We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +1 7204454674 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

In the ever-evolving domain of technology, Cyber Resilience has appeared as a beacon of hope amid the constant fear of cyber threats. As the digital landscape develops and vulnerabilities multiply, organisations and individuals alike must fortify their defences and cultivate the ability to recover swiftly and effectively.
This blog delves into the essence of Cyber Resilience, making you understand —its definition, components, and significance. Join us as we uncover the strategies, challenges, and real-world examples that illustrate the vital role of Cyber Resilience in safeguarding our interconnected world. Read more to learn more about What is Cyber Resilience!
Table of Contents
1) Understanding Cyber Resilience
2) The importance of Cyber Resilience
3) Building Cyber Resilience
4) Challenges in achieving Cyber Resilience
5) Conclusion
Understanding Cyber Resilience
Cyber Resilience has emerged as a critical pillar of modern Cybersecurity strategies. Unlike traditional approaches that focus primarily on preventing cyberattacks, Cyber Resilience acknowledges the inevitability of breaches and disruptions while emphasising an organisation's ability to withstand, respond to, and recover from such incidents.
It encompasses a comprehensive set of strategies, practices, and technologies that collectively fortify an organisation's ability to endure, adapt, and thrive in the face of ever-evolving cyber threats. It acknowledges that the digital landscape is inherently risky and aims to mitigate the impact of incidents rather than solely preventing them.
While Cybersecurity and Cyber Resilience are often used interchangeably, they represent distinct yet complementary concepts. Cybersecurity predominantly concentrates on establishing protective measures to prevent unauthorised access, data breaches, and cyberattacks. It encompasses tools like firewalls, encryption, and intrusion detection systems.
On the other hand, Cyber Resilience transcends the boundaries of prevention to encompass the full spectrum of incident response and recovery. It assumes that breaches are unfortunate and focuses on minimising the damage, reducing downtime, and ensuring that the organisation can continue its operations as smoothly as possible.
The importance of Cyber Resilience
The digital revolution has ushered in remarkable advancements, transforming how we communicate, conduct business, and interact with the world. However, this transformation has also introduced unprecedented challenges, particularly in Cybersecurity. Data breaches, cyber-attacks, and other threats are becoming increasingly sophisticated, and individuals and entities constantly battle safeguarding sensitive information.
In response to this urgent need for enhanced Cybersecurity measures, governments and regulatory bodies have turned their attention to legislation promoting Cybersecurity and Cyber Resilience. The Cyber Resilience Act represents a crucial milestone in this journey towards a more secure digital landscape.
The growing threat of cyberattacks casts a long shadow over individuals, businesses, and governments. The internet has undoubtedly brought unparalleled connectivity, innovation, and progress opportunities. However, it has also exposed us to a new realm of vulnerabilities that malicious actors are all too eager to exploit.
Cyberattacks have evolved from isolated and simplistic attempts to disrupt systems into sophisticated, well-coordinated campaigns that can wreak havoc on a global scale. Gone are the days when hackers operated solely for the thrill of causing chaos or gaining notoriety.
Today, cybercriminals have adopted a professional and profit-driven mindset, often working as part of more extensive criminal networks or state-sponsored entities.
Our increasing dependence on technology has expanded the attack surface for cybercriminals. Internet of Things (IoT) devices, often designed conveniently rather than securely, can serve as network entry points. While offering immense benefits, Cloud Computing also introduces potential vulnerabilities if not properly secured.
Unlock the potential of Cyber Resilience with our RESILIA® Foundation Course.
Building Cyber Resilience
Proactive identification of potential threats is at the core of Cyber Resilience. It constantly monitors network activities and digital environments to detect anomalies, vulnerabilities, and signs of compromise. Threat intelligence leverages data from various sources to predict and counter emerging threats, enabling organisations to take pre-emptive actions.
Understanding an organisation's digital vulnerabilities and potential risks is paramount for effective Cyber Resilience. Comprehensive risk assessments evaluate the organisation's assets, openness, and the potential impact of cyber incidents. This information aids in prioritising resources and efforts toward safeguarding critical assets.
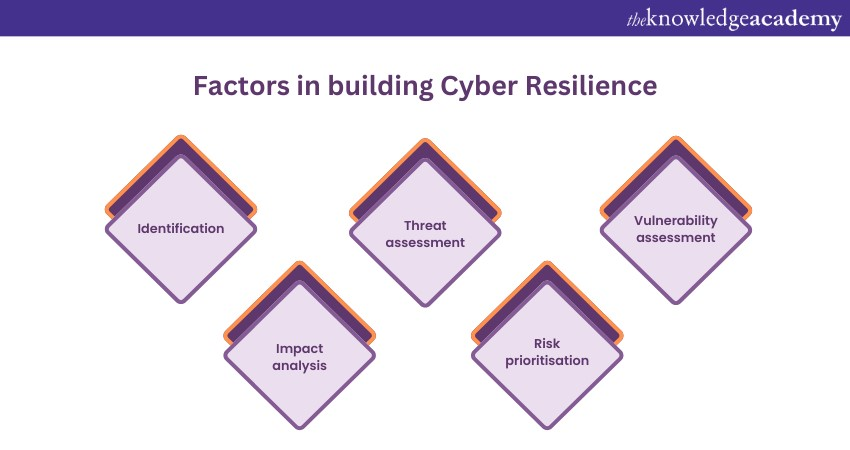
1) Identification: Identify assets, systems, and processes critical to the organisation's operations. This includes both digital and physical assets.
2) Threat assessment: Analyse the potential threats that could target these critical assets. Understand the tactics, techniques, and procedures that cyber attackers might employ.
3) Vulnerability assessment: Evaluate vulnerabilities in the organisation's systems and processes that attackers could exploit. This can involve vulnerability scanning and penetration testing.
4) Impact analysis: Determine the potential impact of a successful cyberattack on the organisation's operations, finances, reputation, and compliance.
5) Risk prioritisation: Assign a risk level to each identified vulnerability based on its likelihood and potential impact. This helps in prioritising resources for mitigation efforts.
To enhance Cyber Resilience, organisations must architect their digital infrastructure with adaptability. Adaptive security architecture focuses on creating multiple layers of defence that can adjust to emerging threats and attacks. Following methods can ensure a secured digital infrastructure:
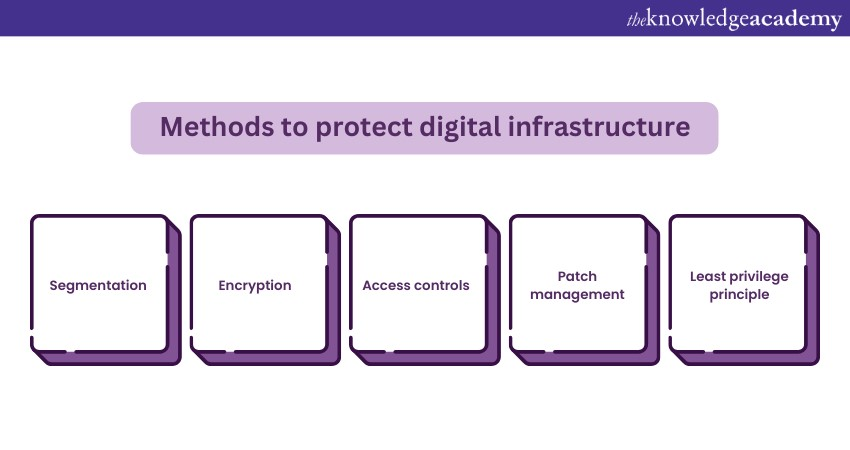
1) Segmentation: Divide the network into segments to restrict the lateral movement of attackers. This limits the potential damage if one part is breached.
2) Encryption: Use encryption to protect data both at rest and in transit. This ensures that even if data is intercepted, it remains unreadable without the appropriate decryption key.
3) Access controls: Implement strict access controls to limit who can access sensitive systems and data. Use multi-factor authentication to enhance security.
4) Patch management: Regularly update software and systems to address known vulnerabilities. Many cyber incidents occur due to outdated software.
5) Least privilege principle: Grant users the minimum access necessary for their roles.
An integral aspect of Cyber Resilience is the development of comprehensive incident response and recovery plans.
1) Developing a response plan: A well-defined response plan outlines roles, responsibilities, communication protocols, and containment strategies that minimise the damage of a cyber incident.
2) Business continuity measures: It ensure critical functions can continue even during an incident, minimising disruption to operations and customer service.
Humans remain critical in cyber incidents, often inadvertently facilitating attacks through social engineering or lack of awareness. Regular training and programs that raise awareness can empower employees to recognise threats and adopt secure behaviours. Following methods describe components of training:
1) Phishing awareness: Educate employees about the dangers of phishing and how to identify suspicious links and attachments.
2) Password hygiene: Promote solid and unique passwords and the practice of not sharing credentials.
3) Social engineering: Train employees to be cautious when sharing sensitive information, even with seemingly legitimate individuals.
4) Data handling: Teach employees proper data handling procedures to prevent accidental data leaks or breaches.
5) Reporting: Establish clear procedures for reporting potential security incidents or concerns to the IT or security team.
Challenges in achieving Cyber Resilience
One of the foremost challenges in building Cyber Resilience is the rapid evolution of cyber threats. Hackers and malicious actors constantly refine their tactics, leverage advanced technologies, and exploit newly discovered vulnerabilities.
This dynamic nature of cyber threats requires organisations to stay vigilant and adaptive, often requiring them to predict the unpredictable. Following ways can be adopted to address the challenges:
1) Threat intelligence: Invest in robust threat intelligence mechanisms that monitor and analyse emerging threats, providing timely information to guide defensive strategies.
2) Agile security measures: Implement agile security practices that swiftly respond to new threats and vulnerabilities, ensuring up-to-date defence mechanisms.
3) Collaborative information sharing: Engage in collaborative efforts with industry peers, governmental agencies, and Cybersecurity communities to share threat intelligence and mitigation strategies.
Resource constraints pose a significant challenge for organisations striving to build Cyber Resilience. Effective Cybersecurity requires financial investments in advanced tools, skilled Cybersecurity personnel, and ongoing training initiatives. Following are the mitigation strategies:
Smaller organisations and those operating on limited budgets often need help to allocate adequate resources to combat cyber threats effectively.
1) Prioritisation: Identify and prioritise critical assets and vulnerabilities, focusing resources on areas that present the highest risk to the organisation.
2) Outsourcing: Consider outsourcing certain Cybersecurity functions, such as penetration testing or incident response, to specialised service providers.
3) Security Awareness: Cultivate a culture of Cybersecurity awareness among all staff members, utilising cost-effective training programs to increase their ability to identify and respond to threats
Equip your organisation with the power of Cyber Resilience. Explore our comprehensive RESILIA® Training and navigate the complex landscape of cyber threats with confidence.
Conclusion
Cyber Resilience is a cornerstone of modern defence strategies in a digital frontier. It's more than a buzzword; it's a perspective that embraces adaptability, preparedness, and continuous improvement. As technology advances and threats become more sophisticated, Cyber Resilience remains a testament to our ability to withstand, adapt to, and recover from the digital realm's challenges. We hope you have now understood What is Cyber Resilience!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming IT Security & Data Protection Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 RESILIA® Foundation and Practitioner
RESILIA® Foundation and Practitioner
Mon 30th Sep 2024
Mon 18th Nov 2024







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


