We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +44 1344 203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Do you want to explore the CompTIA Troubleshooting Steps to fix your network issues? It is a handy set of guidelines that help you resolve your network issues efficiently. When faced with network problems, following these steps can help IT professionals diagnose and troubleshoot network-related matters effectively.
According to CompTIA, more than 500,000 IT professionals have chosen CompTIA Network+ qualifications to begin their IT careers since its establishment. Network technicians can enhance their problem-solving abilities and ensure optimal network performance by following these steps. This blog will walk you through the CompTIA Troubleshooting Steps so that you can identify and fix the problems in your network. Continue reading the blog for more information!
Table of Contents
1) Understanding the CompTIA Troubleshooting Model
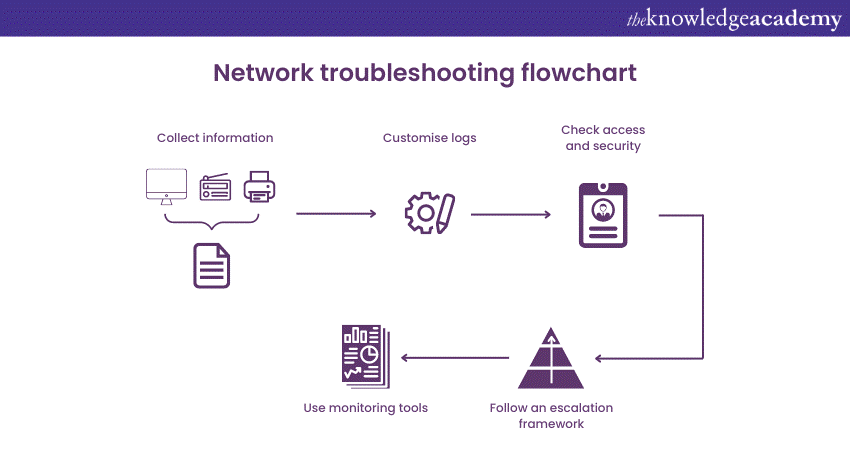
2) Network Troubleshooting
3) CompTIA Troubleshooting steps
4) Network Troubleshooting for devices and network
5) Tools for network Troubleshooting
6) Network Troubleshooting applications
7) Conclusion
Understanding the CompTIA Troubleshooting Model
The CompTIA Troubleshooting model is a systematic approach to resolving network issues. It consists of six stages that guide IT professionals through the troubleshooting process. The stages include:
a) Identify the problem: gather information about the issue by talking to users, examining error messages, and understanding the symptoms.
b) Follow a theory of probable cause: Based on the gathered information, you form hypotheses about the potential causes of the problem. It involves analysing the symptoms and considering factors such as recent changes or known issues that might be responsible.
c) Test the theory to determine the cause: You can perform diagnostic tests to validate or eliminate your hypotheses. This may involve using network monitoring tools, analysing logs, or conducting tests on specific components to pinpoint the root cause.
d) Establish a plan of action: Once the cause is identified, you create a plan to resolve the issue. This plan outlines the steps you'll take to fix the problem, including any necessary configurations, software updates, or hardware replacements.
e) Implement the solution: You execute the plan you've created. You make the necessary changes to the network or escalate the issue to higher-level support if needed.
f) Test system functionality and implement preventive measures: After executing the solution, you verify that the problem is resolved and the network functions correctly. Additionally, you may take preventive measures to avoid similar issues in the future, such as implementing monitoring systems or conducting user training.

Network Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting is a systematic way of finding and fixing issues in a network. Instead of randomly trying things until it works, troubleshooting lets you focus on specific network parts, test them, and keep track of your progress. It's a valuable skill for everyone, whether you're a regular computer user or aiming to become a network engineer. By following a systematic Troubleshooting approach, you can identify and resolve network problems efficiently.
It involves steps like analysing the network components, testing their functionality, and documenting the process. This helps identify the exact cause and apply the appropriate solution. Whether it's a minor glitch or a complex network error, troubleshooting allows you to approach it in a structured manner. This saves time and ensures smooth network operations. So, whether you're troubleshooting at home or pursuing a career in networking, mastering this skill will significantly benefit you in keeping your network up and running smoothly.
CompTIA Troubleshooting Steps
The CompTIA Troubleshooting model can be broken down into simple stages as follows:
Step 1: Identify the problem
The first step in CompTIA Troubleshooting is to identify the symptoms and related issues. Start by gathering information about the topic. Talk to users, look for error messages, and understand the signs. This can help you in figuring out what's wrong with the network. Let's look at the procedures that follow below:
a) Use available network troubleshooting tools to gather information about the network's current status.
b) Replicate the problem on a test device or software to help identify its source.
c) Communicate with network users to understand any problems or challenges they have experienced.
d) Identify the symptoms of the network problem, such as complete loss of connectivity and determine if it affects the entire network or specific users.
e) Investigate any changes that occurred in the network before the issues arose, such as new hardware, increased users, or software upgrades.
f) Define each problem accurately, as multiple issues may coexist. This ensures that others do not hinder solutions for one problem.
g) Following these steps, you can gather important information, diagnose network problems, and address them effectively, leading to a smoother and more reliable network experience.
Learn to identify social engineering attacks and how to classify network attacks by joining our CompTIA Security+ Certification Training Course. Sign up now!
Step 2: Establish a theory of probable cause
You must consider the potential causes of the issue based on the gathered information. Examine the symptoms and take into account any recent changes or problems that may be responsible for the issue. Create a hypothesis based on the factors causing the problem or issue. It helps technicians narrow down their investigation by considering the potential causes most likely responsible for the observed symptoms. The theory of probable cause helps technicians focus their efforts and follow a logical sequence.
Instead of investigating every possible cause, they prioritise the root cause of the problem. This method includes conducting tests, reviewing error messages, and analysing the system's behaviour. By carefully considering these factors, they can eliminate unlikely causes and focus on the most probable ones. This approach saves time and effort and increases the chances of finding an effective solution. The theory of probable cause guides technicians through systematically investigating and resolving technical issues, improving their efficiency and effectiveness in troubleshooting tasks.
Step 3: Test the theory to find out the cause
Conduct tests to confirm or rule out your hypotheses. Use network monitoring tools, check logs, or perform specific tests on components to find the root cause of the problem. Here, you perform diagnostic tests to validate or eliminate your hypotheses. This may involve using network monitoring tools, analysing logs, or testing specific components to identify the root cause. For example, if you think your network router is functioning correctly, use a different router.
Step 4: Create an action plan
Once the cause is identified, you must create a plan to resolve the issue. This plan outlines the steps you'll take to fix the problem, including any necessary configurations, software updates, or hardware replacements. You must rely on one method to implement the solution. Try and test the plan in an isolated environment. Inform the users beforehand to make them aware of the problems occurring from the solution. You should consult a professional if required.
Step 5: Implement the solution or escalate as necessary
In this stage, you execute the plan you've created. You make the changes required to the network or escalate the issue to higher-level support if needed. The essence is putting your plan into action. Take help from network administrators or users if the self-implemented solutions do not provide fruitful outcomes. This step is taken after making a strategy for network repair.
Step 6: Verify full system functionality and implement preventive measures
After implementing the solution, you verify that the problem is resolved and the network functions correctly. Additionally, you may take preventive measures to avoid similar issues in the future, such as implementing monitoring systems or conducting user training.
Step 7: Record the solution
You must document and record each step of the troubleshooting process, including the issues occurring in the network. It is essential to record each phase of the troubleshooting process. The stages include network symptoms, hypothesis, test theory and solutions provided for the problem.
Advance your knowledge and get recognised worldwide with our CompTIA Certification Training Courses. Register now!
Network troubleshooting for devices and network
The process of locating and resolving issues in Computer Networks is known as network troubleshooting. A network consists of numerous interconnected components, including computers, routers, and switches, allowing data transmission and communication between various locations. The flow of information can, however, occasionally be stopped by problems that occur in computer networks. Network troubleshooting is more productive than the other troubleshooting techniques as it helps you focus on specific components and test each for operation.
Troubleshooting for a device
Troubleshooting on an individual device could be necessary if the issue is with a particular gadget, like a computer or a router. This can involve restarting the device, reviewing the network settings, or updating the device's firmware or drivers. It may be necessary to conduct further in-depth troubleshooting, such as reviewing router configurations, examining network traffic, or contacting the internet service provider if the issue is more prevalent and affects many devices or the entire network.
Troubleshooting for network
When troubleshooting a network, the first step is to identify the problem. Consider the signs such as slow internet speed, connectivity issues, or devices not being able to communicate with each other. After the problem is identified, the next step is to isolate the cause. This involves checking the physical connections, verifying network settings, and examining the devices affected.
Accelerate your career in networking with our comprehensive CompTIA Network+ Training Course. Join today!
Tools for network troubleshooting
A wide range of Network Troubleshooting tools exist to identify and resolve network issues. Let's talk about a few tools:
a) Ping: It is a primary network troubleshooting tool that sends a small data packet to a specific IP address or hostname and measures the response time. It helps in determining a device's reachability and measuring network latency.
b) Traceroute: It traces the path network packets take from your device to a destination, showing each hop along the way. It helps identify network congestion, routing issues, or delays by displaying the response times from each intermediate device.
c) Nslookup: This tool returns all the IP addresses related to a hostname. NSlookup is a network troubleshooting tool that helps you find information about domain names and their IP addresses. It translates human-readable domain names into machine-readable IP addresses and vice versa, allowing you to verify DNS configurations and troubleshoot DNS-related issues in just a few clicks.
d) Ifconfig: A tool that supports Windows and checks for network settings and connections. A command-line tool called 'ifconfig' details a computer's network interfaces. Users can see and modify IP addresses, subnet masks, and other network settings for connectivity problems.
e) Tcpdump: The packet sniffing tool 'tcpdump' captures and examines real-time network traffic. It helps users in packet monitoring and analysis, network problem detection, and network communication issue resolution.
f) Route: The IP routing table on a computer or router can be viewed and edited using the command-line tool route. Maintaining optimal network connectivity enables users to monitor and configure routing information, such as default gateways and network routes.
g) Address Resolution Protocol (ARP): It enables mapping an IP address to a Media Access Control (MAC) address. The ARP cache, which holds these mappings, can be viewed and managed by users using the ARP command-line tool. It helps in link-layer Troubleshooting for network connectivity problems.
h) Iptables: It is a firewall tool in Linux systems. It allows users to define rules to control incoming and outgoing network traffic. It helps secure the network by filtering and manipulating packets based on specific criteria.
i) Dig: Domain Information Groper (DIG) is a command-line tool for performing Domain Name System (DNS) queries. It provides information about DNS records, such as IP addresses associated with a domain name. It helps diagnose DNS-related issues and verify DNS configurations.
j) Pathping: A Windows tool called 'pathping' combines ping and traceroute features. For each hop on the network path, it offers information on network delay and packet loss. It assists in identifying troublesome network segments and diagnosing network performance issues.
k) Netstat: It is a command-line tool that focuses on active network connections, listening ports, and network statistics on a computer. It helps users identify established relationships, check the network service status, and diagnose network-related issues.
l) Nmap: It is a network scanning tool that helps users discover and map network hosts and services. It provides information about open ports, Operating Systems, and network services running on target systems. It helps in network discovery and risk assessment.
Network troubleshooting applications
You can use from among several applications to assess the network issues and diagnose challenges. Let's discuss a few:
a) Wi-Fi analyser: An application that scans the Wi-Fi spectrum to locate open networks, measure signal strength, and identify channel congestion, helping diagnose wireless connectivity problems and optimising network performance.
b) Bandwidth speed tester: An application that measures the speed and quality of your internet connection, enabling you to diagnose slow network performance, detect problems, and confirm that your service provider is providing sufficient bandwidth.
c) Packet sniffer: An application used to capture and analyse network traffic, allowing you to inspect the data packets being transmitted, helping identify issues like network congestion or network vulnerabilities.
d) Protocol analyser: A software application that examines network protocols to identify errors, analyse communication patterns, and diagnose problems related to how devices communicate.
e) Port scanner: An application program that scans a target system for open ports, indicating which services are running and potentially highlighting security vulnerabilities or misconfigurations.
Elevate your career in server administration. Join our CompTIA Server+ Certification Training Course today.
Conclusion
Hope you enjoyed reading this informative blog and that it gave you a systematic understanding of CompTIA Troubleshooting Steps. By following these steps, IT professionals can effectively identify, analyse, and resolve problems in a structured manner. CompTIA troubleshooting methodology helps ensure efficient and effective troubleshooting, minimising downtime and improving overall system performance.
Learn the basics of CompTIA A+ Certification under the guidance of expert trainers with our CompTIA Certification. Sign up now!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming IT Infrastructure & Networking Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 CompTIA A+ Course
CompTIA A+ Course
Mon 2nd Dec 2024
Mon 3rd Feb 2025
Mon 7th Apr 2025
Mon 2nd Jun 2025
Mon 4th Aug 2025
Mon 6th Oct 2025
Mon 1st Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


