We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +91 8037244591 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Business Impact Analysis (BIA) is a process that enables businesses to identify and evaluate the potential consequences of disruptive events on their critical functions and processes. By conducting a comprehensive BIA, organisations gain valuable insights into their vulnerabilities, allowing them to develop strategies that minimise the impact of disruptions.
If you wish to uncover the key components of BIA, understand the steps involved in conducting an analysis, and the benefits it brings to the table, this blog might be what you need. Keep reading to learn about Business Impact Analysis, a process that identifies and assesses the potential impact of disruptions on business operations.
Table of Contents
1) Business Impact Analysis definition
2) Business Impact Analysis vs. Risk Assessment
3) Business Impact Analysis vs. Business Continuity Planning
4) Business Impact Analysis vs. Disaster Recovery Planning
5) How to conduct a Business Impact Analysis?
6) Importance of Business Impact Analysis
7) Business Management Templates
8) Key components of Business Impact Analysis
9) Challenges in Business Impact Analysis
10) Conclusion
Business Impact Analysis definition
Business Impact Analysis is a systematic and data-driven approach that assesses the potential impacts of disruptive events on an organisation's critical business functions and processes. It is a vital part of Business Analysis and involves identifying and analysing the interrelationships, and dependencies of various business components, such as people, technology, infrastructure, and information systems. This comprehensive examination enables organisations to prioritise their resources effectively and develop strategic plans that align with the broader goals of Business Analysis, ensuring resilience and continuity in the face of unforeseen disruptions.
The BIA process begins with identifying and prioritising critical business functions. These functions are the backbone of an organisation and are crucial for its survival and continued operations. Once the critical functions are identified, the BIA process moves forward by assessing the potential risks and disruptions that could impact these functions.
The assessment thoroughly examines internal and external factors that could cause disruptions, such as natural disasters, cyber-attacks, supply chain disruptions, regulatory changes, or operational failures. The goal is to understand the likelihood and severity of each risk, enabling organisations to prioritise their response strategies.
What Does Business Impact Ananlysis Address?
At its core, BIA aims to quantify the financial, operational, and reputational consequences of disruptions to critical functions. By conducting a BIA, organisations understand how disruptions can impact their operations, financial stability, reputation, and capacity to deliver customer products or services.
BIA helps organisations allocate resources effectively by analysing the potential impacts of disruptions on critical functions. This allows businesses to develop robust business continuity plans and make informed decisions during crises. It enables organisations to identify vulnerabilities, evaluate disruptions' financial and operational consequences, and develop strategies to mitigate these risks.
Business Impact Analysis vs. Risk Assessment
While a Business Impact Analysis (BIA) and a business Risk Assessment share some similarities as well as have critical differences. A BIA is more detailed and specific as it concentrates on the continuity of business operations, resource availability, and the effects of a potential disruption. It analyses the critical components of a business, such as processes, systems, and people, to identify the impact a disorder could have on them. Risk Assessment evaluates the possibility and stringency of potential business risks. This process is essential to prioritise risks and develop strategies to mitigate them. The risk assessment involves:
a) Identifying potential threats
b) Analysing their likelihood of occurrence
c) Evaluating their potential impact on the business
While both BIA and Risk Assessment are crucial for Business Continuity Planning, they have distinct focuses, with BIA emphasising the analysis of business operations and resources and Risk Assessment concentrating on identifying and prioritising potential risks.
Business Impact Analysis vs. Business Continuity Planning
To ensure that a business can recover from a disruption, conducting a Business Impact Analysis is necessary. A BIA is a crucial component of a Business Continuity Plan as it provides essential data to determine the most critical business processes, identify the impact of any business disruption in those processes, and assess the resources required to restore them. The BIA helps to evaluate fundamental variables and build a comprehensive Business Continuity Plan, which lays out the course of action that needs to be taken to ensure that the business can recover from any unexpected business disruption.
Business Impact Analysis vs. Disaster Recovery Planning
A BIA is helpful in creating a Business Continuity Plan and an essential tool for developing a Disaster Recovery Plan. By identifying potential failure modes and the associated costs, the BIA report provides valuable insights that are then used to formulate a comprehensive disaster recovery plan. This plan ensures that all critical systems and operations are restored in a timely and efficient manner, minimising the impact of the disaster on the organisation.
How to conduct a Business Impact Analysis?
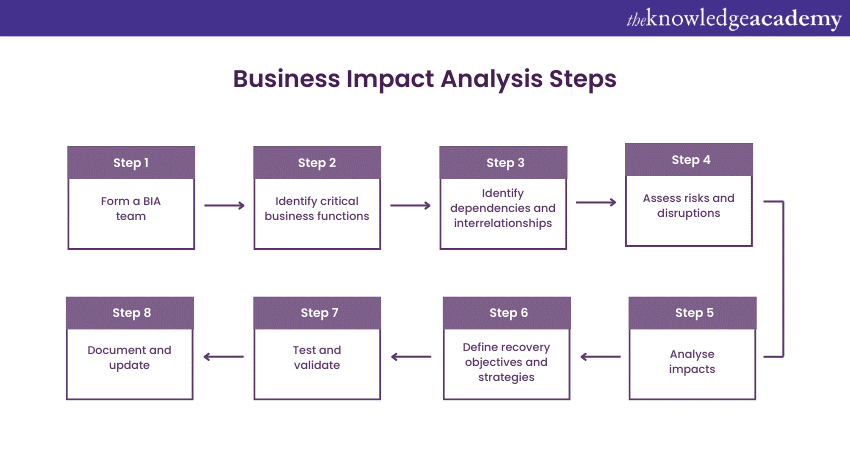
Conducting a thorough Business Impact Analysis requires a structured approach that involves several key steps. By following these steps, organisations can systematically assess the potential impacts of disruptions on their critical business functions and develop effective strategies for business continuity. Here are the steps to conduct a BIA:
Step 1: Form a BIA team
The first step is assembling a multidisciplinary team comprising representatives from various departments and stakeholders. The BIA team should possess a deep understanding of the organisation's operations and processes, as they will be accountable for driving the BIA process, ensuring comprehensive analysis.
Step 2: Identify critical business functions
Working collaboratively with relevant stakeholders, the BIA team identifies and prioritises critical business functions and processes. These core activities are vital for the organisation's survival and continued operations.
Step 3: Identify dependencies and interrelationships
Once the critical business functions are specified, the team discusses the dependencies between each component and information systems. This helps understand the potential impacts of disruptions on interconnected areas and helps develop effective mitigation strategies.
Step 4: Assess risks and disruptions
The BIA team executes a comprehensive Risk Assessment to define potential risks affecting critical functions. This assessment evaluates risks, including natural disasters, cyber-attacks, supply chain disruptions, regulatory changes, and operational failures. The team analyses the likelihood and potential severity of each risk.
Step 5: Analyse impacts
In this step, the team conducts impact analysis to understand the financial and reputational impact of disruptions in critical functions. Organisations can prioritise their recovery efforts and allocate resources effectively by quantifying the possible failures in terms of revenue, customer satisfaction, and brand prominence.
Step 6: Define recovery objectives and strategies
The team describes recovery objectives for each critical function based on the identified risks and impacts. The team then creates strategies and plans to accomplish these objectives effectively, including alternate work arrangements, backup systems, and communication protocols.
Step 7: Test and validation
Organisations should conduct tests and validation exercises to ensure the effectiveness of the BIA findings. This involves simulating different scenarios and evaluating the response and recovery measures. Testing helps in determining areas for improvement in the BIA process and allows organisations to refine their strategies.
Step 8: Document and updation
Documentation is crucial throughout the BIA process. The team should document the findings, analysis, and recommendations. This documentation is a reference for decision-making and auditing purposes. It is important to regularly review and update the BIA documentation to reflect changes in the organisation's operations.
Learn about business finance with BCS Foundation Certificate in Organisational Behaviour Course!
Importance of Business Impact Analysis
BIA plays a critical role in proactively managing risks and developing effective business continuity strategies. Here are some key reasons why BIA is important for organisations:
a) Risk identification and mitigation: BIA helps organisations identify potential risks and disruptions impacting their critical business functions. By understanding these risks, organisations can take proactive measures to mitigate them, reducing the likelihood and severity of potential disruptions.
b) Resource allocation: BIA enables organisations to allocate their resources effectively. Organisations can focus their resources on protecting and recovering critical business functions in the event of disruption by identifying and prioritising critical business functions. This ensures that resources are used efficiently and in alignment with business priorities.
c) Business continuity planning: BIA is the foundation for developing robust Business Continuity Plans. By analysing the potential impacts of disruptions, organisations can develop strategies and procedures to ensure the continuity of critical functions. This includes defining recovery objectives, establishing alternate work arrangements, and implementing backup systems and processes.
d) Decision-making during crises: In times of crisis, organisations need to make rapid and informed decisions. BIA provides valuable insights into the potential impacts of disruptions, allowing organisations to make data-driven decisions that minimise downtime, financial losses, and reputational damage.
e) Compliance and regulatory requirements: Many industries have specific compliance and regulatory requirements related to business continuity and disaster recovery. BIA helps organisations meet these requirements by demonstrating preparedness and resilience to regulatory bodies and stakeholders.
f) Stakeholder confidence: BIA instils confidence in stakeholders, including customers, investors, and business partners. By establishing a proactive approach to Risk Management and business continuity, organisations can build trust and maintain strong relationships with their stakeholders.
Try our BCS Certificate in Modelling Business Processes Course today!
Business Management Templates
Businesses can streamline their work, impress customers to win more deals, and increase their productivity by adopting the following professional templates:
SWOT Analysis Template
Conducting a Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats (SWOT) Analysis is an excellent method to evaluate the present condition of a business. It gives Managers valuable insights into the internal and external elements that constitute their company's business environment, allowing them to make informed decisions.
The analysis assists in identifying the company's strengths and shortcomings and the possibilities and threats in the market. This is an indispensable tool that can assist companies to stay ahead of the competition and achieve sustained success.
Business Case Template
Business Case Template is a comprehensive and adaptable tool that enables Business Managers, Project Managers, and Entrepreneurs to effectively convey their business concepts and strategies to stakeholders and clients. With this template, users can provide detailed information about their business objectives, target market, financial projections, and potential risks to ensure that all parties involved clearly understand the proposed venture.
Executive Summary Template
With an Executive Summary Template, businesses can efficiently and effectively condense their business plans and project proposals into a concise and informative summary. This allows businesses to showcase the value of their projects to stakeholders and clients with ease and clarity.
Key components of Business Impact Analysis
BIA comprises several essential components that help organisations comprehensively understand their critical functions and potential risks. These components guide the analysis process and provide valuable insights into the impacts of disruptions. Here are the key components of BIA:
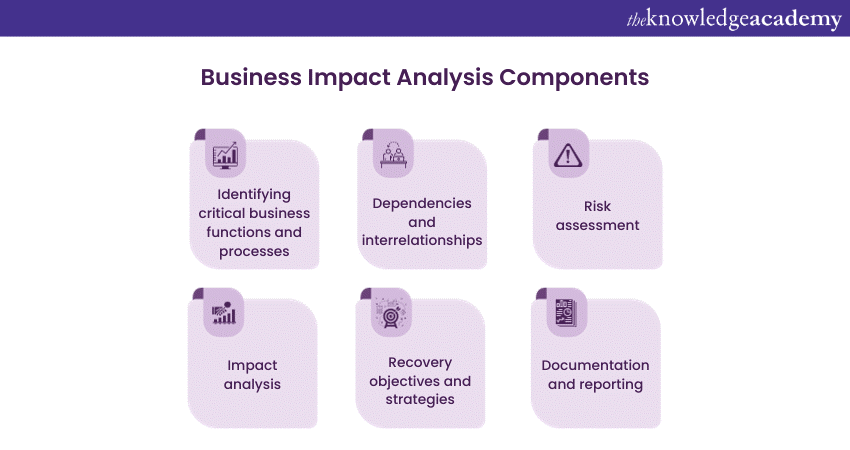
a) Identifying critical business functions and processes: BIA involves identifying and prioritising the critical business functions and processes essential for the organisation's survival and continued operations. These functions can vary depending on the industry and nature of business.
b) Dependencies and interrelationships: BIA thoroughly examines the dependencies and interrelationships between different business components. This includes people, technology, infrastructure, information systems, and external factors such as suppliers and customers. Understanding these dependencies is crucial for assessing the potential impacts of disruptions.
c) Risk assessment: The next component is the assessment of potential risks and disruptions that can impact critical functions. Organisations must identify and evaluate various risks, including natural disasters, cyber-attacks, supply chain disruptions, regulatory changes, and operational failures. This assessment helps in prioritising response strategies and resource allocation.
d) Impact analysis: Impact analysis involves analysing disruptions' financial, operational, and reputational consequences on critical functions. This analysis helps quantify the potential losses in terms of revenue, operational efficiency, customer satisfaction, and brand reputation. Organisations can prioritise their recovery efforts and allocate resources effectively by understanding the impacts.
e) Recovery objectives and strategies: Once the potential risks and impacts are identified, organisations must define recovery objectives for each critical function. Recovery objectives specify the desired timeframe within which operations should be restored. Strategies and plans are then developed to achieve these objectives effectively, including establishing alternate work arrangements, implementing backup systems, and defining communication protocols.
f) Documentation and reporting: It is crucial to document the BIA process's findings, analysis, and recommendations. This documentation serves as a reference for future planning, decision-making, and auditing purposes. Reports should be comprehensive and must provide a clear understanding of the identified risks, impacts, recovery strategies, and resource requirements.
Interested in Business Analysis Training? Try our BCS Certificate in Requirements Engineering Course!
Challenges in Business Impact Analysis
While Business Impact Analysis offers valuable insights and benefits, it also comes with certain challenges and limitations. Here are some of the common challenges organisations may face when conducting a BIA:
a) Data availability and accuracy: Obtaining accurate and up-to-date data can be challenging. Organisations may need help in gathering relevant information about critical functions, dependencies, and interrelationships, which can impact the accuracy and effectiveness of the BIA process.
b) Complexity and scope: BIA involves analysing various components and their interdependencies, making it a complex and time-consuming process. Organisations with a large scope or complex operations may find it challenging to comprehensively assess all critical functions and their potential impacts.
c) Subjectivity and assumptions: BIA relies on assumptions and subjective judgments to evaluate the potential impacts of disruptions. These assumptions may not always accurately reflect the real-world scenario, leading to potential gaps or inaccuracies in the analysis.
d) Changing business environment: The business environment is constantly evolving, and new risks and dependencies can emerge. BIA findings may become outdated if not regularly examined and updated to reflect changes in the organisation's operations and external factors.
e) Resource constraints: Conducting a thorough BIA requires dedicated time, expertise, and resources. Organisations with limited resources or competing priorities may struggle to allocate sufficient resources to perform a comprehensive analysis.
f) Interpretation and implementation challenges: BIA findings need to be effectively interpreted and translated into actionable strategies and plans. Organisations may face challenges in implementing the recommended measures and integrating them into their existing business processes.
Conclusion
Conducting a thorough Business Impact Analysis is essential for organisations to identify and mitigate risks, allocate resources effectively, and develop robust business continuity plans. By proactively assessing potential impacts, organisations can enhance their resilience and ensure continuity in the face of disruptions.
Interested in Business Analysis Training? Try our BCS Foundation Certificate in Business Analysis Course!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming Business Analysis Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 BCS Certificate in Business Analysis Practice
BCS Certificate in Business Analysis Practice
Sat 4th May 2024
Mon 13th May 2024
Tue 28th May 2024
Mon 10th Jun 2024
Mon 24th Jun 2024
Mon 8th Jul 2024
Sat 20th Jul 2024
Mon 22nd Jul 2024
Mon 5th Aug 2024
Mon 16th Sep 2024
Mon 30th Sep 2024
Mon 28th Oct 2024
Sat 2nd Nov 2024
Mon 25th Nov 2024
Mon 9th Dec 2024









 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


