We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

In modern business, data has become the lifeblood that fuels decision-making, strategy formulation, and overall organisational success. However, the raw data itself is often overwhelming and complex to understand. This is where Business Objects Reporting comes into play. It serves as a powerful tool that transforms raw data into actionable insights. This blog will give a quick overview of What is Business Objects Reporting, understand its components, and how it contributes to informed decision-making.
Table of Contents
1) What is Business Objects Reporting?
2) Components of Business Objects Reporting
a) Data source
b) Universe designer
c) Report designer
d) Central Management Server
3) How does Business Objects Reporting system work?
4) Conclusion
What is Business Objects Reporting?
Business Objects Reporting is a robust business intelligence tool designed to facilitate data analysis, visualisation, and reporting within organisations. It empowers users to transform raw data from various sources into meaningful and interactive reports, dashboards, and visualisations. This tool simplifies the process of data analysis by providing a user-friendly interface that caters to both technical and non-technical users.
Supercharge your data reporting skills with our Business Objects Web Intelligence Reporter Course. Sign up today!
Components of Business Objects Reporting
Business Objects Reporting comprises several interconnected components that work in harmony to create a seamless reporting experience.
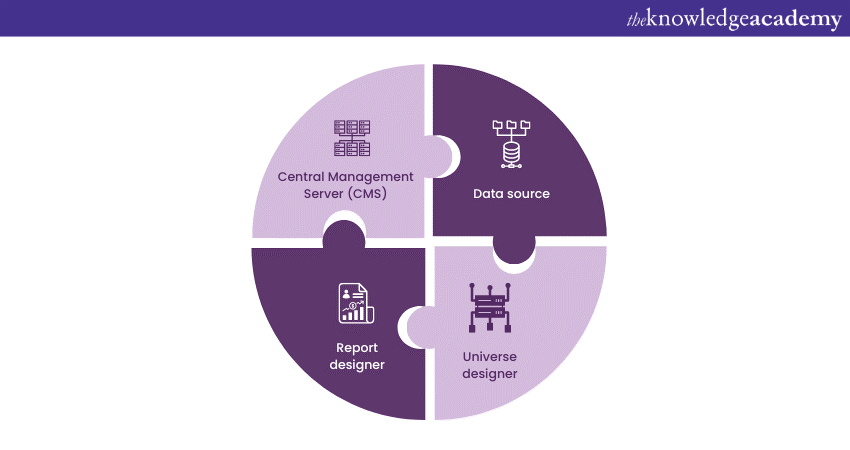
a) Data source
The data source is the foundation of Business Objects Reporting. It refers to the databases, spreadsheets, or other data repositories that store the raw information. Business Objects Reporting can connect to a variety of data sources, allowing users to retrieve and analyse data from multiple origins.
b) Universe designer
Universe designer acts as a semantic layer that bridges the gap between technical data and end-user understanding. It creates a virtual layer that simplifies complex data structures and provides users with a more intuitive way to interact with data. Universes define relationships, hierarchies, and business terminology, making it easier to build reports.
c) Report designer
The Report Designer is where the magic happens. Users can create visually appealing reports by selecting data from the universe and arranging it in tables, charts, graphs, and more. This component offers various customisation options to tailor reports to specific requirements.
d) Central Management Server (CMS)
The Central Management Server (CMS) is the administrative hub of Business Objects Reporting. It manages user access, security settings, report scheduling, and distribution. The CMS ensures that the right people have access to the right reports while maintaining data integrity.
Unlock the power of data insights with our Business Objects Reporting Course - Join now to transform your reporting skills and drive informed decisions!
How does Business Objects Reporting system work?
Business Objects Reporting operates through a sequence of steps that transform data into insightful reports:
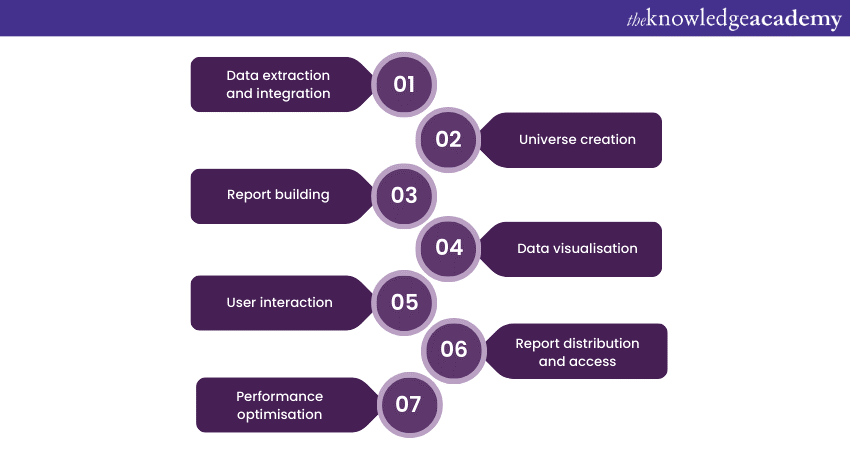
1) Data extraction and integration
The journey begins with data extraction from diverse sources such as databases, spreadsheets, and other data repositories. This extracted data may be scattered across various systems and formats. Business Objects Reporting integrates this disparate data, bringing it together into a unified view. Integration involves cleansing, transforming, and conforming the data to ensure consistency and accuracy.
2) Universe creation
The Universe Designer component of Business Objects Reporting plays a crucial role in simplifying the interaction between users and complex data structures. This is achieved through the creation of a "universe," which acts as a semantic layer. The universe defines business terminology, relationships, and hierarchies, making data more comprehensible to users. It essentially serves as a bridge, translating technical data into a user-friendly language.
3) Report building
Once the universe is in place, users can harness the power of the Report Designer to create insightful reports. The Report Designer offers a user-friendly interface that allows users to select data elements from the universe and arrange them in tables, charts, graphs, and other visualisations. This component offers a range of customisation options, enabling users to tailor their reports to specific requirements.
4) Data visualisation
The heart of Business Objects Reporting lies in its ability to convert raw data into visually engaging and informative representations. Users can select from a variety of visualisation options, including pie charts, bar graphs, line charts, and heat maps. These visualisations make it easier to spot patterns, trends, and anomalies within the data, enabling more effective decision-making.
5) User interaction
Business Objects Reporting goes beyond static reports. It empowers users to interact with the data and explore different dimensions. Users can apply filters, drill down into specific data points, and customise their views based on their requirements. This level of interactivity ensures that users can extract the exact insights they need, enhancing the value of the reporting process.
6) Report distribution and access
The Central Management Server (CMS) component ensures that the right people have access to the right reports at the right time. It manages user permissions, security settings, and report distribution. Users may schedule reports to be generated and distributed automatically, streamlining the flow of information throughout the organisation. This facilitates collaborative decision-making by ensuring that relevant stakeholders have access to up-to-date insights.
7) Performance optimisation
Business Objects Reporting also includes mechanisms for optimising performance. Aggregations, caching, and efficient query processing are employed to ensure that reports are generated swiftly and efficiently, even when dealing with large datasets. This responsiveness is critical for maintaining user engagement and productivity.

Conclusion
This blog covered an overview of What is Business Objects Reporting, its components and its process. Business Objects Reporting bridges the gap between raw data and informed decision-making. By providing a user-friendly interface, powerful visualisations, and streamlined reporting processes, it empowers organisations to unlock the true potential of their data.
Elevate your data visualisation skills with our Microsoft Power BI Training— Register now!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming Office Applications Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Microsoft Power BI Course
Microsoft Power BI Course
Wed 15th May 2024
Wed 5th Jun 2024
Wed 19th Jun 2024
Wed 3rd Jul 2024
Wed 17th Jul 2024
Wed 7th Aug 2024
Wed 21st Aug 2024
Wed 4th Sep 2024
Wed 18th Sep 2024
Wed 9th Oct 2024
Wed 23rd Oct 2024
Wed 6th Nov 2024
Wed 20th Nov 2024
Wed 4th Dec 2024
Wed 11th Dec 2024
Wed 18th Dec 2024







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


