We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on + 1-866 272 8822 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
In today’s dynamic and competitive business landscape, organisations constantly explore ways to streamline operations, reduce waste, and deliver exceptional customer value. The Six Sigma Lean Process has emerged as a powerful methodology in this quest for excellence.
By fusing the principles of Lean Manufacturing and Six Sigma, this approach offers a holistic framework that tackles waste reduction, process optimisation, and quality enhancement. Today, the world’s leading companies have employed the methodology to make their business more efficient.
So, it’s time for you to develop improved and efficient operations for your organisation. Not sure how? Read this blog to obtain knowledge of Six Sigma Lean Processes and explore its core concepts, benefits, and real-world applications. You will also learn about how to get certified in lean six sigma. Read more to learn more!
Table of contents
1) What is Lean Six Sigma?
2) The DMAIC Methodology – An overview
3) Applications of Lean Six Sigma
4) Benefits of implementing Lean Six Sigma
5) Conclusion
What is Lean Six Sigma?
Lean Six Sigma is a dynamic methodology that has gained significant popularity in the realm of Process Improvement and business excellence. It combines two well-established approaches, Lean Manufacturing and Six Sigma, to create a comprehensive framework for achieving operational efficiency and quality enhancement.
At its core, Lean Six Sigma is rooted in the pursuit of perfection and the relentless drive to eliminate waste, reduce variations, and deliver exceptional value to customers. Lean focuses on waste reduction and process optimisation, while Six Sigma targets defect and variation reduction.
By integrating the principles and tools from Lean Manufacturing and Six Sigma, this methodology offers a structured and data-driven approach to Process Improvement. Furthermore, organisations benefit from this comprehensive framework that addresses process efficiency and quality improvement. These benefits include:
a) Identifying and eliminating waste
b) Reducing defects and variations
c) Enhancing productivity
d) Reducing costs
e) Improving customer experiences
Lean Six Sigma career path is not limited to a specific industry or sector. Its principles and tools can be applied across various domains, including manufacturing, healthcare, service, finance, and more. In summary, a Lean Six Sigma Career Path offers a broad spectrum of opportunities, allowing individuals to navigate through different industries, assume varying roles, and continuously grow their skills and impact.

The DMAIC Methodology – An overview
The Define, Measure, Analyse, Improve, and Control (DMAIC) Methodology is a fundamental framework within Lean Six Sigma. It guides organisations through the process of Process Improvement. The five key stages, i.e., Define, Measure, Analyse, Improve, and Control, assists in achieving sustainable and effective results. Let’s have a detailed look at what these stages comprise:
Define
The primary focus of the Define stage is on setting a solid foundation for the improvement project. This stage sets the groundwork for the entire process and ensures alignment with the organisation’s goals and objectives. During this stage, the project team engages in the following key activities:
a) Problem identification: The team identifies the specific problem or opportunity for improvement that the project aims to address. It includes understanding the current state of the process and analysing data.
b) Project Scope definition: Defining the project’s scope is crucial to ensure that efforts are directed towards a well-defined area. The team specifies which processes or areas will be included or excluded.
c) Goal setting: Clear and measurable goals are established to guide the project towards success. These goals should be aligned with the organisation’s strategic objectives and address the identified problem or opportunity.
d) Stakeholder analysis: Understanding the expectations and requirements of stakeholders is essential for project success. The team identifies and engages with relevant stakeholders, such as customers, employees, and management, to incorporate their perspectives into the project.
e) Project Charter creation: A Project Charter is developed to document the purpose, objectives, scope, deliverables, and key stakeholders of the project. This charter serves as a guiding document throughout the improvement journey.
Measure
The Measure stage is a critical component of the DMAIC Methodology in Lean Six Sigma. It focuses on gathering data and establishing a baseline to clearly understand the process’s current state being improved. During the Measure phase, the project team engages in the following key activities:
a) Data collection: The team identifies the relevant data points and measures that must be collected to assess the current process performance. This involves selecting appropriate data collection methods, such as direct observation, surveys, etc.
b) Process mapping: A process map or flowchart is created to visually represent the sequence of steps and activities involved in the process. This helps identify bottlenecks, redundancies, and areas of improvement.
c) Data analysis: The collected data is analysed to determine the current performance and identify variations or trends. Statistical tools and techniques are employed to gain insights into the process.
d) Measurement System Analysis (MSA): The reliability and accuracy of the measurement systems are evaluated through MSA. This ensures that the information can be trusted and used for analysis.
e) Establishing process baseline: The team establishes a baseline measurement to understand the process’s current performance levels. This baseline serves as a reference for evaluating the effectiveness of improvement efforts.
Analyse
The Analyse stage is another critical part of the DMAIC Methodology. This stage focuses on gaining deeper insights into the root causes of process issues and identifying opportunities for improvement. The following are the key activities taken up by the project team during Analyse stage:
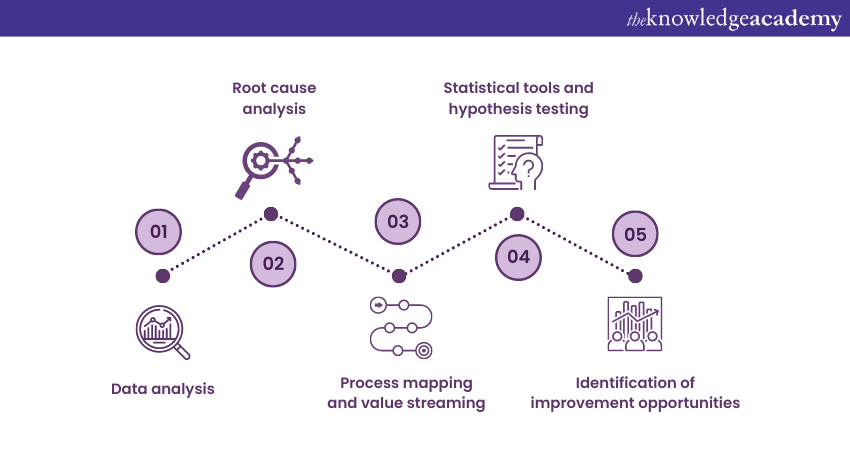
a) Data analysis: The team analyses the data collected during the Measure stage to identify patterns, trends, and potential sources of variation. Tools like Pareto Charts, Histograms, and Scatter Plots are employed to facilitate data analysis.
b) Root cause analysis: Root cause analysis techniques, including the 5 Whys or cause-and-Fishbone diagrams, are utilised to systematically identify the underlying causes contributing to process issues. This helps the team understand the fundamental reasons behind the observed variations or problems.
c) Process mapping and value streaming: The team further examines the process map created during the Measure stage to identify non-value-added activities, bottlenecks, and waste areas. It helps them visualise the flow of activities and identify opportunities for process optimisation.
d) Statistical tools and hypothesis testing: Advanced statistical techniques, including hypothesis testing, are applied to validate assumptions and test hypotheses. The team also identifies significant factors influencing process performance. This helps them determine which variables impact the process most and guide them towards improvement.
e) Identification of improvement opportunities: Based on the findings from the analysis, the team identifies specific improvement opportunities and prioritises them based on their potential impact on process performance.
Improve
The Improve stage focuses on generating and implementing solutions to address the root causes identified during the Analyse stage. It aims to achieve significant Process Improvements. The project team engages in the following key activities during the Improve stage:
a) Brainstorming and solution generation: The team engages in collaborative brainstorming sessions to generate potential solutions and improvement ideas.
b) Evaluating and selecting solutions: The team evaluates the generated solutions based on predefined criteria, such as feasibility, impact, and alignment with project goals. Solutions with the highest scope of improvement are selected for further analysis and implementation.
c) Pilot testing and validation: Before implementing solutions on a larger scale, the team conducts pilot tests or small-scale experiments to validate their effectiveness. This allows for adjustments and fine-tuning before full implementation.
d) Implementation planning: Detailed plans are developed to guide the implementation of the selected solutions. This includes defining roles and responsibilities, establishing timelines, and allocating necessary resources.
e) Implementation of solutions: The selected solutions are implemented according to the developed plans. The team closely monitors the implementation process to address potential issues or barriers.
f) Monitoring performance: During and after the implementation of solutions, performance indicators are closely monitored to assess the impact of the improvements. This ensures the desired results are achieved, and the implemented changes are sustainable.
Boost your career prospects in Project Management with our Six Sigma Training now!
Control
The Control stage is the final stage within the DMAIC Methodology of Lean Six Sigma. It aims to ensure that the improvements are made during the Improve stage. It also ensures that those improvements are sustained over time and continue to deliver the desired outcomes. The following are the key activities involved during the Control stage:
a) Developing control plans: Control plans are developed to outline the measures and actions required to maintain improved process performance. These plans define the Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to be monitored, the frequency of data collection, and the responsible individuals or teams for monitoring and analysis.
b) Implementing process controls: Process controls are established to prevent deviations from the desired process state and to address potential issues proactively.
c) Training and skill development: The team ensures that relevant stakeholders are trained on the new processes, controls, and procedures. This empowers them to execute their responsibilities and maintain improved process performance effectively.
d) Continuous monitoring and analysis: The team continues to monitor the process performance by collecting and analysing relevant data. Statistical Process Control (SPC) tools are used to identify any variations. This ensures that the process remains within the desired performance range.
e) Process audits and reviews: Periodic audits and reviews are conducted to examine the success of the control measures. They are also used to recognise opportunities for further improvement. Lessons learned from the previous processes are documented, and best practices are shared within the organisation.
f) Documenting and communicating results: The project team documents the results and achievements of the improvement efforts. The findings are communicated to relevant stakeholders to showcase the success and encourage further adoption of the Lean Six Sigma principles.
Applications of Lean Six Sigma
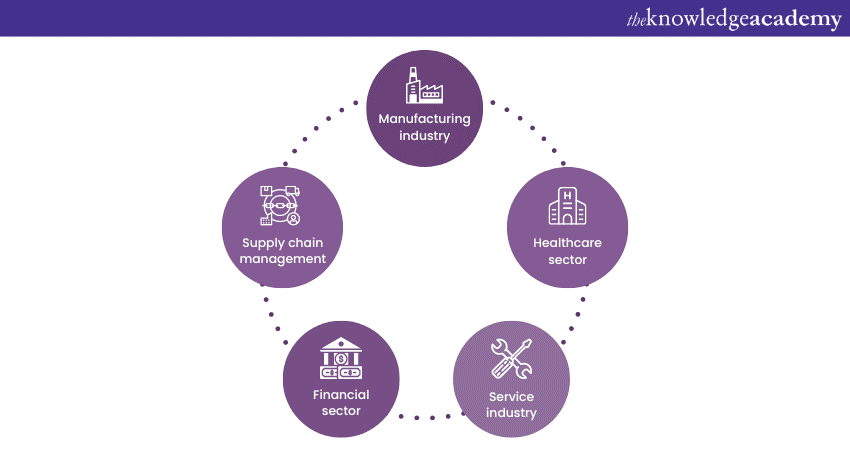
Lean Six Sigma finds application in diverse industries and sectors, bringing notable improvements to operational efficiency. Let’s explore some common areas where Lean Six Sigma is applied:
a) Manufacturing: In manufacturing industry, the Lean Six Sigma is used to streamline processes, reduce waste, and enhance product quality.
b) Healthcare: Lean Six Sigma is instrumental in healthcare industry for improving patient safety, reducing medical errors, and enhancing healthcare delivery processes.
c) Service: In the service industry, Lean Six Sigma helps enhance service quality, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction. It enables businesses to streamline processes and eliminate non-value-added activities.
d) Financial sector: Lean Six Sigma is applied in the financial sector to improve transaction accuracy, streamline loan processing, and enhance compliance with regulations.
e) Supply chain management: This methodology plays a significant role in supply chain management by improving inventory management, reducing lead times, and enhancing overall supply chain efficiency.
Gain an understanding of Lean Process Mapping with our Certified Lean Foundation & Practitioner Course!
Benefits of implementing Lean Six Sigma
The Lean Six Sigma methodology offers numerous benefits to organisations that adopt its principles. Let’s explore some of the key advantages of implementing Lean Six Sigma:
1) Improved efficiency: The methodology assists organisations in streamlining processes, reducing waste, and eliminating non-value-added activities. This further leads to increased efficiency and productivity.
2) Enhanced quality: By focusing on defect reduction and Process Improvement, Lean Six Sigma enables organisations to deliver higher-quality products and services. As a result, it adds to improved customer satisfaction and loyalty.
3) Cost savings: Lean Six Sigma helps identify and eliminate process inefficiencies. Therefore, leading to significant cost savings through reduced rework, scrap, and overall operational expenses.
4) Data-driven decision-making: This methodology uses statistical analysis and data to make informed decisions. This enables organisations to identify root causes, validate improvements, and drive evidence-based decision-making.
5) Cultural transformation: Implementing Lean Six Sigma fosters a culture of continuous improvement. It means that employees are empowered to identify opportunities for improvement, contribute to problem-solving, and embrace a learning and developing mindset.
6) Customer focus: Lean Six Sigma also strongly emphasises understanding customer needs and delivering value. Organisations can improve customer satisfaction and obtain a competitive edge by aligning processes with customer requirements.
7) Employee engagement: Involving employees in Lean Six Sigma initiatives promotes employee engagement, ownership, and collaboration. This leads to a motivated workforce actively driving Process Improvements and achieving organisational goals.
Conclusion
Incorporating the Six Sigma Lean Process into the fabric of an organisation enables a systematic approach to Process Improvement and fosters a culture of innovation and excellence. By harnessing the power of this methodology, businesses can optimise their operations, exceed customer expectations, and achieve long-term success in today’s rapidly changing business environment.
Acquire the skills to drive Process Improvement and enhance efficiency in your organisation with our Lean Six Sigma Certification Training.
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming Business Improvement Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Lean Six Sigma Green Belt
Lean Six Sigma Green Belt
Mon 4th Nov 2024
Mon 2nd Dec 2024
Mon 13th Jan 2025
Mon 10th Mar 2025
Mon 19th May 2025
Mon 21st Jul 2025
Mon 15th Sep 2025
Mon 17th Nov 2025
Mon 15th Dec 2025
 Halloween sale! Upto 40% off - Grab now
Halloween sale! Upto 40% off - Grab now







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


