We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +61 272026926 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
In the world of finance, Portfolio Management plays a crucial role in helping individuals and organisations make informed investment decisions. Whether you're an experienced investor or an amateur, understanding the basics of What is Portfolio Management is essential to maximise returns and minimise risks.
Explore What is Portfolio Management with our blog . Gain insights into its definition, importance, effective strategies, and essential tips to avoid common mistakes.
Table of Contents
1) Understanding “What is Portfolio Management?”
2) Components of a portfolio
3) Portfolio Management strategies
4) Benefits of implementing Portfolio Management
5) Common mistakes in Portfolio Management
6) Conclusion
Understanding What is Portfolio Management?
Portfolio Management refers to the strategic process of overseeing and managing a collection of investments, known as a portfolio, intending to achieve specific financial objectives. It involves carefully analysing and selecting investment options, monitoring their performance, and making informed decisions to optimise the portfolio's risk and return.
In Portfolio Management, investors or Portfolio Managers consider various factors such as the investor's risk tolerance, investment goals, time horizon, and market conditions. They aim to strike a balance between generating higher returns and minimising potential risks by diversifying the portfolio across different asset classes, industries, and geographic regions.
Components of a portfolio
A portfolio consists of various components that work together to form a comprehensive investment strategy. These components help investors diversify their holdings, manage risk, and align their investments with their financial goals. The key components of a portfolio include:
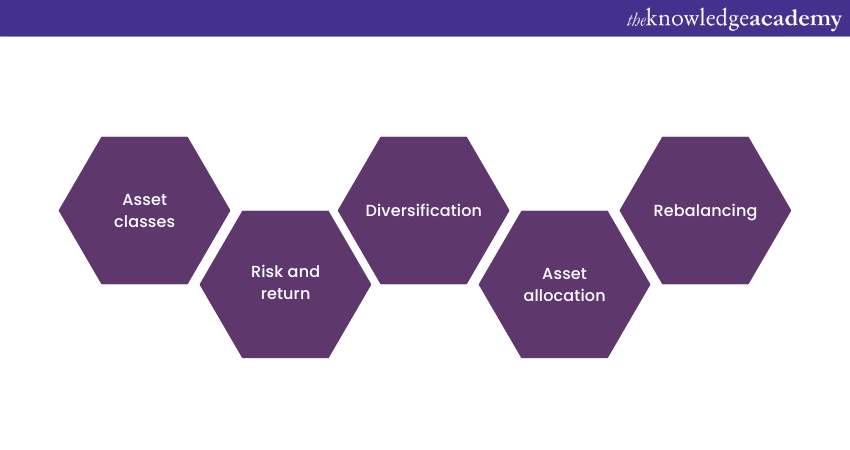
Risk and return
When constructing a portfolio, investors must consider the relationship between risk and return. Generally, investments with higher potential returns come with higher levels of risk. It is crucial to balance seeking higher returns and managing the associated risks. Investors should assess their risk tolerance and financial goals to determine the appropriate allocation of assets within their portfolio.
Diversification
Diversification is a vital principle in Portfolio Management. It involves spreading investments across diverse asset classes, industries, and geographic regions. By diversifying, investors aim to reduce the impact of any single investment's poor performance on the overall portfolio. The process helps mitigate risk and can enhance the portfolio's potential for long-term growth.
Asset allocation
Asset allocation refers to the strategic distribution of investments across different asset classes. The allocation depends on the investor's risk tolerance, investment horizon, and financial objectives. A well-designed asset allocation strategy considers factors such as age, financial goals, and time horizon. It helps create a balanced portfolio that aligns with the investor's risk appetite and maximises the potential for returns.
Rebalancing
Over time, the performance of different investments within a portfolio may deviate from the desired asset allocation. Rebalancing involves periodically reviewing and adjusting the portfolio to maintain the desired allocation. This process ensures the portfolio remains aligned with the investor's goals and risk tolerance. Rebalancing may involve selling overperforming assets and buying underperforming ones, returning the portfolio to its target allocation.
Master the art of Portfolio Management, drive strategic value, and lay a solid foundation for success with our Management Of Portfolios (MOP) Foundation Course!
Portfolio Management strategies
Portfolio Management strategies involve implementing specific approaches to guide investment decisions and optimise the performance of a portfolio. These strategies consider various factors, such as the investor's risk tolerance, investment goals, and market conditions. Here are some commonly used Portfolio Management strategies:
Active vs passive management
Active management involves actively selecting and managing individual investments to outperform the market. Portfolio Managers conducting active management often engage in extensive research, analysis, and frequent buying and selling of assets. In contrast, passive management involves investing in index funds or Exchange-traded Funds (ETFs) that look to replicate the performance of a particular market index. Passive strategies generally require less frequent trading and focus on long-term investment goals.
Growth vs value investing
Growth investing focuses on identifying companies with high growth potential. These companies often reinvest their earnings back into the business to fuel expansion. Growth investors seek companies with strong revenue and earnings growth, usually in technology, healthcare, and other innovative sectors. Value investing, on the other hand, involves seeking undervalued companies whose stock prices may not reflect their intrinsic value. Value investors look for companies that may be temporarily out of favour or undervalued by the market.
Long-term vs short-term investing
Long-term investing involves holding investments for an extended period, often years or even decades. Long-term investors aim to capitalise on compounding returns and the potential for growth over time. They generally take a more patient and less reactive approach to market fluctuations. In contrast, short-term investing takes advantage of short-term market trends and price movements. Short-term investors may engage in more frequent trading and try to profit from market volatility.
Tactical vs strategic asset allocation
Tactical asset allocation involves making short-term adjustments to the portfolio's asset allocation based on current market conditions and economic outlook. Portfolio Managers employing this strategy may increase or decrease exposure to specific asset classes to take advantage of perceived opportunities or manage risk. Strategic asset allocation, on the other hand, focuses on long-term objectives and adheres to a predetermined asset allocation strategy. Strategic allocation decisions are typically based on an investor's risk profile and long-term goals.
Risk management strategies
Risk management strategies aim to minimise potential losses and protect the portfolio during adverse market conditions. These strategies may include diversification, hedging, or employing defensive investment approaches. Portfolio Managers may use derivatives, options, or other risk management tools to mitigate specific risks associated with certain investments or market events.
Benefits of implementing Portfolio Management
Implementing Portfolio Management offers several benefits to investors. By adopting effective Portfolio Management practices, individuals and organisations can maximise the potential for returns while minimising risks. Here are the key benefits of implementing Portfolio Management:
Risk-return optimisation
Portfolio Management enables investors to optimise the risk-return trade-off. By carefully selecting investments and balancing the portfolio's asset allocation, investors can tailor the risk exposure to their comfort level while seeking higher potential returns. The Portfolio Management process involves assessing an investor's risk tolerance, financial goals, and investment horizon to determine the optimal mix of assets that align with their objectives. Through diversification and risk management techniques, Portfolio Management aims to achieve an optimal balance between risk and return.
Active monitoring and adjustments
Effective Portfolio Management involves continuous monitoring of investments and making informed adjustments when necessary. Regularly reviewing the portfolio's performance and comparing it to established benchmarks allows investors to identify underperforming assets or sectors. By actively managing the portfolio, investors can take advantage of emerging opportunities, respond to market trends, and mitigate potential risks. This proactive approach helps investors stay on track towards their financial goals and adapt to changing market conditions.
Long-term financial discipline
Portfolio Management promotes long-term financial discipline. It encourages investors to focus on their overarching investment objectives rather than getting swayed by short-term market fluctuations or impulsive investment decisions. By setting clear investment goals and aligning their portfolio accordingly, investors are more likely to stay committed to their long-term plans and resist emotional reactions to market volatility. This disciplined approach can lead to better investment outcomes and a greater likelihood of achieving financial objectives.
Professional expertise and guidance
Implementing Portfolio Management often involves seeking professional expertise and advice. Financial Advisors or Portfolio Managers bring their knowledge and experience to the table, providing valuable insights and recommendations. They can assist investors in constructing a well-balanced portfolio, selecting suitable investments, and managing risk effectively. By working with professionals, investors can benefit from their expertise and access to sophisticated tools and resources, enhancing their Portfolio Management capabilities.
Performance evaluation and transparency
Portfolio Management facilitates thorough performance evaluation and transparency. By monitoring the portfolio's performance, investors can assess the progress towards their investment goals and evaluate the effectiveness of their investment strategy. This evaluation allows for informed decision-making and adjustments as needed. Additionally, implementing Portfolio Management practices provides transparency, enabling investors to clearly understand their investments, associated risks, and the factors influencing their portfolio's performance.
Learn how to identify techniques for maintaining Portfolios! Sign up for our Management of Portfolios (MoP®) Foundation & Practitioner Course now!
Common mistakes in Portfolio Management
Listed below are some common mistakes in Portfolio Management:
Lack of diversification
Failing to diversify is a prevalent mistake in Portfolio Management. Investing too heavily in a single asset class, industry, or geographic region exposes the portfolio to unnecessary risk. A lack of diversification can leave the portfolio vulnerable to significant losses if a particular investment or sector performs poorly. Proper diversification helps mitigate risk and provides the potential for better risk-adjusted returns.
Chasing past performance
Chasing past performance is a mistake that occurs when investors make investment decisions solely based on recent performance. Assuming that investments that have performed well in the past will continue to do so can lead to disappointment. Past performance cannot guarantee future results, and investment strategies or market conditions may change. It is therefore crucial to conduct thorough research and consider the fundamentals of an investment rather than relying solely on historical performance.
Neglecting risk management
Failing to manage risk adequately is a significant Portfolio Management mistake. Each investment carries a certain level of risk, and ignoring or underestimating these risks can have detrimental consequences. Proper risk management involves diversifying investments, understanding risk-return trade-offs, and employing risk management techniques such as stop-loss orders or hedging strategies. Ignoring risk can expose the portfolio to unnecessary volatility and potential losses.
Overtrading
Overtrading, or excessive buying and selling of investments, is a common mistake that can incur unnecessary costs and reduce overall returns. Frequent trading can increase transaction fees, taxes, and potential timing errors. It is essential to distinguish between strategic adjustments based on careful analysis and impulsive trading driven by short-term market fluctuations. Overtrading can disrupt the intended long-term investment strategy and increase the risk of poor decision-making.
Lack of regular portfolio review
Neglecting regular portfolio review and monitoring is a mistake that can result in missed opportunities or holding underperforming investments. Regularly reviewing the portfolio's performance, comparing it against established benchmarks, and assessing individual holdings is essential. This allows investors to identify and address any underperforming assets, make necessary adjustments, and ensure that the portfolio remains aligned with the investor's goals and market conditions.
Unlock the power of effective portfolio, programme, and Project Management, and drive organisational success with our comprehensive P3O® Training. Join now!
Conclusion
In conclusion, this blog explains why investors must know What is Portfolio Management and why they should implement it before making risky investments. By implementing diversification, active monitoring, and risk management strategies, investors can optimise their portfolios for long-term success. Avoiding common mistakes such as emotional investing and neglecting regular review ensures a disciplined and informed approach. With careful planning, prudent decision-making, and a focus on long-term objectives, Portfolio Management empowers investors to navigate market complexity and work towards financial prosperity.
Transform your approach to Portfolio Management, maximise strategic alignment, and achieve organisational excellence with our comprehensive MoP® Management of Portfolios Courses!
Frequently Asked Questions

Portfolio Management is a valuable skill that can help you achieve your career goals. By learning how to select, prioritise, and execute the right projects, you can demonstrate your strategic thinking, leadership, and problem-solving abilities. Portfolio Management can also open up opportunities for advancement, as it is a key function in many organisations.

Portfolio Management aligns the projects and initiatives of an organisation with its strategic objectives and available resources. It ensures that the organisation invests in the most valuable and feasible opportunities and delivers the expected outcomes and benefits. Portfolio Management also enables the organisation to adapt to changing market conditions and customer needs and optimise its performance and agility.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various MoP® Management of Portfolios courses, including MoP® Foundation and Practitioner courses. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Portfolio Management methodologies.
Our Portfolio Management blogs covers a range of topics related to PRINCE2, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Business skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Management of Portfolios (MoP®) Foundation & Practitioner
Management of Portfolios (MoP®) Foundation & Practitioner
Mon 6th May 2024
Mon 16th Sep 2024
Mon 9th Dec 2024







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


