We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +60 1800812339 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
In the digital labyrinth of ones and zeros, where software dances with hardware, there exists a silent sentinel—the unsung hero of organisational efficiency. Meet IT Asset Management (ITAM), the wizard behind the server rack curtain. But What is IT Asset Management and how does it function?
Imagine a bustling library, shelves stacked with books of code, servers humming like diligent librarians. ITAM is the meticulous librarian who knows every tome’s location, its torn and folded pages, and even the coffee stains on the cover. This blog will delve into What is IT Asset Management in detail and help you understand every small detail about it.
Table of Contents
1) What is an IT Asset?
2) What is IT Asset Management (ITAM)?
3) Importance of IT Asset Management
4) How an IT Asset Management Process Operates?
5) Types of IT Asset Management
6) Stages of an IT Asset Lifecycle
7) Advantages of IT Asset Management
8) Conclusion
What is an IT Asset?
An Information Technology or IT Asset is an inanimate or nonphysical resource which an organisation employs to help it sustain its information technology infrastructure or function. Such Assets are the basic hardware component set, i.e. servers, computers, network devices and storage system, as well as software applications, licenses, databases, and digital content. Alongside that, IT Assets also consist of data, information, and intellectual property, which is held and managed by the organisation.
Efficient IT Asset Management requires considering their life cycles, their impact on the organisation's activities, and their value for the business. It comprises of reporting that goes on within the scope of actions like procurement, deployment, maintenance, monitoring, and removal. Proper IT Asset Management will help organisations to maximise resource efficiency, cut costs, handle risks, meet legal requirements, and push forward the goals of a business in the modern digital world.
What is IT Asset Management (ITAM)?
IT Asset Management (ITAM) is a comprehensive tool used for managing IT Assets from procurement up to the disposal stage within an organisation. It represents the management of the technology and software components with the aim of making the most of them and minimising risk exposure. ITAM includes the acquisition, installation and upgrade, maintenance, and disposal of IT equipment. The strategic objectives of ITAM involve optimisation of Asset utilisation, cost containment, adherence with licensing agreements and good governance and elimination of security threats like unauthorised access and loss of confidential data.
When implemented correctly, organisations will benefit from increased operational efficiency, better decision-making and support for the strategic aims of the company through the alignment of IT investments with business needs. Furthermore, ITAM gives information about Asset performance and usage, so organisations can make strategic judgments about where to allocate their resources, when to upgrade and invest in new technologies.
Importance of IT Asset Management
As we've explained the fundamentals of IT Asset Management, understanding its principles and processes lays the groundwork for recognising its profound importance. Now, let's journey deeper into the IT Asset Management to uncover its central role in driving organisational efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and strategic decision-making.
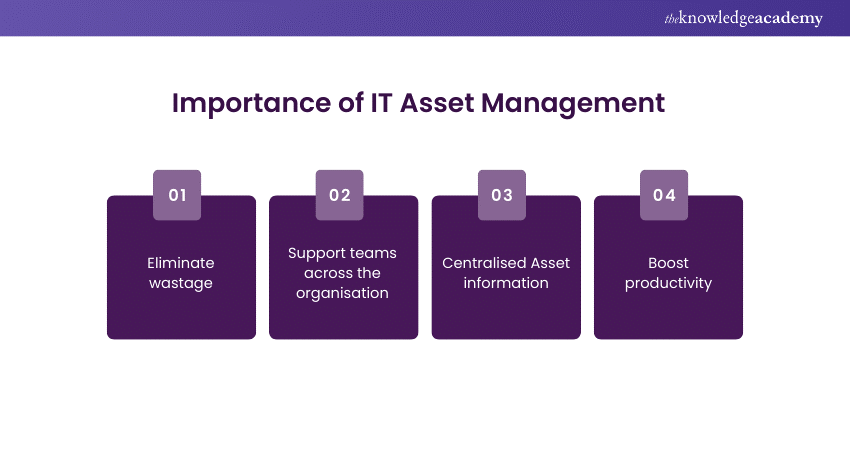
1) Eliminate wastage
ITAM helps the organisation in finding Assets that are underutilised or redundant, so that reallocation is done more effectively. That will also help optimise IT investments, which are synonymous with better management of an organisation's investments, leading to reduced unnecessary expenses and cost savings that improve financial performances.
2) Support teams across the organisation
ITAM supports the setup of the organisation's different teams, since through full functionality, they will have ways of ensuring that team members have the required tools and resources that enable them to provide effective performance. ITAM allows for the central management of all organisation IT Assets, thus supports proper coordination, communication, and productivity among different departments and teams in an organisation.
3) Centralised Asset information
ITAM centralises information about IT Assets, including specifications, configuration, warranties, and licenses. It is this repository that then helps organisations keep accurate records, follow up on lifecycles of Assets, and make essential decisions regarding procurement, maintenance, and retirement of Assets.
4) Boost productivity
Properly streamlined ITAM through effective management ensures that all teams across the organisation get the required tools and resources as and when required. The employees' concentration will be on the very core of the Asset and not being bothered by those related to its compatibility, availability, or maintenance. This, therefore, achieves better productivity and performance.
Elevate your IT Service Management proficiency with our ITIL® 4 Foundation Certification Course – Join today!
How an IT Asset Management process operates?
Now that we've grasped the critical significance of IT Asset Management in optimising organisational performance, let's look at the inner workings of this indispensable process. By understanding how IT Asset Management operates in practice, we can uncover the strategies, tools, and methodologies that enable businesses to effectively manage and maximize the value of their IT assets.
1) Asset identification
In IT Asset Management (ITAM), every procedure calls for the identification of all Assets. This involves cataloging everything concerning organisational IT, from the hardware and software to, in some cases, digital resources. Each Asset shall be documented against its make, model, and user or department assigned. Identification of the Asset may be done through physical audits, scrutiny of purchase records, and through automatic discovery tools to ensure that at any point in time, the Asset register reflects all Assets in existence and that it is accurate in content.
2) Asset tracking
Once the identification of Assets is done, tracking falls into the picture. It is described by following up on the movement, utilisation, and status of each Asset within its life cycle. There are strong mechanisms of Asset tracking with details of movements, transfers, and changes in ownership or responsibility for that particular Asset. Technologies involved include barcode labels, RFID tags, or the use of Asset Management software, all implemented in the true and efficient tracking of Assets. This is through regular auditing and reconciliations to confirm the location and state of Assets from what has been recorded by an organisation, inclusive of policies.
Unlock your potential in Cybersecurity with our CISM Training. Join today and advance your career to the next level!
3) Asset maintenance
In the end, Asset maintenance is key to ITAM as it basically integrates all activities toward keeping functionality, security, and compliance of IT Assets. The stage represents some proactive and reactive efforts into fixing issues related to the Asset and keeping up with operational integrity. The routine is also maintained with the help of updating software, checking up on hardware, and renewing the licenses of Assets, therefore ensuring the Assets are in their optimised condition.
To do this, the practices of security issues are also made to keep the Assets safe through antivirus scanning, vulnerability assessment, and access control checks. Compliance checks are being done periodically to maintain the licensing agreement, conform to the regulatory requirements, and comply with the set of internal policies. That also helps in ensuring maintenance against the set standards, reducing risks, which make the organisation more operational efficient, and Asset life will be extended.
Learn about the core Service Management activities with our ITIL® 4 Specialist: Create Deliver and Support Certification Course – Register today!
Types of IT Asset Management
From centralized systems to decentralized approaches, understanding the types of IT Asset Management enables us to grasp the breadth of strategies available for effectively managing and optimizing IT assets within organizations.
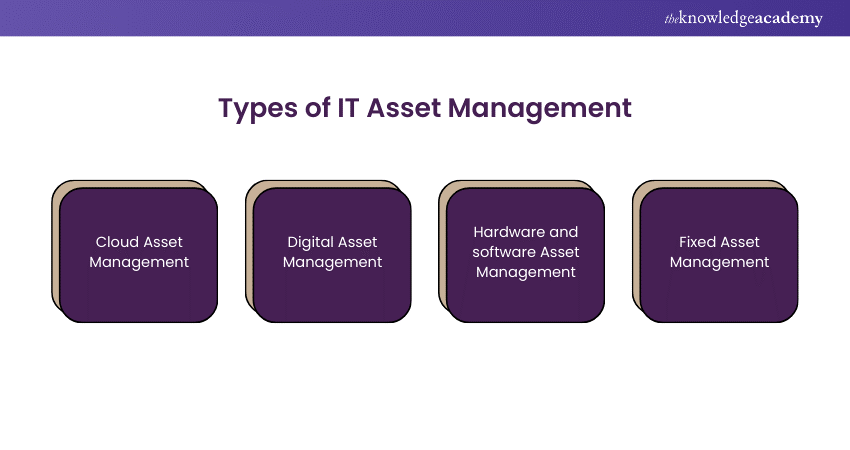
1) Cloud Asset Management
This term directly relates to the management process—essentially tracking and optimisation—of the IT Assets hosted and operated within the cloud. These Assets contain virtual servers, software storage resources, among other serviceable or applicable services or applications offered on a service basis. Management in the cloud includes a sophisticated set of functionality, including Asset tracking for usage, cost, and performance metrics that would deliver efficient use of resources, cost control, and service-level agreement fulfillment.
2) Digital Asset Management
A kind of IT-based management and organisation of digital documents, images, videos, and multimedia. It involves storage, cataloging, retrieval, and sharing of the digital Assets supporting the various business processes, marketing campaigns, and support to creativity. Overall, this solution for managing digital Assets usually provides metadata tagging, version control, permission, and digital rights management in the workflow of collaborating related to Assets in a streamlined manner.
3) Hardware and software Asset Management
In general, hardware and software Asset Management includes the operational tracking and management of physical and virtual IT-based Assets that are deployed within organisational infrastructure. This may include licenses, servers, networking hardware, computers, printers, software applications, and other required hardware. Hardware and software Asset Management processes include inventory management, license compliance, software deployment, patch management, and life-cycle tracking to ensure Asset utilisation is optimised, cost reduced, and risk is mitigated relating to software audits and security vulnerabilities.
4) Fixed Asset Management
Fixed Asset Management comprises monitoring and managing tangible Assets owned by the organisation and in use over a long period. This may include Assets such as buildings, equipment, machinery, and vehicles. The simplest sense of the word implies Asset Management in fixed Assets, accurate keeping of records with respect to acquisition, depreciation, timely maintenance, and in-time disposal according to both accounting standards, tax regulations, and financial reporting needs.
Additionally, fixed Asset Management solutions may include such characteristics as Asset tracking, maintenance schedules, and Asset valuations and forecasting to maximise Asset performance and gain return-on-investment potential.
Solve crimes with just your screen and keyboard. Sign up for our Computer Forensics Foundation Training - Register now
Stages of an IT Asset Lifecycle
1) Planning
The first phase in the IT Asset Life-cycle, planning, has the objectives of assessing the organisational needs of the IT Assets, defining requirements for the Assets, and laying down strategies of acquiring and managing the Assets in an effective way. This includes identifying business objectives and evaluating existing infrastructure to draw up policies and procedures for the maintenance of Assets in line with organisational objectives and budgetary limitations.
2) Acquiring
This includes procurement activities in the manner required by laid-down plans and requirements. These activities include searching for suppliers, preparation of inquiries, negotiations of contracts, and buying hardware, software, licenses, or services. Budgetary constraints, quality standards, and compliance requirements of regulatory bodies and internal policies of the organisation are the prerequisites that an organisation must meet in its acquisitions.
3) Commission
Once acquired, IT Assets are commissioned or deployed into the organisation's infrastructure. This includes setting up the hardware, installing the software, setting up the connection of the devices to the network, and integrating Assets to the current systems and workflow. Commissioning involves test operations of the Assets for functionality, performance, and compatibility with business needs to achieve outcomes.
4) Maintenance
The maintenance phase deals with sustaining and continuous maintenance of information technology Assets during their life cycle. It includes updating software, normal checking, and providing for preventive maintenance and timely fixing of failures or defects. Maintenance efforts shall be endeavored to fine-tune Asset performances so that the highest uptime is attained with the maximum uninterrupted business operations.
5) Retirement
At long last, the Assets are used up in the IT environment at the completion of their useful life or when they become technologically obsolete, which triggers the retirement phase. Such activity included Asset decommissioning, withdrawal from service, and disposal in an environmentally sound manner. The organisation may dispose of the retired Assets for sale, recycling, donation, or secure destruction in accordance with environmental consideration, data security concern, and regulatory compliance requirement. In fact, retirement covers updating Asset records, license reclamation, and redeployment of the resources for re-acquiring Assets in the future, thus completing the loop of the lifecycle.
Build the best Network Security systems, sign up for our Network Defence Training - register now!
Advantages of IT Asset Management
a) Cost savings: The rational use of resources ensures the minimisation of excess purchasing in running finances and avoids over-licensing or underutilisation of software.
b) Improved decision-making: Provides accurate, up-to-date information for improved decision-making towards aligning IT investments with business objectives.
c) Regulatory compliance: Maintains compliance with licensing agreements, regulatory requirements, and industry standards that may result in legal risks.
d) Enhanced security: Controls access to sensitive data and systems, hence reducing the occurrences of security breaches and unauthorised access.
e) Increased productivity: Minimises disruptions for optimised workflow efficiency and supports business continuity for increased productivity.
f) Asset lifecycle optimisation: Manage Assets proactively for increased lifecycle, maximum ROI, and minimal environmental impact.
Conclusion
In conclusion, IT Asset Management (ITAM) is crucial for organisations to effectively manage and optimise their IT assets throughout their lifecycle. By implementing robust ITAM practices, businesses can improve cost efficiency, compliance, and security while maximising the value derived from their IT investments, ultimately driving overall operational excellence and success.
Learn IT Asset Management for cost-efficiency and compliance with our ITIL® 4 Specialist: IT Asset Management Course – Join today!
Frequently Asked Questions

The three core deliverables of IT Asset Management are:
1) Maintaining a comprehensive IT Asset inventory
2) Optimising resource utilisation to maximise cost-effectiveness
3) Ensuring ongoing software license compliance

An IT asset can be any hardware, software, or digital information of business value. This includes things like laptops, servers, software licenses, and even digital databases.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various ITIL® Certification Training including ITIL® 4 Specialist: IT Asset Management Training, ITIL® 4 Foundation Certification Course, ITIL® 4 Specialist: Create Deliver and Support Certification Course and ITIL® 4 Strategist: Direct, Plan and Improve Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into ISO 20000 IT Service Management.
Our IT Service Management Blogs cover a range of topics offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your IT Service Management skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming IT Service Management Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 ITIL® 4 Specialist: IT Asset Management Training
ITIL® 4 Specialist: IT Asset Management Training
Tue 11th Jun 2024
Mon 26th Aug 2024
Mon 16th Dec 2024









 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


