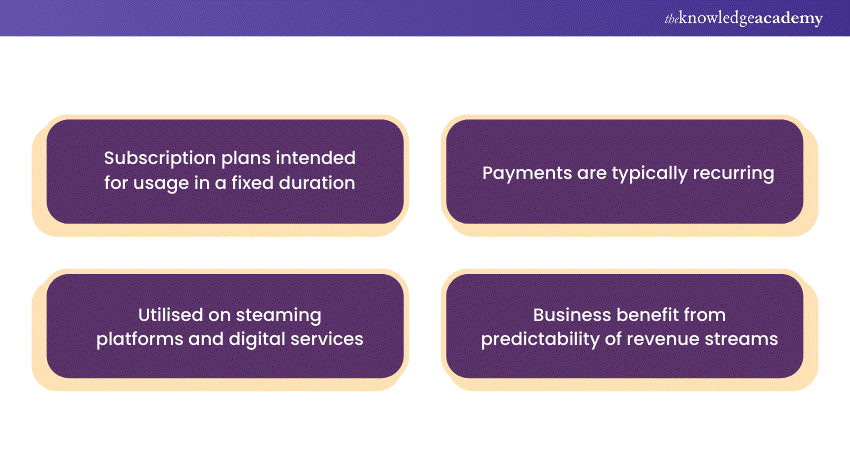
Subscription plans are structured offerings by businesses that provide users with access to products or services for a specified duration in exchange for recurring payments. Typically associated with software, streaming platforms, publications, and other digital services, subscription plans offer users flexibility and continuous access to content or features.
These plans often come in various tiers, each offering different levels of access, features, or additional perks based on the subscription level and pricing. Common subscription models include monthly, annual, or tiered options, allowing users to choose plans that align with their needs and budget. Businesses benefit from the predictability of revenue streams, fostering customer loyalty through continuous service and regular updates.
Subscription plans have become a prevalent and versatile business model in the digital age, providing both consumers and businesses with a sustainable and scalable approach to accessing and delivering products and services.
h) Outbound data costs
Outbound data costs refer to the expenses associated with transmitting data from a user's network to external servers or destinations. In the realm of telecommunications and cloud services, these costs are often incurred based on the volume of data sent from a user's system to servers hosted by a service provider or another external entity.
For businesses and individuals utilising cloud platforms, streaming services, or sending large quantities of data over the internet, outbound data costs are a critical consideration. Service providers typically charge for the data leaving their network, and pricing models may vary, encompassing factors such as data volume, destination, and network infrastructure.
Managing outbound data costs is essential for optimising expenses and ensuring cost-effectiveness in data-intensive operations. This involves strategic planning, utilisation of content delivery networks (CDNs) for efficient data distribution, and awareness of how outbound data usage aligns with service provider pricing structures.
i) HTTP/HTTPS requests
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) and its secure counterpart HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) are fundamental protocols governing data communication on the World Wide Web. These protocols facilitate the exchange of information between a client (typically a web browser) and a server. HTTP/HTTPS requests are the mechanisms through which a client communicates with a server to retrieve or send data.
HTTP operates over a clear text, making it susceptible to security risks. In contrast, HTTPS encrypts the data exchanged between the client and server, ensuring a secure and private connection. Requests in these protocols are initiated by the client, specifying actions such as retrieving a webpage, submitting form data, or fetching resources like images or scripts. Each request includes a method (GET, POST, etc.), headers, and, in the case of HTTPS, encrypted data, collectively forming the foundation of seamless and secure web communication.
j) SSL/TSL certification
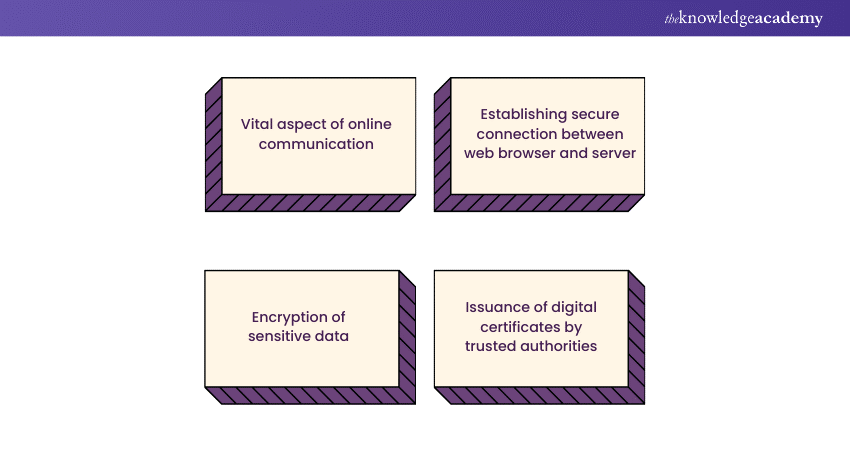
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) and its successor, TLS (Transport Layer Security), certification are crucial aspects of securing online communication. These cryptographic protocols establish a secure connection between a user's web browser and a server, ensuring that sensitive data, such as login credentials and financial information, is encrypted and protected from unauthorised access during transmission.
SSL/TLS certification involves the issuance of digital certificates by trusted Certificate Authorities (CAs). These certificates verify the identity of the website and enable the encryption of data exchanged between the user and the server. The certification process includes domain validation, organisation validation, or extended validation, depending on the level of assurance required.
Websites with SSL/TLS certification display a padlock icon in the address bar, indicating a secure connection. This not only safeguards user privacy but also builds trust and confidence in online interactions, making SSL/TLS certification an essential component of web security.
Conclusion
We hope that you have understood the distinguishing parameters between Cloudflare vs Cloudfront, and that it requires careful consideration of factors like performance, security, and pricing. While Cloudflare excels in global networking and DDoS protection, CloudFront integrates seamlessly with AWS services. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for optimising web delivery and enhancing online experiences.







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course




 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


